referene
referene
referene
referene
1.What is sudo command in linux?
2.What is /etc/sudoers file?
3.What is purpose of visudo.
4.Explain four types of aliases.
5.How to give root user all of the superuser privileges.
6.How to user can run all commands on all hosts, as all users and groups.
7.you want is enable another user with the same powers as root
8.you want is enable another user with the only run certain commands
9.how to give superuser permissions to groups.
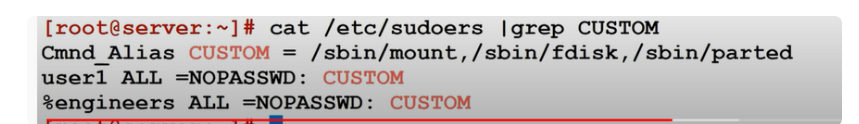
10.you want is enable another user with the only run certain commands using Cmnd_Alias
11.how to enable some user_alias to use some privileges to some Cmnd_Alias
- how to Search custom commands using pipe grep .
- allow user to run any commands without password
What is sudo command in linux?
In a typical linux server you have three types of users:
super or root user has full access to server
system user (non-interactive) has limited access to server
normal user (interactive) has limited access to server
Root or super user has administrative permissions and can perform all operations or run any command on a server while normal user can not run all commands.
Sometimes, you may want multiple users to login to your server and perform different operations some of them may need to run some specific commands that normal user do not have access to.
Sudo utility is designed to overcome this proble, Normally sudo user can run all commands but in some case we want normal user to have access to specific commands.
What is /etc/sudoers file?
The /etc/sudoers file controls who can run what commands. Normal linux user can not run all commands however in some case if you want them ro run privileged commands you can define them in /etc/sudoers file.
The sudo command is basically a command that allow user to execute a command as another user. It is basically allowing normal users to execute commands usually reserved to the root user.
The visudo command is a safe and secure way of editing the /etc/sudoers file on the linux system.
What is purpose of visudo
The visudo command is a safe and secure way of editing the /etc/sudoers file on UNIX and Linux systems. /etc/sudoers is instumental for gaining privileged access via sudo command.
Since the sudoers file determines which users can run administrative tasks, those requiring superuser privileges, it is a good idea to take some precautions when editing it, and that’s what visudo does.
It locks the sudoers file so it cannot be edited by anyone else simultaneously. It also checks the syntax of your edits and provides basic sanity checks. If someone else is editing the file you’ll get a message to try later, and if there are errors in your edits it wont save them.
Preventing simultaneous editing by someone else is helpful to ensure your edits aren’t lost, and saving a sudoers file without errors is important because you could otherwise end up locked out of your system. An unreadable sudoers file will prevent you from running administrative tasks by using the sudo command or becoming root, and editing the sudoers file itself requires those privileges. So you really don’t want to screw that one up.
Visudo is basically a wrapper for a text editor such as vi or nano. Vi is traditionally the default unless your distribution or OS has something else set up. For basics on how to use vi for editing check out the vi survival guide.
Explain four types of aliases
you can set up aliases to group multiple entries into a single one for use in these statements
There are four types of aliases:
- User_Alias for listing users,
- Runas_Alias for listing users a given user can run as,
- Host_Alias for listing hosts,
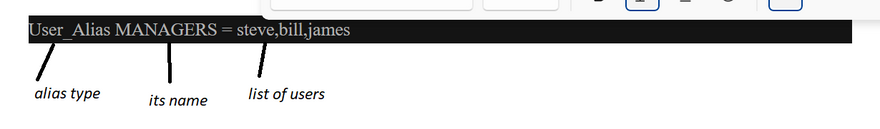
- Cmnd_Alias for listing commands. To set up an alias just state the alias type, its name, and then the list of users, hosts or commands you want to associate it with. For example to set up a User_Alias you can do this:
** User Aliases**
User Alias are used to specify groups of users. You can specify usernames, system groups (prefixed by a %) and netgroups (prefixed by a +) as follows:
# setting ADMINS alias for system group admin
User_Alias ADMINS = %admin
# DEVS alias is set for users sandip, john and brad
User_Alias DEVS =sandip, john, brad
# DEVOPS alias set for users sandip and mac
User_Alias DEVOPS = sandip, mac
# You can also use ! to exclude users from an alias
User_Alias LIMITED_USERS = USERS, !DEVS, !DEVOPS
** Runsas Aliases**
Runas Aliases are almost the same as user aliases but you are allowed to specify users by uid's.
# UID 0 is normally used for root
# Note the hash (#) on the following line indicates a uid, not a comment.
Runas_Alias ROOT = #0
# setting ADMINS alias for system group admin
# with the addition of "root"
Runas_Alias ADMINS = %admin, root
** Host Aliases**
A host alias is a list of hostname, ip addresses, networks and netgroups (prefixed with a +).
# This is all the servers
Host_Alias SERVERS = 192.168.0.1, 192.168.0.2, server1
# This is the whole network
Host_Alias NETWORK = 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0
# And this is every machine in the network that is not a server
Host_Alias WORKSTATIONS = NETWORK, !SERVERS
** Command Aliases**
Command aliases are lists of commands and directories. If you specify a directory it will include any file within that directory but not in any subdirectories.
# All the shutdown commands
Cmnd_Alias HTTPD_CMDS = /sbin/service httpd start, /sbin/service httpd stop
# Web commands
Cmnd_Alias APACHE_CMDS = /etc/init.d/apache2
All the other aliases follow the same format only with the different specified type, and listing different types of things, like users, hosts or commands. If we wanted to put the three commands from the above example with the “daniel” user under an alias we could do this:
And then instead of listing these two commands in our configuration for daniel we can just specify the READ alias:
How to give root user all of the superuser privileges
How to user can run all commands on all hosts, as all users and groups
you want is enable another user with the same powers as root
you want is enable another user with the only run certain commands
how to give superuser permissions to groups
*you want is enable another user with the only run certain commands using Cmnd_Alias *.
how to enable some user_alias to use some privileges to some Cmnd_Alias
how to Search custom commands using pipe grep
allow user to run any commands without password











Top comments (0)