tutorial_using_tasks
gradle-build
Gradle Projects
Types of Tasks
Default task
Custom tasks
gradle -q upper
gradle -q count
Task dependencies
Lazy dependsOn
Copy
Delete
Gradle Projects
a project is a collection of one or more tasks. A project represents a library JAR or a web application. It may also serve a distribution ZIP, which is assembled from the JARs of different projects. A project could be deploying our application to staging or production environments. A project could be deploying our application to the staging or production environment. Every Gradle build contains one or more projects. We can relate it with an example of a building; it can have any numbers of floors
Types of Tasks
There are two types of tasks in Gradle. They are as following:
- Default task
- Custom task
Default task
Default tasks are predefined tasks of Gradle. We can define it in our projects. Gradle let us define one or more default tasks that are executed if no other tasks are specified.
Custom tasks
Gradle allows us to create tasks; these tasks are called custom tasks. Custom tasks are user-defined tasks that are built to perform some specific work.
Syntax:
Task task_name{
group "-------group_name for task-------'
description '-------description of the task-------'
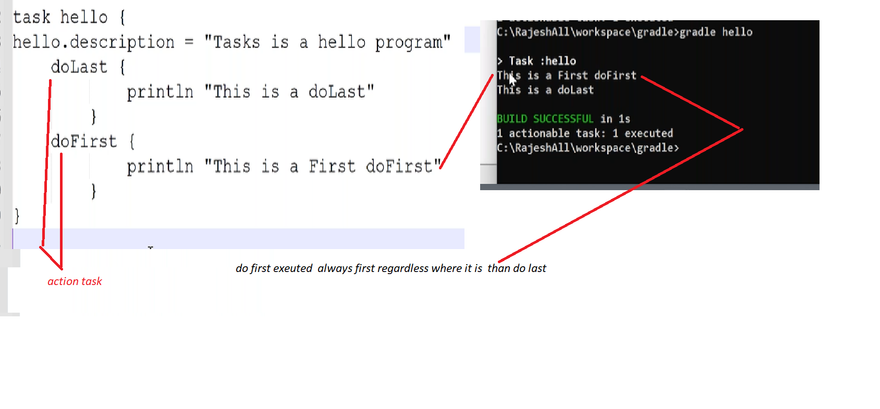
doLast{
-------code for execution-------
-----------------------------------
-----------------------------------
}
}
Follow the below steps to create a custom task:
Step1: Create a Gradle project. To create a Gradle project, open eclipse and navigate to new-> other and select the Gradle project. After that, follow some necessary steps.
Step2: Explore the project and open build.gradle file.
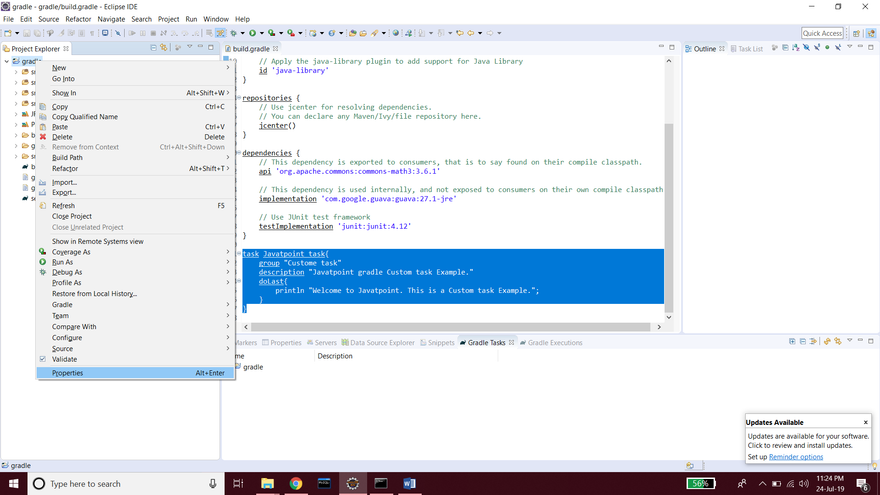
Step3: Add task code in build.gradle file. Consider the example below:
task Javatpoint_task{
group "Custom task"
description "Javatpoint Gradle Custom task Example."
doLast{
println "Welcome to Javatpoint. It is a Custom task Example.";
}
}
Step 4: Open the command line and change directory to the Gradle project's location. Also, we can do so from the eclipse, right-click on the project and select properties. **
In address bar type cmd to open the command line in this directory
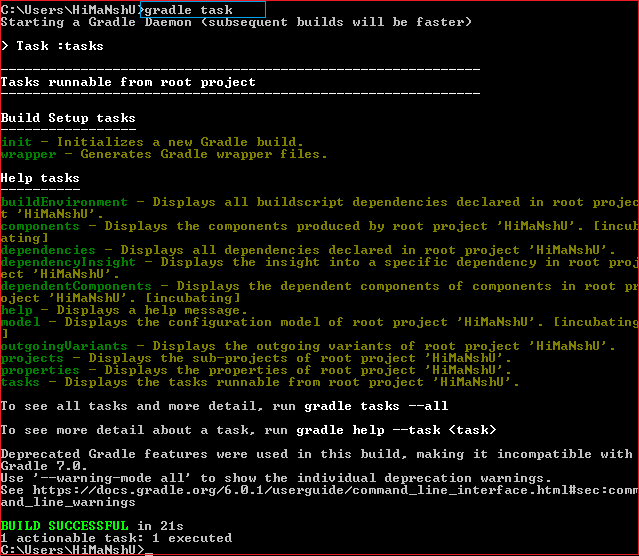
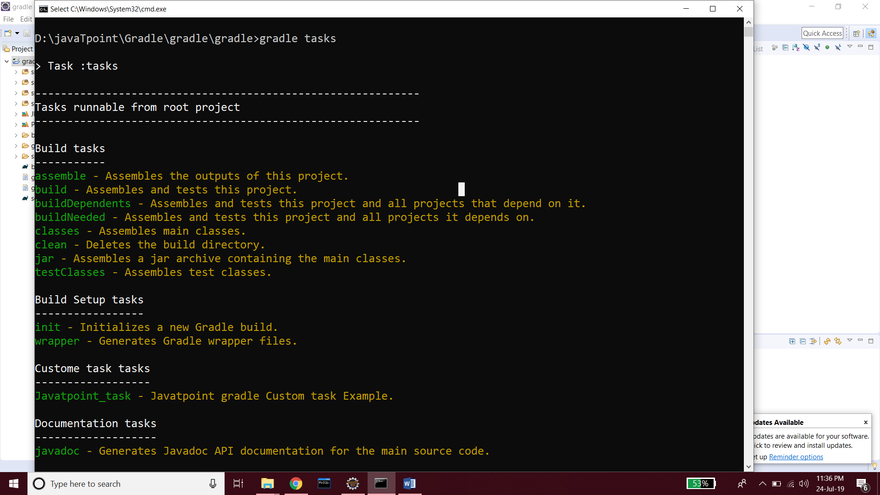
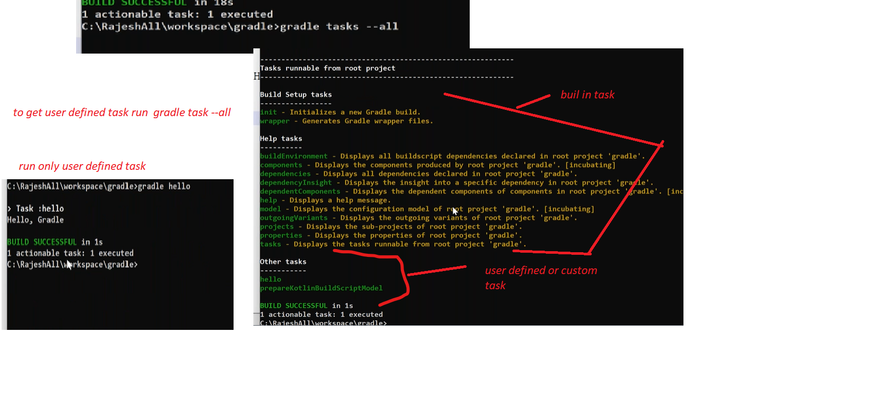
Step5: To know the default tasks and define the task in the project, type the gradle tasks command.
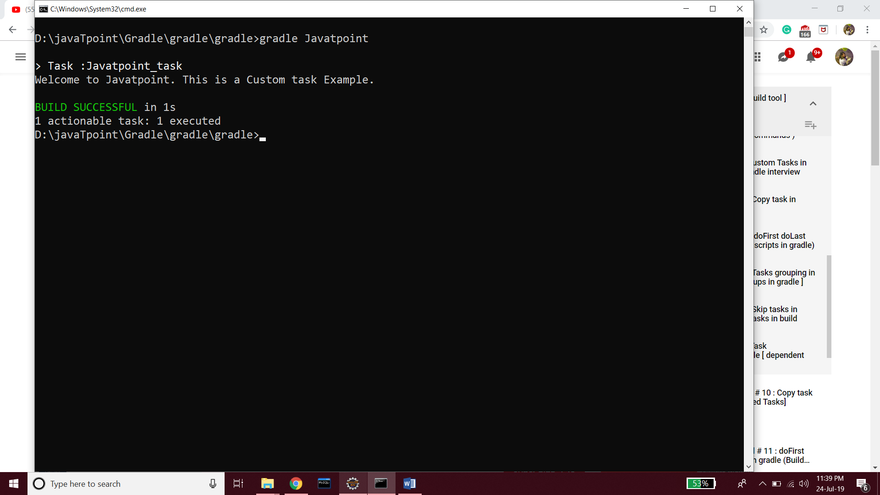
Step6: Now, to execute our custom task, run the command gradle taskname (as task name is Javatpoint, so gradle javatpoint). Consider the below output:
Defining tasks using a DSL specific syntax
tasks.register('upper') {
doLast {
String someString = 'mY_nAmE'
println "Original: $someString"
println "Upper case: ${someString.toUpperCase()}"
}
}
Output of gradle -q upper
> gradle -q upper
Original: mY_nAmE
Upper case: MY_NAME
tasks.register('count') {
doLast {
4.times { print "$it " }
}
}
Output of gradle -q count
> gradle -q count
0 1 2 3
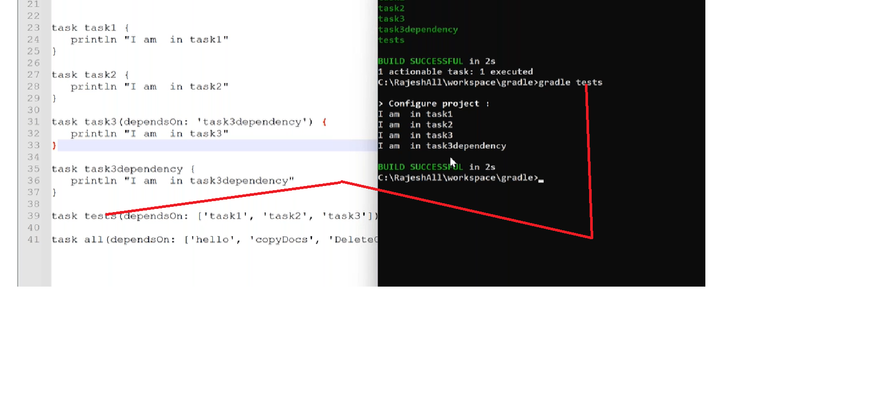
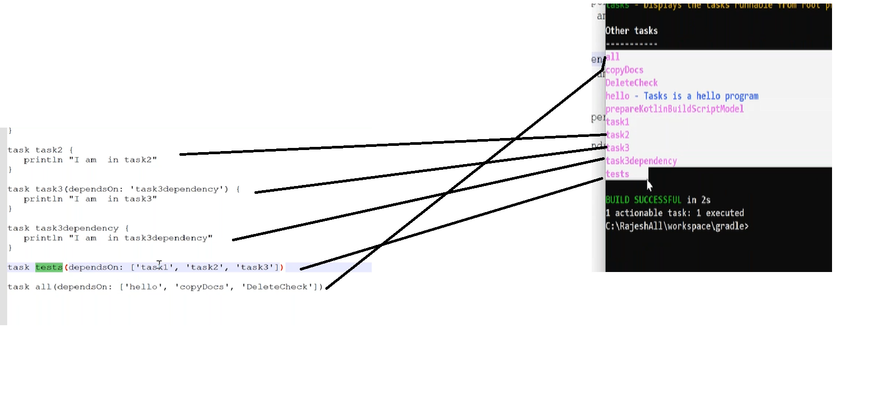
Task dependencies
you can declare tasks that depend on other tasks.
tasks.register('hello') {
doLast {
println 'Hello world!'
}
}
tasks.register('intro') {
dependsOn tasks.hello
doLast {
println "I'm Gradle"
}
}
Output of gradle -q intro
> gradle -q intro
Hello world!
I'm Gradle
Lazy dependsOn - the other task does not exist (yet)
tasks.register('taskX') {
dependsOn 'taskY'
doLast {
println 'taskX'
}
}
tasks.register('taskY') {
doLast {
println 'taskY'
}
}
Output of gradle -q taskX
> gradle -q taskX
taskY
taskX
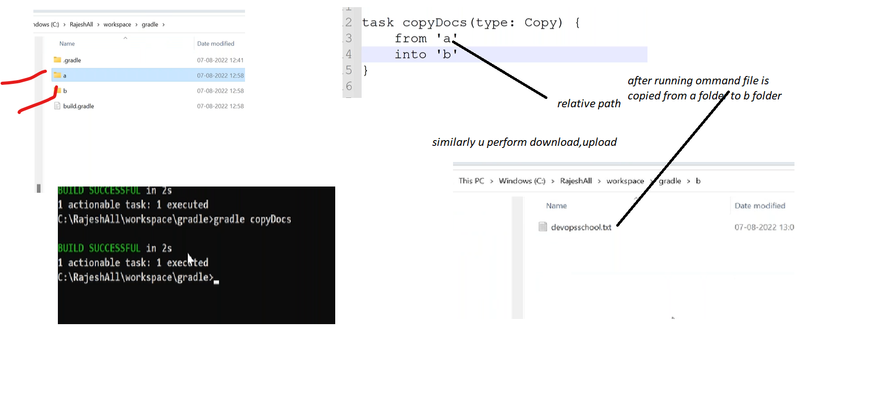
Copy
Copies files into a destination directory. This task can also rename and filter files as it copies. The task implements CopySpec for specifying what to copy.
Examples:
task copyDocs(type: Copy) {
from 'src/main/doc'
into 'build/target/doc'
}
//for Ant filter
import org.apache.tools.ant.filters.ReplaceTokens
//for including in the copy task
def dataContent = copySpec {
from 'src/data'
include '*.data'
}
task initConfig(type: Copy) {
from('src/main/config') {
include '**/*.properties'
include '**/*.xml'
filter(ReplaceTokens, tokens: [version: '2.3.1'])
}
from('src/main/config') {
exclude '**/*.properties', '**/*.xml'
}
from('src/main/languages') {
rename 'EN_US_(.*)', '$1'
}
into 'build/target/config'
exclude '**/*.bak'
includeEmptyDirs = false
with dataContent
}
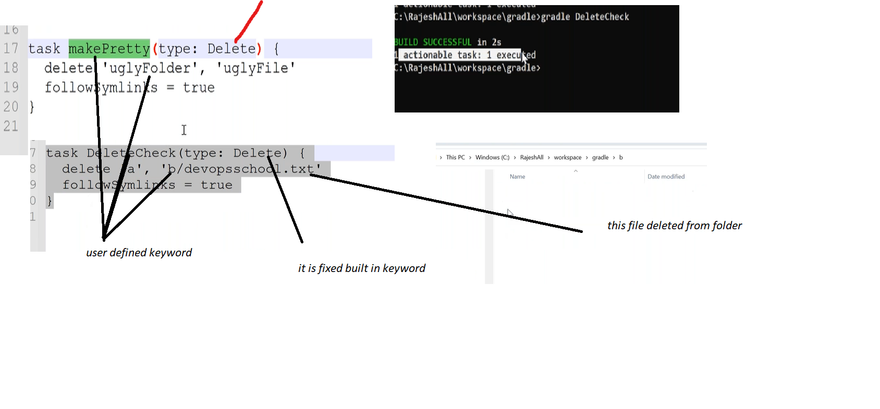
** Delete**
Deletes files or directories. Example:
task makePretty(type: Delete) {
delete 'uglyFolder', 'uglyFile'
followSymlinks = true
}
Be default symlinks will not be followed when deleting files. To change this behavior call Delete.setFollowSymlinks(boolean) with true. On systems that do not support symlinks, this will have no effect.


Top comments (0)