Scalar Types
Integers
Floating-Point Types
Boolean (bool)
Character (char)
Compound Types
Tuples
Arrays
Notes on Rust Types
Interview Questions & Answers on Rust Data Types
MCQs on Rust Data Types (With Answers)
Rust is a statically typed language, which means every value has a specific type known at compile time. The compiler often infers types, but sometimes you need to annotate them explicitly so Rust knows exactly what you mean.
Rust’s data types are broadly grouped into Scalar and Compound types:
Scalar Types
Scalar types represent a single value. Rust has four primary scalar types:
Integers
Whole numbers without a fractional part.
Examples include:
i8, i16, i32, i64, i128 (signed)
u8, u16, u32, u64, u128 (unsigned)
isize, usize (pointer-sized)
let a: i32 = 42;
let b: u8 = 255;
let c: isize = 10; // size depends on platform
👉 Signed integers store negative and positive values; unsigned hold only zero and positive.
▶️ 2. Floating-Point Types
Numbers with decimals.
let x = 3.14; // f64 (default)
let y: f32 = 2.5; // f32
f32 — 32-bit float
f64 — 64-bit float (default)
▶️ 3. Boolean (bool)
True or false values.
let is_active: bool = true;
let is_done = false; // type inferred
▶️ 4. Character (char)
A Unicode scalar value, not just ASCII.
let letter: char = 'R';
let emoji: char = '🦀';
Each char is 4 bytes, capable of representing many languages and emojis.
Compound Types
Compound types group multiple values into one type.
Tuples
A fixed-length collection of values of possibly different types.
let tup: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);
let (x, y, z) = tup; // destructure
You can access elements by position:
println!("{}", tup.1); // prints 6.4
Arrays
A fixed-length collection where all elements must have the same type.
let nums: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let repeated = [3; 5]; // [3, 3, 3, 3, 3]
The length is part of the type.
📌
Notes on Rust Types
🧠 Type Inference
Rust often infers the type from context, so you don’t always need an explicit annotation.
⛔ Type Safety
Trying to assign a value of one type to a variable of another type without casting causes a compile-time error.
🧪 Quick Example Program
fn main() {
// Scalar example
let age: u32 = 30;
let price = 99.99; // f64 inferred
let is_ready: bool = true;
let symbol: char = 'R';
// Compound example
let person: (&str, u32) = ("Alice", 28);
let numbers: [i32; 3] = [10, 20, 30];
println!("{}, {}, {}, {}", age, price, is_ready, symbol);
println!("Name: {}, Age: {}", person.0, person.1);
println!("Array first element: {}", numbers[0]);
}
💡
Summary
Category Types
Scalar i8, u32, f32, f64, bool, char
Compound Tuples (T1, T2, ...), Arrays [T; N]
These built-in types give Rust predictable, efficient, and safe handling of data—key for systems programming.
Interview Questions & Answers on Rust Data Types
Basic Level
- What are data types in Rust?
Answer:
Data types define the kind of data a variable can hold. Rust is a statically typed language, meaning all variable types must be known at compile time.
- How are data types classified in Rust?
Answer:
Rust data types are mainly classified into:
Scalar types
Compound types
- What are scalar data types in Rust?
Answer:
Scalar types represent a single value. Rust has four scalar types:
Integers
Floating-point numbers
Boolean
Character
- Explain integer data types in Rust.
Answer:
Integer types store whole numbers and are divided into:
Signed (i8, i16, i32, i64, i128)
Unsigned (u8, u16, u32, u64, u128)
Pointer-sized (isize, usize)
let a: i32 = -10;
let b: u32 = 20;
- What is the default integer type in Rust?
Answer:
The default integer type is i32, because it provides a good balance between performance and memory usage.
- What are floating-point types in Rust?
Answer:
Rust has two floating-point types:
f32 (32-bit)
f64 (64-bit, default)
let x = 3.14; // f64
let y: f32 = 2.5;
- What is the bool data type?
Answer:
The bool type represents logical values:
true
false
let is_valid: bool = true;
- What is the char data type in Rust?
Answer:
char represents a single Unicode scalar value and occupies 4 bytes.
let c: char = 'A';
let emoji: char = '🦀';
Intermediate Level
- What are compound data types in Rust?
Answer:
Compound types group multiple values into one type. Rust provides:
Tuples
Arrays
- Explain tuples in Rust.
Answer:
Tuples store multiple values of different types in a fixed order.
let person: (&str, u32) = ("Alice", 30);
- How do you access tuple elements?
Answer:
Using dot notation or destructuring.
let x = person.0;
let (name, age) = person;
- Explain arrays in Rust.
Answer:
Arrays store multiple values of the same type with a fixed length.
let numbers: [i32; 3] = [1, 2, 3];
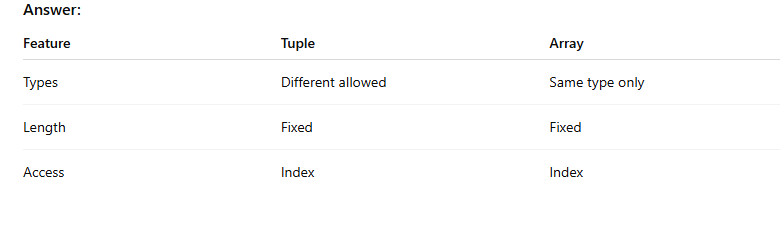
- What is the difference between tuple and array?
MCQs on Rust Data Types (With Answers)
MCQs – Basics
- Rust is a ______ typed language.
A. Dynamically
B. Statically
C. Weakly
D. Loosely
✅ Answer: B
- Which is the default integer type in Rust?
A. i64
B. i32
C. u32
D. isize
✅ Answer: B
- Which data type represents a single Unicode value?
A. String
B. char
C. &str
D. u8
✅ Answer: B
- How many bytes does a char occupy in Rust?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 4
D. 8
✅ Answer: C
MCQs – Scalar Types
- Which of the following is NOT a scalar type?
A. Integer
B. Boolean
C. Character
D. Tuple
✅ Answer: D
- Which floating-point type is default in Rust?
A. f32
B. f64
C. f16
D. f128
✅ Answer: B
- Which integer type is unsigned?
A. i32
B. isize
C. u8
D. i128
✅ Answer: C
MCQs – Compound Types
- Which compound type allows mixed data types?
A. Tuple
B. Array
C. Vector
D. HashMap
✅ Answer: A
- Which compound type requires all elements to be the same type?
A. Tuple
B. Array
C. Enum
D. Struct
✅ Answer: B
- Which statement about arrays is correct?
A. Arrays can grow dynamically
B. Arrays have fixed length
C. Arrays allow mixed types
D. Arrays skip bounds checking
✅ Answer: B
Tricky MCQs
- What happens if you access an array index out of bounds?
A. Undefined behavior
B. Runtime panic
C. Compile error
D. Memory corruption
✅ Answer: B
- Which type is best for indexing arrays?
A. i32
B. usize
C. u8
D. f64
✅ Answer: B
- Type inference in Rust happens at:
A. Runtime
B. Compile time
C. Link time
D. Execution end
✅ Answer: B
- Which allows different types in a single variable?
A. Array
B. Tuple
C. Integer
D. Boolean
✅ Answer: B
- Rust prevents many errors related to data types at:
A. Runtime
B. Deployment
C. Compile time
D. Production
✅ Answer: C
One-Line Interview Summary
Rust data types are strictly enforced at compile time, divided into scalar and compound types, ensuring safety, predictability, and memory correctness.
SUMMARY
Scalar Types
Integers
Floating-Point Types
Boolean (bool)
Character (char)
Compound Types
Tuples
Arrays
Notes on Rust Types
Type Inference
Type Safety

Top comments (0)