In JavaScript, call(), apply(), and bind() are methods that can be used with functions.
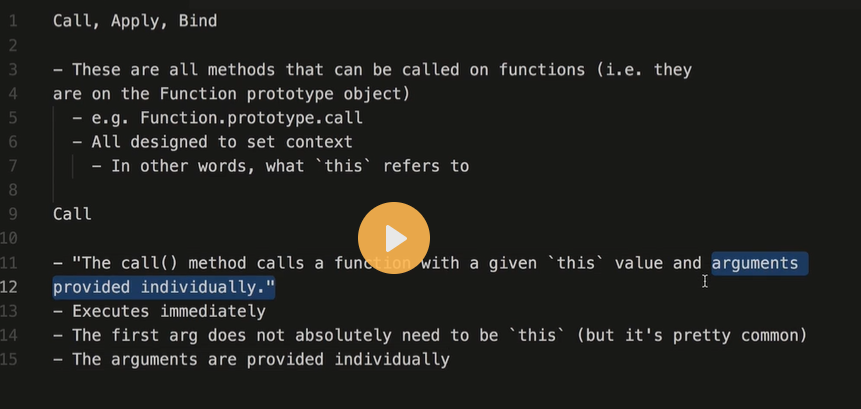
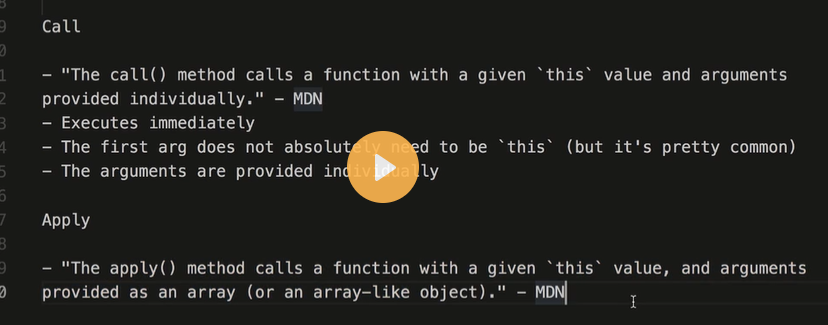
- call() The call() method is a method that is available on every function object in JavaScript. It allows you to call a function with a given this value and arguments provided individually. Here's an example:
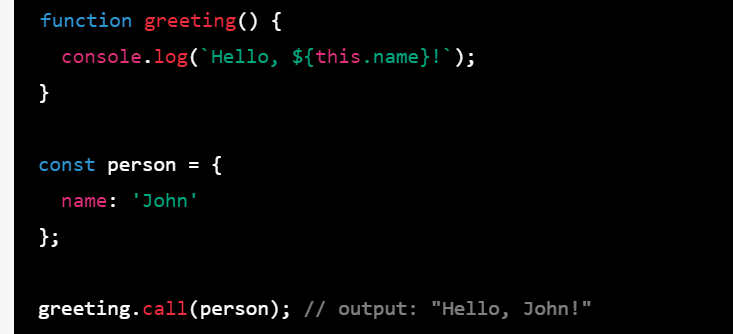
function greeting() {
console.log(`Hello, ${this.name}!`);
}
const person = {
name: 'John'
};
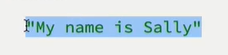
greeting.call(person); // output: "Hello, John!"
In this example, we define a function greeting() that logs a greeting message with the value of the name property of the this object. We also define an object person that has a name property set to 'John'. We then call the call() method on the greeting() function with person as the this value. The greeting() function is then called with person as the this value and logs the greeting message with the name 'John'.
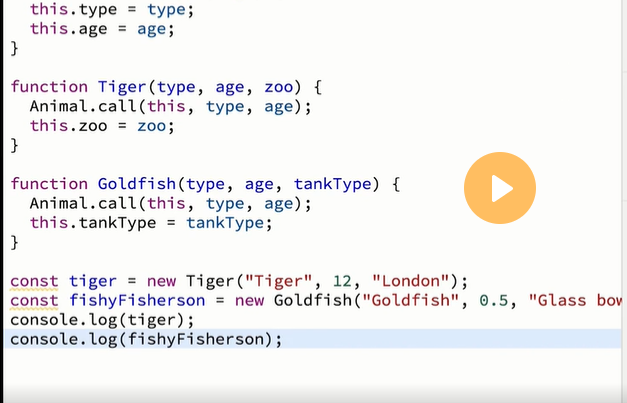
In javasript
In OUTPUT
===============================================
In javasript
In OUTPUT
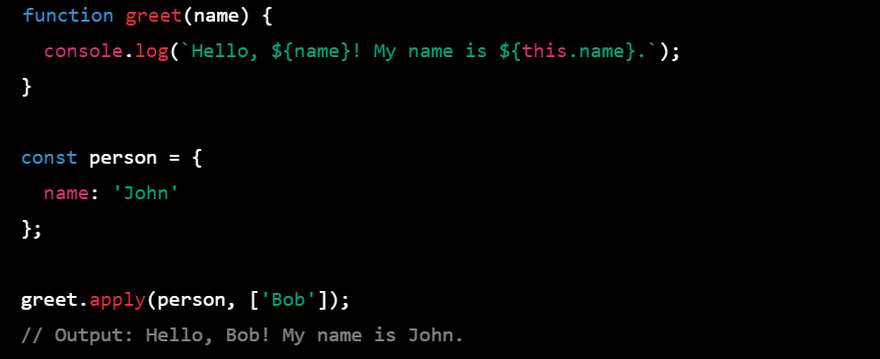
- apply() The apply() method is a method that is available on every function object in JavaScript. It allows you to call a function with a given this value and arguments provided as an array (or an array-like object). Here's an example:
function sum(x, y, z) {
return x + y + z;
}
const args = [1, 2, 3];
const result = sum.apply(null, args);
console.log(result); // output: 6
In this example, we define a function sum() that takes three arguments and returns their sum. We then define an array args that contains the values we want to pass to the function. We call the apply() method on the sum() function with null as the this value and args as the array of arguments. The sum() function is then called with null as the this value and the arguments [1, 2, 3], and returns the sum 6.
===============================================
In javasript
In OUTPUT
====================================
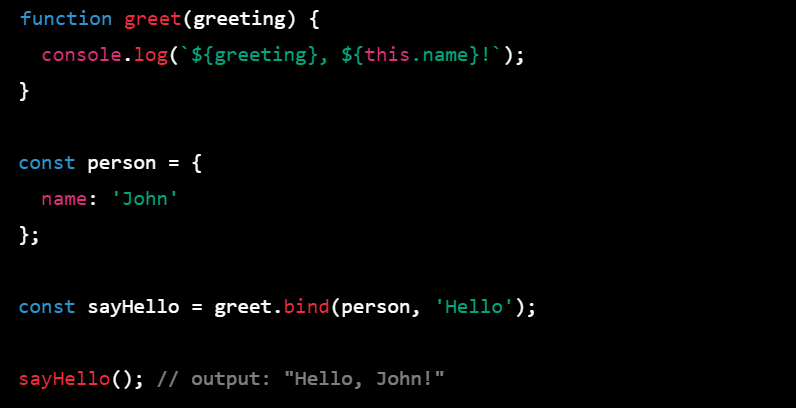
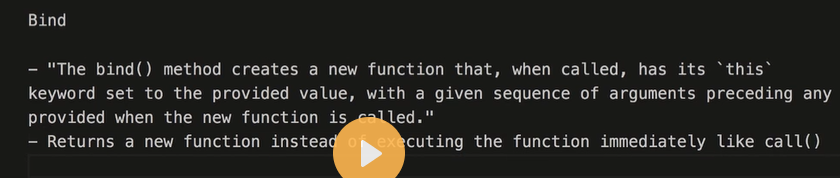
- bind() The bind() method is a method that is available on every function object in JavaScript. It allows you to create a new function with a given this value and optionally pre-set arguments. Here's an example:
function greet(greeting) {
console.log(`${greeting}, ${this.name}!`);
}
const person = {
name: 'John'
};
const sayHello = greet.bind(person, 'Hello');
sayHello(); // output: "Hello, John!"
In this example, we define a function greet() that logs a greeting message with the value of the name property of the this object and an optional greeting parameter. We also define an object person that has a name property set to 'John'. We then call the bind() method on the greet() function with person as the this value and the value 'Hello' as the pre-set greeting argument. The bind() method returns a new function sayHello() that has person as the this value and 'Hello' as the pre-set greeting argument. We call sayHello() and it logs the greeting message 'Hello, John!'.
===============================================
In javasript
In OUTPUT













Top comments (0)