Flask-Queue-Worker is useful for executing long-running tasks asynchronously so that the main Flask app remains responsive. Below are some real-world scenarios where you can use it, along with example use cases
Background AI Content Generation
✅ Scenario: A user submits a request to generate AI-based content (e.g., blog, summary, or chatbot response).
🔧Example Use Case
- A user requests an AI-generated blog post.
- The task is queued and processed in the background.
- The user gets a task_id and can check progress later
.
Example API Flow
User requests content generation:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/generate -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"prompt": "Write an article about space exploration"}'
Response:
{ "job_id": "xyz123" }
User checks task status:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/xyz123
Response:
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "response": "Space exploration has advanced significantly over the past decades..." }
Asynchronous Image Processing
Scenario: Users upload an image that needs background processing (e.g., resizing, filtering, or AI-based enhancements).
🔧 Example Use Case
A user uploads an image.
The image is processed (resized, enhanced, etc.) in the background.
The user receives a link to download the processed image.
Example API Flow
User uploads an image for enhancement:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/enhance-image -F "image=@input.jpg"
Response:
{ "job_id": "abc123" }
User checks task status:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/abc123
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "image_url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000/downloads/output.jpg" }
Video Transcoding in the Background
Scenario: Users upload videos, and the system processes (converts, compresses, or enhances) them asynchronously.
🔧 Example Use Case
- User uploads a large video file.
- The system queues it for compression and format conversion.
- User gets a link to the processed video when ready . Example API Flow User uploads a video for processing:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/convert-video -F "video=@input.mp4"
Response:
{ "job_id": "video456" }
User checks task status:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/video456
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "video_url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000/downloads/output.mp4" }
Asynchronous Email Sending
Scenario: Users perform an action (e.g., registration, password reset), and an email needs to be sent without delaying the response.
🔧 Example Use Case
User signs up or requests a password reset.
Email sending is queued as a background job.
The user receives a confirmation response immediately.
Example API Flow
User registers for an account:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/register -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"email": "user@example.com"}'
Response:
{ "message": "Registration successful. Check your email!" }
Background worker sends email asynchronously.}
Web Scraping & Data Extraction
Scenario: A user requests data from a website, and scraping runs in the background to avoid blocking the app.
🔧 Example Use Case
- User requests product prices from an e-commerce site.
- The scraping task is queued and runs asynchronously.
- The user retrieves results when ready . Example API Flow User requests a product price comparison:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/scrape-prices -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"url": "https://www.example.com/product"}'
Response:
{ "job_id": "scrape789" }
User checks scraping progress:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/scrape789
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "prices": [{"store": "Amazon", "price": "$50"}, {"store": "eBay"}
Generating Reports in the Background
Scenario: Users request reports, which are generated asynchronously to avoid blocking the main application.
🔧 Example Use Case
A user requests a financial or analytics report.
The report generation runs in the background.
The user receives a download link when it’s ready.
Example API Flow
User requests report generation:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/generate-report -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"report_type": "sales"}'
Response:
{ "job_id": "report001" }
User checks report status:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/report001
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "report_url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000/downloads/sales_report.pdf" }
Background Machine Learning Model Training
Scenario: Users upload training data, and a machine learning model is trained asynchronously.
🔧 Example Use Case
- A user submits a dataset.
- The model is trained in the background.
- The user can later download the trained model . Example API Flow User submits dataset for training:
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/train-model -F "dataset=@data.csv"
Response:
{ "job_id": "ml_training123" }
User checks model training progress:
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/ml_training123
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "model_url": "http://127.0.0.1:5000/downloads/trained_model.pk"}
Example of single Queue
Install Required Dependencies
pip install flask-queue
Flask Back-End (app.py)
This script handles background content generation using Flask-Queue-Worker.
import os
import uuid
import time
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify, send_from_directory
from flask_queue import Queue
from multiprocessing import Process, Manager
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
# Initialize Flask app
app = Flask(__name__, static_folder="static")
# Initialize in-memory queue (No Redis, just Python's built-in multiprocessing)
task_manager = Manager()
queue = Queue(app, backend=task_manager.dict())
# Set OpenAI API Key (Replace with your actual API Key)
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your_openai_api_key"
# Initialize LangChain Model
chat_model = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4", temperature=0.7)
def generate_content(job_id, prompt, task_store):
"""
Function that generates content using LangChain and stores the result.
Runs in the background via Flask-Queue-Worker.
"""
task_store[job_id] = {"status": "PROCESSING"}
try:
response = chat_model([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
task_store[job_id] = {"status": "COMPLETED", "response": response.content}
except Exception as e:
task_store[job_id] = {"status": "FAILED", "error": str(e)}
@app.route('/generate', methods=['POST'])
def generate():
"""
API endpoint to trigger content generation in the background.
"""
data = request.get_json()
prompt = data.get("prompt", "")
if not prompt:
return jsonify({"error": "Prompt is required"}), 400
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.task_store[job_id] = {"status": "QUEUED"}
# Enqueue the task (Worker will pick it up)
queue.enqueue(generate_content, job_id, prompt)
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/task-status/<job_id>', methods=['GET'])
def get_task_status(job_id):
"""
API endpoint to check the status of a background task.
"""
task = queue.task_store.get(job_id)
if not task:
return jsonify({"status": "NOT_FOUND"}), 404
return jsonify(task)
@app.route('/')
def serve_index():
"""Serve the HTML front-end"""
return send_from_directory("static", "index.html")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
2️⃣ Front-End (static/index.html)
This HTML + JavaScript UI triggers the Flask API and checks job status.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Flask Queue Background Task</title>
<style>
body {
font-family: Arial, sans-serif;
max-width: 600px;
margin: 50px auto;
text-align: center;
}
input, button {
padding: 10px;
font-size: 16px;
}
#status {
margin-top: 20px;
font-weight: bold;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Generate AI Content (Background Task)</h2>
<input type="text" id="prompt" placeholder="Enter prompt here" />
<button onclick="generateContent()">Generate</button>
<p id="status"></p>
<p id="result"></p>
<script>
let jobId = "";
function generateContent() {
const prompt = document.getElementById("prompt").value;
if (!prompt) {
alert("Please enter a prompt");
return;
}
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Submitting request...";
document.getElementById("result").innerText = "";
fetch("/generate", {
method: "POST",
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify({ prompt })
})
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
jobId = data.job_id;
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Processing... (Checking every 3s)";
checkStatus();
})
.catch(error => {
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Error: " + error;
});
}
function checkStatus() {
if (!jobId) return;
fetch(`/task-status/${jobId}`)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(data => {
if (data.status === "PROCESSING") {
setTimeout(checkStatus, 3000);
} else if (data.status === "COMPLETED") {
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Completed!";
document.getElementById("result").innerText = data.response;
} else {
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Task Failed!";
}
})
.catch(error => {
document.getElementById("status").innerText = "Error: " + error;
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
3️⃣ Worker Process (worker.py)
This script processes jobs in the queue.
from flask_queue import Worker
from app import queue
if __name__ == '__main__':
worker = Worker(queue)
worker.work()
4️⃣ Running the Application
Step 1: Start Flask Server
python app.py
Flask runs on http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
The front-end UI is accessible at http://127.0.0.1:5000/.
Step 2: Start the Worker
In a new terminal:
python worker.py
This processes jobs from the queue asynchronously.
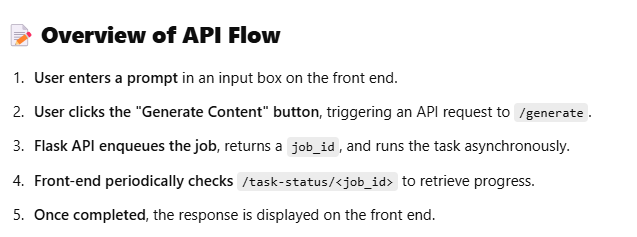
5️⃣ How It Works (Step-by-Step)
- User enters a prompt and clicks "Generate".
- Front-end calls /generate, returns job_id.
- Flask queues the task.
- Worker processes the task in the background.
- Front-end polls /task-status/ every 3 seconds.
- Once completed, the AI-generated response is displayed . 6️⃣ Example Usage User Triggers API
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/generate -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"prompt": "Write about AI"}'
Response:
{ "job_id": "abc123" }
Check Task Status
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/abc123
Response (Processing):
{ "status": "PROCESSING" }
Response (Completed):
{ "status": "COMPLETED", "response": "AI has revolutionized technology..." }
Example of Multiple Queue
Install Required Dependencies
Ensure you have Python installed, then install the required packages:
pip install flask flask-queue langchain openai pandas
- Create Flask App with Background Queue Create a file app.py and include endpoints for all seven scenarios.
import os
import uuid
import time
import pandas as pd
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
from flask_queue import Queue
from multiprocessing import Process, Manager
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
# Initialize Flask app
app = Flask(__name__)
# In-memory queue (No Redis, uses Python’s multiprocessing)
task_manager = Manager()
queue = Queue(app, backend=task_manager.dict())
# OpenAI API Key (Replace with your key)
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your_openai_api_key"
# Initialize LangChain model
chat_model = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4", temperature=0.7)
def update_task_status(job_id, status, result=None):
"""Update the status of a queued task"""
queue.task_store[job_id] = {"status": status, "result": result}
def generate_content(job_id, prompt):
"""Generates AI content using LangChain"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
try:
response = chat_model([HumanMessage(content=prompt)])
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", response.content)
except Exception as e:
update_task_status(job_id, "FAILED", str(e))
def enhance_image(job_id, image_path):
"""Simulate Image Processing"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(5) # Simulate processing time
processed_image = f"{image_path}_enhanced.jpg"
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", processed_image)
def convert_video(job_id, video_path):
"""Simulate Video Transcoding"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(10) # Simulate conversion
converted_video = f"{video_path}_converted.mp4"
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", converted_video)
def send_email(job_id, email):
"""Simulate Email Sending"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(3) # Simulate sending delay
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", f"Email sent to {email}")
def scrape_prices(job_id, url):
"""Simulate Web Scraping"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(5) # Simulate scraping
prices = [{"store": "Amazon", "price": "$50"}, {"store": "eBay", "price": "$55"}]
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", prices)
def generate_report(job_id, report_type):
"""Simulate Report Generation"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(7) # Simulate report creation
report_url = f"http://127.0.0.1:5000/downloads/{report_type}_report.pdf"
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", report_url)
def train_model(job_id, dataset_path):
"""Simulate ML Model Training"""
update_task_status(job_id, "PROCESSING")
time.sleep(15) # Simulate training
trained_model_path = f"{dataset_path}_trained.pkl"
update_task_status(job_id, "COMPLETED", trained_model_path)
@app.route('/generate', methods=['POST'])
def generate():
"""Trigger AI content generation"""
data = request.get_json()
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(generate_content, job_id, data["prompt"])
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/enhance-image', methods=['POST'])
def enhance():
"""Trigger image enhancement"""
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(enhance_image, job_id, "input.jpg")
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/convert-video', methods=['POST'])
def convert():
"""Trigger video processing"""
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(convert_video, job_id, "input.mp4")
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/send-email', methods=['POST'])
def email():
"""Trigger email sending"""
data = request.get_json()
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(send_email, job_id, data["email"])
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/scrape-prices', methods=['POST'])
def scrape():
"""Trigger web scraping"""
data = request.get_json()
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(scrape_prices, job_id, data["url"])
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/generate-report', methods=['POST'])
def report():
"""Trigger report generation"""
data = request.get_json()
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(generate_report, job_id, data["report_type"])
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/train-model', methods=['POST'])
def train():
"""Trigger ML model training"""
job_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
queue.enqueue(train_model, job_id, "dataset.csv")
return jsonify({"job_id": job_id}), 202
@app.route('/task-status/<job_id>', methods=['GET'])
def get_task_status(job_id):
"""Check the status of a background task"""
task = queue.task_store.get(job_id)
if not task:
return jsonify({"status": "NOT_FOUND"}), 404
return jsonify(task)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)
- Create a Worker Process Create a file worker.py to run queued tasks.
from flask_queue import Worker
from app import queue
if __name__ == '__main__':
worker = Worker(queue)
worker.work()
- Run Flask & Worker Start the Flask Server
python app.py
Start the Worker
Open another terminal and run:
python worker.py
- Test the API Trigger AI Content Generation
curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:5000/generate -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"prompt": "Write an article about AI"}'
Check Task Status
curl -X GET http://127.0.0.1:5000/task-status/your_job_id
Example Response:
{
"status": "COMPLETED",
"result": "Artificial Intelligence has transformed the world by..."
}
- Summary ✔ 7 Background Tasks Implemented ✔ No Redis Needed (Fully Python-based Queue) ✔ Flask-Queue-Worker Handles Task Execution ✔ Flask Stays Responsive While Tasks Run in the Background
🚀 Now, your Flask API supports multiple background processing scenarios! Let me know if you

Top comments (0)