Creating a Laravel package for a custom Markdown plugin
Creating a Laravel package for likes or comment plugin
How to enable or disable plugin
How to locate plugin package in laravel project
Roles of minimum-stability in Composer
Composer Package Manager plays a critical role in creating custom plugins in Laravel. It provides the tools and structure necessary for developing, managing, and distributing reusable and modular code. Here's an overview of Composer's role in creating custom plugins for Laravel:
Creating a Laravel package for a custom Markdown plugin
Set Up the Package Directory
Create a directory for the Markdown package:
mkdir MarkdownPlugin
cd MarkdownPlugin
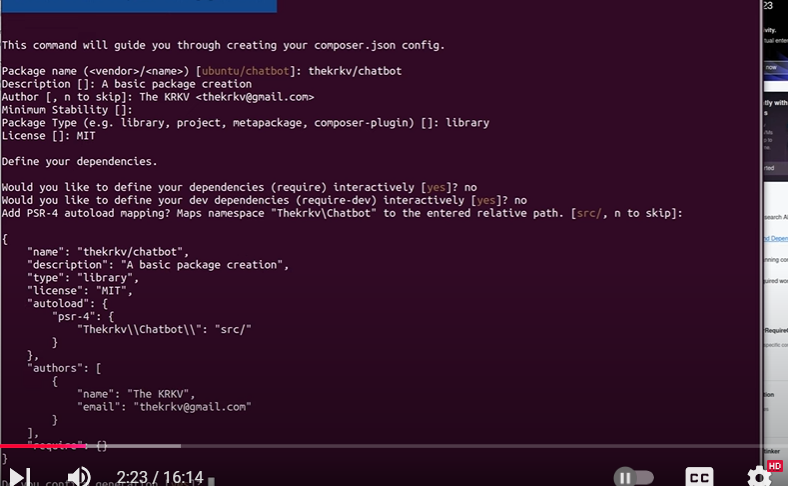
composer init
Provide details like the package name, description, and namespace. For example:
Name: my-vendor/markdown-plugin
Description: A custom Markdown plugin for Laravel
Autoload: PSR-4, namespace MarkdownPlugin\\, directory src/.
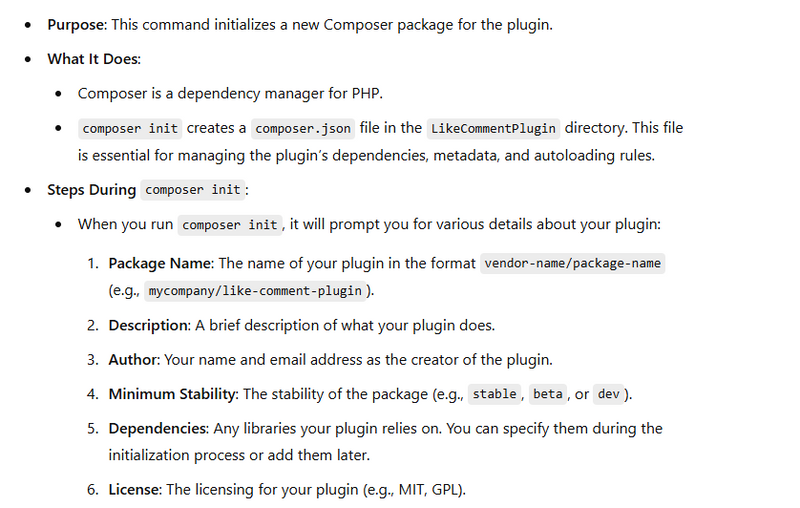
Purpose of composer init
A composer.json file is created with the following basic structure
{
"name": "vendor-name/like-comment-plugin",
"description": "A plugin for adding likes and comments functionality.",
"type": "library",
"license": "MIT",
"authors": [
{
"name": "Your Name",
"email": "your-email@example.com"
}
],
"require": {}
}
Directory Structure
MarkdownPlugin/
├── src/
│ ├── MarkdownService.php
│ ├── MarkdownPluginServiceProvider.php
│ ├── Facades/
│ │ └── Markdown.php
│ ├── Views/
│ │ └── markdown.blade.php
│ └── Commands/
│ └── RenderMarkdown.php
├── config/
│ └── markdown-plugin.php
├── tests/
│ └── ExampleTest.php
├── composer.json
└── README.md
Create the Markdown Processor
Markdown Service
src/MarkdownService.php
<?php
namespace MarkdownPlugin;
use Parsedown;
class MarkdownService
{
protected $parsedown;
public function __construct()
{
$this->parsedown = new Parsedown();
}
public function parse($markdown)
{
return $this->parsedown->text($markdown);
}
public function parseToHtml($markdown)
{
return $this->parsedown->setBreaksEnabled(true)->text($markdown);
}
}
Service Provider
src/MarkdownPluginServiceProvider.php
<?php
namespace MarkdownPlugin;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class MarkdownPluginServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register()
{
$this->app->singleton('markdown', function () {
return new MarkdownService();
});
}
public function boot()
{
// Publish configuration file
$this->publishes([
__DIR__ . '/../config/markdown-plugin.php' => config_path('markdown-plugin.php'),
]);
// Publish views
$this->loadViewsFrom(__DIR__ . '/Views', 'markdown-plugin');
}
}
Markdown Facade
src/Facades/Markdown.php
<?php
namespace MarkdownPlugin\Facades;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
class Markdown extends Facade
{
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'markdown';
}
}
Custom Artisan Command
src/Commands/RenderMarkdown.php
<?php
namespace MarkdownPlugin\Commands;
use Illuminate\Console\Command;
use MarkdownPlugin\Facades\Markdown;
class RenderMarkdown extends Command
{
protected $signature = 'markdown:render {text}';
protected $description = 'Render Markdown text to HTML';
public function handle()
{
$text = $this->argument('text');
$html = Markdown::parseToHtml($text);
$this->info("Rendered HTML:\n$html");
}
}
View File
src/Views/markdown.blade.php
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Markdown Preview</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
{!! $html !!}
</div>
</body>
</html>
Configuration File
config/markdown-plugin.php
<?php
return [
'default_breaks_enabled' => true,
];
Composer Autoloading
Update composer.json:
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"MarkdownPlugin\\": "src/"
}
}
Run:
composer dump-autoload
Integrate with Laravel
Add Package Locally
Add the package path to the Laravel app:
"repositories": [
{
"type": "path",
"url": "../MarkdownPlugin"
}
],
Require the package:
composer require my-vendor/markdown-plugin
Register Service Provider and Facade
In config/app.php:
'providers' => [
MarkdownPlugin\MarkdownPluginServiceProvider::class,
],
'aliases' => [
'Markdown' => MarkdownPlugin\Facades\Markdown::class,
],
Test the Markdown Plugin
Add Routes
In routes/web.php:
use Markdown;
Route::get('/markdown', function () {
$markdown = "# Welcome to Markdown Plugin\nThis is **bold text** and _italic text_.";
$html = Markdown::parseToHtml($markdown);
return view('markdown-plugin::markdown', compact('html'));
});
Run the Custom Command
php artisan markdown:render "Hello **Markdown**!"
Creating a Laravel package for likes or comment plugin
Set Up the Package
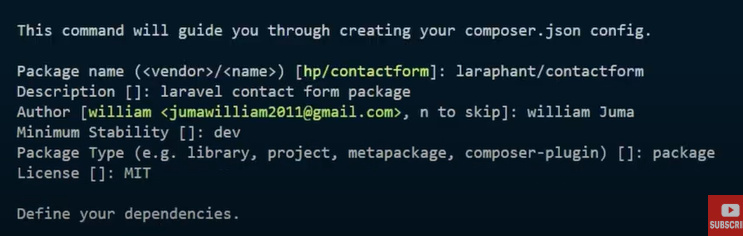
Create a new directory for your package and initialize it with Composer:
mkdir LikeCommentPlugin
cd LikeCommentPlugin
composer init
Name: my-vendor/like-comment-plugin
Description: A Laravel plugin for likes and comments
Autoload: PSR-4, namespace LikeCommentPlugin\\, directory src/
Directory Structure
Create the following structure:
LikeCommentPlugin/
├── src/
│ ├── LikeService.php
│ ├── CommentService.php
│ ├── LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider.php
│ ├── Facades/
│ │ ├── Like.php
│ │ └── Comment.php
│ ├── Models/
│ │ ├── Like.php
│ │ └── Comment.php
│ └── Http/
│ ├── Controllers/
│ │ ├── LikeController.php
│ │ └── CommentController.php
│ └── Requests/
│ ├── LikeRequest.php
│ └── CommentRequest.php
├── migrations/
│ ├── create_likes_table.php
│ └── create_comments_table.php
├── config/
│ └── like-comment.php
├── tests/
│ └── ExampleTest.php
├── composer.json
└── README.md
Create Models
Like Model
src/Models/Like.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Like extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['user_id', 'likeable_id', 'likeable_type'];
public function likeable()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
Comment Model
src/Models/Comment.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Models;
use Illuminate\Database\Eloquent\Model;
class Comment extends Model
{
protected $fillable = ['user_id', 'content', 'commentable_id', 'commentable_type'];
public function commentable()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
Database Migrations
Create Likes Table
migrations/create_likes_table.php
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateLikesTable extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('likes', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->unsignedBigInteger('user_id');
$table->morphs('likeable');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('likes');
}
}
Create Comments Table
migrations/create_comments_table.php
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreateCommentsTable extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('comments', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->unsignedBigInteger('user_id');
$table->text('content');
$table->morphs('commentable');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('comments');
}
}
Create Services
Like Service
src/LikeService.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Models\Like;
class LikeService
{
public function toggleLike($userId, $likeable)
{
$like = $likeable->likes()->where('user_id', $userId)->first();
if ($like) {
$like->delete();
return 'Unliked';
}
$likeable->likes()->create(['user_id' => $userId]);
return 'Liked';
}
}
Comment Service
src/CommentService.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Models\Comment;
class CommentService
{
public function addComment($userId, $commentable, $content)
{
return $commentable->comments()->create([
'user_id' => $userId,
'content' => $content,
]);
}
}
Service Provider
src/LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function register()
{
$this->app->singleton('like', function () {
return new LikeService();
});
$this->app->singleton('comment', function () {
return new CommentService();
});
}
public function boot()
{
$this->loadMigrationsFrom(__DIR__ . '/../migrations');
$this->publishes([
__DIR__ . '/../config/like-comment.php' => config_path('like-comment.php'),
]);
}
}
Create Controllers
Like Controller
src/Http/Controllers/LikeController.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Facades\Like;
class LikeController extends Controller
{
public function toggleLike(Request $request, $likeableType, $likeableId)
{
$likeable = app($likeableType)->findOrFail($likeableId);
$result = Like::toggleLike(auth()->id(), $likeable);
return response()->json(['message' => $result]);
}
}
Comment Controller
src/Http/Controllers/CommentController.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Facades\Comment;
class CommentController extends Controller
{
public function addComment(Request $request, $commentableType, $commentableId)
{
$request->validate(['content' => 'required|string']);
$commentable = app($commentableType)->findOrFail($commentableId);
$comment = Comment::addComment(auth()->id(), $commentable, $request->content);
return response()->json(['comment' => $comment]);
}
}
Facades
Like Facade
src/Facades/Like.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Facades;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
class Like extends Facade
{
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'like';
}
}
Comment Facade
src/Facades/Comment.php
<?php
namespace LikeCommentPlugin\Facades;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Facade;
class Comment extends Facade
{
protected static function getFacadeAccessor()
{
return 'comment';
}
}
Integrate with Laravel
Add the package path in your Laravel app's composer.json:
"repositories": [
{
"type": "path",
"url": "../LikeCommentPlugin"
}
]
Require the package:
composer require my-vendor/like-comment-plugin
Register the service provider and facades in config/app.php:
'providers' => [
LikeCommentPlugin\LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider::class,
],
'aliases' => [
'Like' => LikeCommentPlugin\Facades\Like::class,
'Comment' => LikeCommentPlugin\Facades\Comment::class,
],
Test with Routes
Add routes in routes/web.php:
use LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers\LikeController;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers\CommentController;
Route::post('/like/{type}/{id}', [LikeController::class, 'toggleLike']);
Route::post('/comment/{type}/{id}', [CommentController::class, 'addComment']);
How to enable or disable plugin
Create a Table to Store Plugin States
Add a migration for a plugins table to manage the state of each plugin.
php artisan make:migration create_plugins_table
In the migration file:
<?php
use Illuminate\Database\Migrations\Migration;
use Illuminate\Database\Schema\Blueprint;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Schema;
class CreatePluginsTable extends Migration
{
public function up()
{
Schema::create('plugins', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name')->unique();
$table->boolean('is_enabled')->default(false);
$table->timestamps();
});
}
public function down()
{
Schema::dropIfExists('plugins');
}
}
Run the migration:
php artisan migrate
Seed the Plugin Table with Default Plugins
Create a seeder to add default plugins (Markdown, Likes, and Comments) into the plugins table.
php artisan make:seeder PluginSeeder
In PluginSeeder.php:
<?php
namespace Database\Seeders;
use Illuminate\Database\Seeder;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class PluginSeeder extends Seeder
{
public function run()
{
DB::table('plugins')->insert([
['name' => 'Markdown', 'is_enabled' => true],
['name' => 'Likes', 'is_enabled' => true],
['name' => 'Comments', 'is_enabled' => true],
]);
}
}
Run the seeder:
php artisan db:seed --class=PluginSeeder
Middleware to Check Plugin State
Create middleware to handle plugin activation.
php artisan make:middleware CheckPluginStatus
In CheckPluginStatus.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class CheckPluginStatus
{
public function handle(Request $request, Closure $next, $plugin)
{
$isEnabled = DB::table('plugins')->where('name', $plugin)->value('is_enabled');
if (!$isEnabled) {
abort(403, "The {$plugin} plugin is currently disabled.");
}
return $next($request);
}
}
Register the middleware in app/Http/Kernel.php:
protected $routeMiddleware = [
// other middleware
'plugin.check' => \App\Http\Middleware\CheckPluginStatus::class,
];
Add Plugin Enable/Disable Logic
Create a controller to toggle plugin states.
php artisan make:controller PluginController
In PluginController.php:
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class PluginController extends Controller
{
public function togglePlugin($pluginName)
{
$plugin = DB::table('plugins')->where('name', $pluginName)->first();
if (!$plugin) {
return response()->json(['message' => 'Plugin not found'], 404);
}
$isEnabled = !$plugin->is_enabled;
DB::table('plugins')->where('name', $pluginName)->update(['is_enabled' => $isEnabled]);
$status = $isEnabled ? 'enabled' : 'disabled';
return response()->json(['message' => "{$pluginName} plugin has been {$status}."]);
}
}
Define Routes for Plugin Management
Add routes to enable or disable plugins in routes/web.php:
use App\Http\Controllers\PluginController;
Route::post('/plugin/toggle/{name}', [PluginController::class, 'togglePlugin'])->name('plugin.toggle');
Restrict Plugin Functionality Based on State
Update your plugin logic (Markdown, Likes, Comments) to check if the plugin is enabled before performing actions. Use the plugin.check middleware for specific routes.
Example for Routes
use LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers\LikeController;
use LikeCommentPlugin\Http\Controllers\CommentController;
Route::middleware(['plugin.check:Likes'])->group(function () {
Route::post('/like/{type}/{id}', [LikeController::class, 'toggleLike']);
});
Route::middleware(['plugin.check:Comments'])->group(function () {
Route::post('/comment/{type}/{id}', [CommentController::class, 'addComment']);
});
Route::middleware(['plugin.check:Markdown'])->group(function () {
Route::get('/markdown', function () {
return "Markdown plugin is active!";
});
});
Frontend Interface to Manage Plugins
Add a basic UI in Blade to manage plugin states.
Example Blade File: resources/views/plugins/index.blade.php
@extends('layouts.app')
@section('content')
<div class="container">
<h1>Manage Plugins</h1>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Plugin</th>
<th>Status</th>
<th>Action</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach($plugins as $plugin)
<tr>
<td>{{ $plugin->name }}</td>
<td>{{ $plugin->is_enabled ? 'Enabled' : 'Disabled' }}</td>
<td>
<form action="{{ route('plugin.toggle', $plugin->name) }}" method="POST">
@csrf
<button class="btn btn-primary">
{{ $plugin->is_enabled ? 'Disable' : 'Enable' }}
</button>
</form>
</td>
</tr>
@endforeach
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
@endsection
Controller to Fetch Plugin Data
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
class PluginManagementController extends Controller
{
public function index()
{
$plugins = DB::table('plugins')->get();
return view('plugins.index', compact('plugins'));
}
}
Define the route for the management page:
Route::get('/plugins', [PluginManagementController::class, 'index'])->name('plugins.index');
Testing
Access the /plugins page to view and toggle plugins.
Test routes for each plugin, ensuring they are blocked when disabled and accessible when enabled.
Use the PluginController API for toggling plugin states dynamically.
How to locate plugin package in laravel project
Directory Structure
Assume your htdocs directory has the following structure:
htdocs/
├── laravel-project/ # Your Laravel application
│ ├── composer.json
│ ├── app/
│ ├── config/
│ └── ...
├── plugin/ # Your plugin directory
│ ├── src/
│ ├── composer.json
│ ├── migrations/
│ ├── config/
│ └── ...
Update Laravel Project's composer.json
In the laravel-project/composer.json, add the plugin directory as a path repository under the repositories section.
Open laravel-project/composer.json.
Add the following:
"repositories": [
{
"type": "path",
"url": "../plugin"
}
]
=====================OR========================================
{
"require": {
"php": "^8.0",
"my-vendor/like-comment-plugin": "*"
},
"repositories": [
{
"type": "path",
"url": "../my-plugins/LikeCommentPlugin"
}
]
}
Require the plugin package:
cd laravel-project
composer require my-vendor/like-comment-plugin
my-vendor/like-comment-plugin must match the "name" field in the composer.json file of your plugin.
Step 2: Configure Your Plugin's composer.json
In the plugin/composer.json file, ensure the following configurations are set:
Example plugin/composer.json:
{
"name": "my-vendor/like-comment-plugin",
"description": "A Laravel plugin for likes and comments",
"type": "library",
"autoload": {
"psr-4": {
"LikeCommentPlugin\\": "src/"
}
},
"extra": {
"laravel": {
"providers": [
"LikeCommentPlugin\\LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider"
],
"aliases": {
"Like": "LikeCommentPlugin\\Facades\\Like",
"Comment": "LikeCommentPlugin\\Facades\\Comment"
}
}
}
}
Step 3: Verify the Plugin Structure
Ensure the plugin directory structure matches the expected PSR-4 autoloading format.
Example Directory Structure:
plugin/
├── src/
│ ├── LikeService.php
│ ├── CommentService.php
│ ├── LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider.php
│ ├── Facades/
│ │ ├── Like.php
│ │ └── Comment.php
│ ├── Models/
│ │ ├── Like.php
│ │ └── Comment.php
│ └── Http/
│ ├── Controllers/
│ │ ├── LikeController.php
│ │ └── CommentController.php
│ └── Requests/
│ ├── LikeRequest.php
│ └── CommentRequest.php
├── migrations/
│ ├── create_likes_table.php
│ └── create_comments_table.php
├── config/
│ └── like-comment.php
├── composer.json
└── README.md
Step 4: Test the Integration
Run Composer Dump-Autoload
Run the following command inside the laravel-project directory to ensure Composer recognizes the plugin:
composer dump-autoload
Verify Service Provider
The LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider from your plugin should automatically register. If not, manually add it to config/app.php:
'providers' => [
// Other service providers
LikeCommentPlugin\LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider::class,
],
Publish Plugin Assets (Optional)
If your plugin provides migrations, configuration, or other resources, you can publish them using:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="LikeCommentPlugin\LikeCommentPluginServiceProvider"
Step 5: Use the Plugin
Routes:
If your plugin registers routes (e.g., Http/routes.php in the plugin), ensure they are loaded properly. For example:
Route::middleware('web')->group(function () {
Route::post('/like/{type}/{id}', [LikeController::class, 'toggleLike']);
Route::post('/comment/{type}/{id}', [CommentController::class, 'addComment']);
});
Plugin Features:
You can now use the plugin features (e.g., Like and Comment facades) in your Laravel project:
use Like;
use Comment;
Like::toggleLike($userId, $likeable);
Comment::addComment($userId, $commentable, $content);
Step 6: Development and Testing
Local Development: Any changes in the plugin directory will immediately reflect in the Laravel project due to the path repository configuration.
Testing: Run the Laravel project's tests to verify the plugin's functionality:
php artisan test
Step 7: (Optional) Distribute the Plugin
If you want to distribute the plugin in the future:
Push the plugin to a Git repository.
Register it on Packagist for global availability.
Roles of minimum-stability in Composer
Roles of minimum-stability in Composer
Controls Dependency Versions:
It determines which versions of the packages Composer is allowed to consider when resolving dependencies.
Packages are released in various stability levels:
stable
RC (Release Candidate)
beta
alpha
dev
Allows Development Versions:
If "minimum-stability": "dev", Composer will allow development versions of packages to be installed. This is especially useful during the development phase of a package when you might want to use other libraries or dependencies that are still in development.
Defaults to Stable Without It:
If minimum-stability is not defined, Composer defaults to stable. This means only stable versions of packages will be considered unless explicitly required in the require section with a version constraint that specifies otherwise.
Overrides Stability Constraints:
When set to dev, Composer will consider any version (including unstable ones) that matches your requirements, even if a stable version exists.
How It Affects the Output
If "minimum-stability": "dev" is included:
Composer will consider dev versions for all dependencies.
You may end up installing development versions of packages, which can:
Introduce unstable or experimental code into your project.
Potentially cause bugs or breaking changes as development versions are often incomplete.
If "minimum-stability": "dev" is excluded:
Composer will only consider stable versions unless a package explicitly requires a development version (e.g., ^2.0@dev).
This results in a more stable and reliable project.
Best Practices
Use "minimum-stability": "dev" only during development or if you're creating a library/plugin where dependencies may still be in development.
Add "prefer-stable": true to ensure that Composer will prioritize stable versions whenever available, even when minimum-stability is set to dev.
Example with prefer-stable:
{
"minimum-stability": "dev",
"prefer-stable": true
}
Avoid using "minimum-stability": "dev" in production projects as it may introduce unexpected and unstable updates.

Top comments (0)