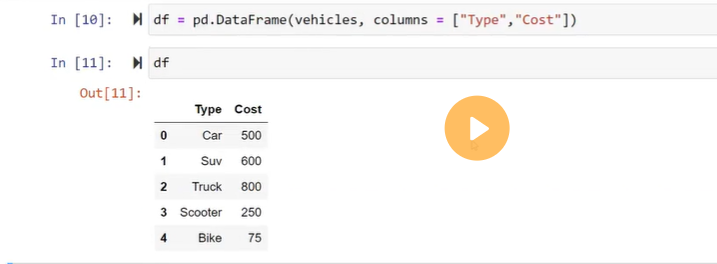
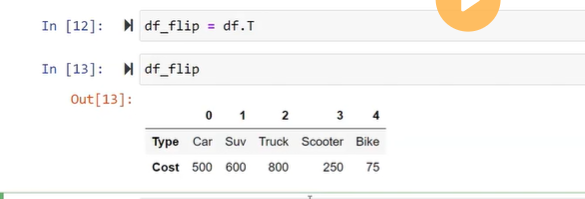
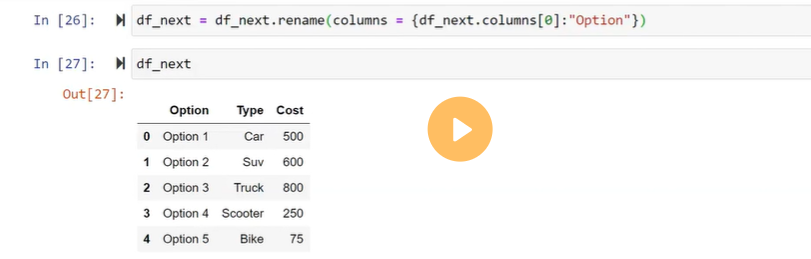
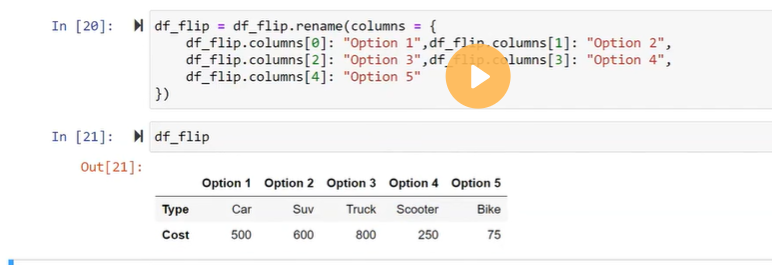
Create a dataframe using List
Create Dataframe from dict of ndarray/lists
Create a indexes Dataframe using arrays
Create Dataframe from list of dicts
Create Dataframe using the zip() function
Pandas Dataframe from Dicts of series.
A Data Frame is a two-dimension collection of data. It is a data structure where data is stored in tabular form. Datasets are arranged in rows and columns; we can store multiple datasets in the data frame. We can perform various arithmetic operations, such as adding column/row selection and columns/rows in the data frame.
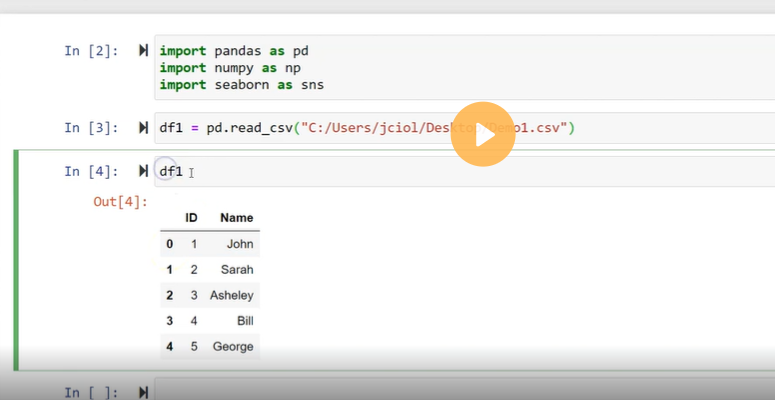
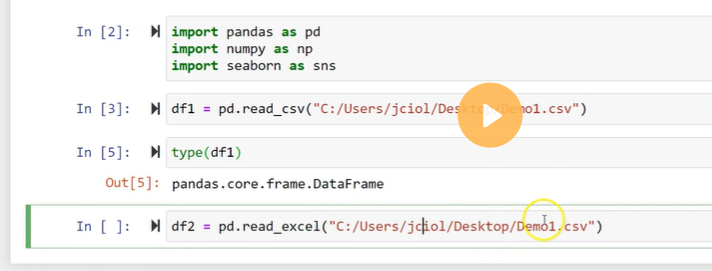
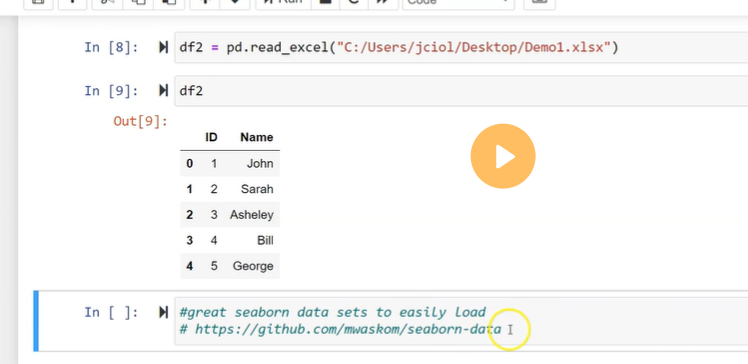
We can import the DataFrames from the external storage; these storages can be referred to as the SQL Database, CSV file, and an Excel file. We can also use the lists, dictionary, and from a list of dictionary, etc.
In this tutorial, we will learn to create the data frame in multiple ways. Let's understand these different ways.
First, we need to install the pandas library into the Python environment.
An empty dataframe
We can create a basic empty Dataframe. The dataframe constructor needs to be called to create the DataFrame. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
# import pandas as pd
import pandas as pd
# Calling DataFrame constructor
df = pd.DataFrame()
print(df)
Output:
Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []
Method - 2: Create a dataframe using List
We can create dataframe using a single list or list of lists. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
# importing pandas library
import pandas as pd
# string values in the list
lst = ['Java', 'Python', 'C', 'C++',
'JavaScript', 'Swift', 'Go']
# Calling DataFrame constructor on list
dframe = pd.DataFrame(lst)
print(dframe)
Output:
0 Java
1 Python
2 C
3 C++
4 JavaScript
5 Swift
6 Go
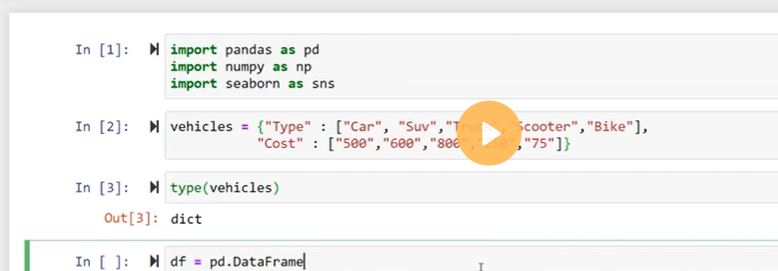
Method - 3: Create Dataframe from dict of ndarray/lists
The dict of ndarray/lists can be used to create a dataframe, all the ndarray must be of the same length. The index will be a range(n) by default; where n denotes the array length. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
import pandas as pd
# assign data of lists.
data = {'Name': ['Tom', 'Joseph', 'Krish', 'John'], 'Age': [20, 21, 19, 18]}
# Create DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Print the output.
print(df)
Output:
Name Age
0 Tom 20
1 Joseph 21
2 Krish 19
3 John 18
Method - 4: Create a indexes Dataframe using arrays
Let's understand the following example to create the indexes dataframe using arrays.
Example -
# DataFrame using arrays.
import pandas as pd
# assign data of lists.
data = {'Name':['Renault', 'Duster', 'Maruti', 'Honda City'], 'Ratings':[9.0, 8.0, 5.0, 3.0]}
# Creates pandas DataFrame.
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index =['position1', 'position2', 'position3', 'position4'])
# print the data
print(df)
Output:
Name Ratings
position1 Renault 9.0
position2 Duster 8.0
position3 Maruti 5.0
position4 Honda City 3.0
Explanation -
In the above code, we have defined the column name with the various car names and their ratings. We used the array to create indexes.
Method - 5: Create Dataframe from list of dicts
We can pass the lists of dictionaries as input data to create the Pandas dataframe. The column names are taken as keys by default. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
# the example is to create
# Pandas DataFrame by lists of dicts.
import pandas as pd
# assign values to lists.
data = [{'A': 10, 'B': 20, 'C':30}, {'x':100, 'y': 200, 'z': 300}]
# Creates DataFrame.
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Print the data
print(df)
Output:
A B C x y z
0 10.0 20.0 30.0 NaN NaN NaN
1 NaN NaN NaN 100.0 200.0 300.0
Let's understand another example to create the pandas dataframe from list of dictionaries with both row index as well as column index.
Example - 2:
Output:
x y
first 1.0 2.0
second NaN NaN
x y1
first 1.0 NaN
second NaN NaN
Let's understand another example to create dataframe by passing lists of dictionary and rows.
Example - 3
# The example is to create
# Pandas DataFrame by passing lists of
# Dictionaries and row indices.
import pandas as pd
# assign values to lists
data = [{'x': 2, 'z':3}, {'x': 10, 'y': 20, 'z': 30}]
# Creates padas DataFrame by passing
# Lists of dictionaries and row index.
dframe = pd.DataFrame(data, index =['first', 'second'])
# Print the dataframe
print(dframe)
Output:
x y z
first 2 NaN 3
second 10 20.0 30
We have discussed the three ways to create the dataframe using the lists of dictionary.
Method - 6: Create Dataframe using the zip() function
The zip() function is used to merge the two lists. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
# The example is to create
# pandas dataframe from lists using zip.
import pandas as pd
# List1
Name = ['tom', 'krish', 'arun', 'juli']
# List2
Marks = [95, 63, 54, 47]
# two lists.
# and merge them by using zip().
list_tuples = list(zip(Name, Marks))
# Assign data to tuples.
print(list_tuples)
# Converting lists of tuples into
# pandas Dataframe.
dframe = pd.DataFrame(list_tuples, columns=['Name', 'Marks'])
# Print data.
print(dframe)
Output:
[('john', 95), ('krish', 63), ('arun', 54), ('juli', 47)]
Name Marks
0 john 95
1 krish 63
2 arun 54
3 juli 47
Method - 7: Create Dataframe from Dicts of series
The dictionary can be passed to create a dataframe. We can use the Dicts of series where the subsequent index is the union of all the series of passed index value. Let's understand the following example.
Example -
Pandas Dataframe from Dicts of series.
import pandas as pd
# Initialize data to Dicts of series.
d = {'Electronics' : pd.Series([97, 56, 87, 45], index =['John', 'Abhinay', 'Peter', 'Andrew']),
'Civil' : pd.Series([97, 88, 44, 96], index =['John', 'Abhinay', 'Peter', 'Andrew'])}
# creates Dataframe.
dframe = pd.DataFrame(d)
# print the data.
print(dframe)
Output:
Electronics Civil
John 97 97
Abhinay 56 88
Peter 87 44
Andrew 45 96

Top comments (0)