Application of Redis in different field
Implemention of Redis in News Website
Implemention of Redis in Ecommerce Website
Difference Between Redis::set and Cache::remember in Laravel
Application of Redis in different field
Web Development
Use Case: Caching
Example: A news website like BBC or CNN uses Redis to cache frequently accessed content (e.g., homepage data, popular articles) to reduce load times and database queries.
Use Case: Session Store
Example: E-commerce platforms like Amazon store user session data in Redis for quick retrieval, enabling faster page reloads and cart retrievals.
Gaming
Use Case: Leaderboards
Example: Online games like Fortnite use Redis Sorted Sets to manage real-time leaderboards efficiently.
Use Case: Real-Time Updates
Example: Multiplayer games store game state data in Redis for real-time synchronization between players.
FinTech
Use Case: Transaction Caching
Example: Payment gateways like PayPal use Redis to cache transaction data to ensure high availability and low latency.
Use Case: Rate Limiting
Example: Banking apps limit the number of OTP requests or login attempts using Redis as a counter.
Healthcare
Use Case: Patient Record Management
Example: Healthcare platforms like MyChart use Redis for quick access to patient records and appointment schedules.
Use Case: Real-Time Monitoring
Example: IoT devices in hospitals use Redis to store and analyze patient vitals in real-time.
E-commerce
Use Case: Shopping Cart Management
Example: Platforms like Shopify use Redis to manage shopping cart data for faster retrieval and a smoother user experience.
Use Case: Inventory Management
Example: Redis is used to track inventory changes in real-time to prevent overselling.
Media and Entertainment
Use Case: Content Recommendation
Example: Netflix uses Redis to store user viewing histories and generate personalized recommendations.
Use Case: Analytics
Example: Redis stores real-time engagement metrics for videos, such as likes, views, and shares.
Social Media
Use Case: News Feeds
Example: Platforms like Twitter use Redis to store and display real-time feeds to users.
Use Case: Messaging
Example: Redis powers real-time messaging systems, enabling low-latency communication between users.
IoT and Industry 4.0
Use Case: Sensor Data Storage
Example: Smart home systems like Nest store sensor readings in Redis for immediate processing and decision-making.
Use Case: Real-Time Analytics
Example: Manufacturing units use Redis to store and analyze sensor data for predictive maintenance.
Travel and Hospitality
Use Case: Dynamic Pricing
Example: Airlines and hotels use Redis to calculate real-time pricing based on demand and availability.
Use Case: Search and Recommendations
Example: Booking platforms like Expedia use Redis to cache search results and provide faster recommendations.
Education
Use Case: Learning Management Systems
Example: Platforms like Coursera use Redis to cache course data and user progress for better performance.
Use Case: Real-Time Notifications
Example: Redis Pub/Sub is used to notify students about live class schedules or assignment deadlines.
Retail
Use Case: Personalized Promotions
Example: Retail apps use Redis to store customer data and deliver targeted ads or discounts in real time.
Use Case: Queue Management
Example: Redis is used to manage online order queues during high-traffic events like Black Friday sales.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Use Case: Feature Store
Example: Redis is used in ML pipelines to store features for quick access during model training and serving.
Use Case: Model Serving
Example: AI systems like chatbots cache frequently used data and responses in Redis for faster interactions.
Real-Time Collaboration Tools
Use Case: Document Editing
Example: Tools like Google Docs use Redis to store real-time changes and synchronize them across multiple users.
Use Case: Messaging and Notifications
Example: Redis Pub/Sub is used to handle real-time messaging in platforms like Slack.
Caching Database Queries
Reduce database load by caching query results.
Example:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
$users = Cache::remember('users_list', 3600, function () {
return \App\Models\User::all(); // Fetch data from DB only if not cached
});
Command to Clear Cache:
php artisan cache:clear
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Models\User;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class UserController extends Controller
{
// Fetch a user by ID with caching
public function getUser($id)
{
// Define a cache key
$cacheKey = "user_{$id}";
// Fetch user from cache or database
$user = Cache::remember($cacheKey, 3600, function () use ($id) {
return User::find($id); // Fetch from database if not in cache
});
if (!$user) {
return response()->json(['message' => 'User not found'], 404);
}
return response()->json($user);
}
// Clear a specific user's cache
public function clearUserCache($id)
{
$cacheKey = "user_{$id}";
Cache::forget($cacheKey);
return response()->json(['message' => "Cache cleared for user {$id}"]);
}
// Create a new user (also clears cache)
public function createUser(Request $request)
{
$request->validate([
'name' => 'required|string|max:255',
'email' => 'required|email|unique:users,email',
]);
$user = User::create($request->all());
// Clear cache for this user (just in case)
Cache::forget("user_{$user->id}");
return response()->json(['message' => 'User created successfully', 'user' => $user]);
}
}
Creating a User
Use a POST request to create a new user:
POST http://localhost/user
Content-Type: application/json
{
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com"
}
Response:
{
"message": "User created successfully",
"user": {
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe",
"email": "johndoe@example.com",
"created_at": "2024-12-10T10:00:00.000000Z",
"updated_at": "2024-12-10T10:00:00.000000Z"
}
}
Session Storage in Redis
Store user sessions in Redis for fast access.
SESSION_DRIVER=redis
Code Example: Session data is automatically stored in Redis. You can retrieve or update sessions as usual:
session(['user_name' => 'John Doe']);
echo session('user_name'); // Output: John Doe
Redis Command to View Sessions:
redis-cli
keys * # View all keys
get laravel_session:your_session_id # Retrieve a specific session
Rate Limiting
Use Redis to limit the rate of API requests to protect your application from abuse.
Code Example:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\RateLimiter;
RateLimiter::for('api', function ($job) {
return Limit::perMinute(60)->by($job->user_id);
});
// Middleware usage
Route::middleware('throttle:api')->group(function () {
Route::get('/user', function () {
return 'API Response';
});
});
Command to Monitor:
redis-cli monitor
Queue Management
Redis is often used as a queue backend to process jobs efficiently.
Update .env:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=redis
Code Example:
dispatch(new \App\Jobs\ProcessDataJob($data));
Run Queue Worker:
php artisan queue:work --queue=default
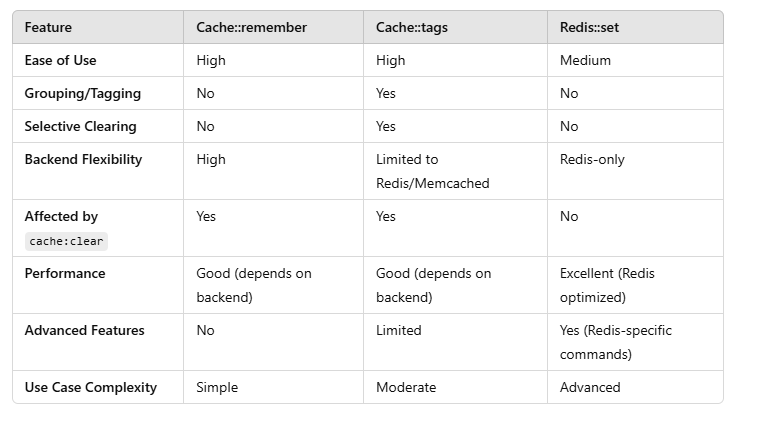
Cache Tags
Use Redis cache tags for grouping related cache items, making it easier to clear related data.
Cache::tags(['users', 'admins'])->put('user_1', $userData, 3600);
Cache::tags(['users', 'admins'])->put('user_2', $userData, 3600);
Cache::tags(['users'])->flush();
Storing Complex Data
Redis supports storing serialized objects or JSON data for complex queries.
$data = ['name' => 'John', 'email' => 'john@example.com'];
// Store JSON
Cache::put('user:1', json_encode($data), 3600);
// Retrieve JSON
$user = json_decode(Cache::get('user:1'), true);
redis-cli
get user:1
Expiring Counters
Implement counters that expire after a certain time.
Redis::incr('page_views');
Redis::expire('page_views', 3600); // Expire after 1 hour
$pageViews = Redis::get('page_views');
Real-Time Notifications
Store real-time notifications in Redis for fast retrieval.
Code Example:
Redis::publish('notifications', json_encode([
'user_id' => 1,
'message' => 'You have a new message!',
]));
Subscribe to Channel (Client-Side): Use socket.io or similar technologies to listen for the Redis notifications channel.
=====================================================================
Implemention of Redis in News Website
In env mention
CACHE_DRIVER=redis
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
use App\Models\News;
class NewsController extends Controller
{
public function getHomePageNews()
{
$news = Cache::remember('home_page_news', 3600, function () {
return News::latest()->take(5)->get();
});
return response()->json($news);
}
}
Second Way
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis;
use App\Models\News;
class NewsController extends Controller
{
public function getHomePageNews()
{
// Check if news exists in Redis
if (Redis::exists('home_page_news')) {
// Fetch from Redis
$news = json_decode(Redis::get('home_page_news'));
} else {
// Fetch from DB and store in Redis
$news = News::latest()->take(5)->get();
Redis::set('home_page_news', $news->toJson());
Redis::expire('home_page_news', 3600); // Set TTL (time-to-live) in seconds
}
return response()->json($news);
}
}
Third Way
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
use App\Models\News;
class NewsController extends Controller
{
public function getHomePageNews()
{
$news = Cache::tags(['news'])->remember('home_page_news', 3600, function () {
return News::latest()->take(5)->get();
});
return response()->json($news);
}
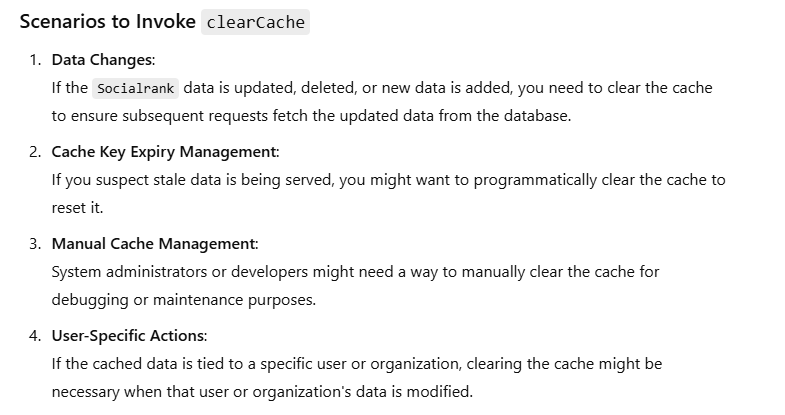
public function clearNewsCache()
{
Cache::tags(['news'])->flush(); // Clear only the news-related cache
return response()->json(['message' => 'News cache cleared.']);
}
}
Fourth way
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis;
use App\Models\News;
class NewsController extends Controller
{
public function getHomePageNews()
{
// Check if the key exists in Redis
if (Redis::exists('home_page_news')) {
// Fetch data from Redis
$news = json_decode(Redis::get('home_page_news'));
} else {
// Fetch data from the database and store it in Redis
$news = News::latest()->take(5)->get();
Redis::set('home_page_news', $news->toJson()); // Store as JSON in Redis
Redis::expire('home_page_news', 3600); // Optional: Set expiration time in seconds
}
return response()->json($news);
}
public function clearNewsCache()
{
// Clear the Redis key manually
Redis::del('home_page_news');
return response()->json(['message' => 'Cache cleared.']);
}
}
Difference Between Redis::set and Cache::remember in Laravel
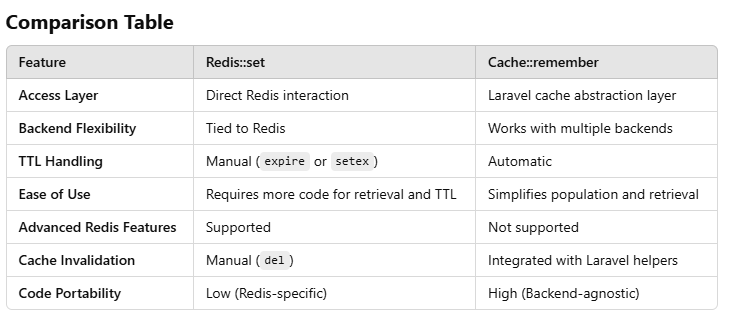
Both Redis::set and Cache::remember allow data storage for quick retrieval, but they are used differently and serve distinct purposes in Laravel applications.
Redis::set
The Redis::set method directly interacts with Redis as a key-value store, bypassing Laravel’s cache abstraction layer.
Key Characteristics:
Direct Access: Interacts directly with Redis, giving you full control over Redis commands.
Low-Level API: Allows for fine-grained operations like setting expiration (expire), incrementing counters, or working with Redis data types (e.g., hashes, sets).
No Abstraction: Does not use Laravel’s caching system, so it won't benefit from cache tagging or integration with other storage mechanisms.
Persistence: Only works with Redis, so switching to another cache backend (like Memcached) would require significant code changes.
Example:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Redis;
// Set a value in Redis
Redis::set('key', 'value');
// Get the value
$value = Redis::get('key');
// Set a value with expiration (TTL in seconds)
Redis::set('key', 'value');
Redis::expire('key', 3600); // Expires after 1 hour
Advantages:
- Direct and efficient.
- Full control over Redis-specific features.
- Can work with Redis advanced data types (e.g., lists, sets).
- Disadvantages:
- Requires manual handling of TTLs and cache invalidation.
- Tied to Redis, limiting flexibility if backend changes . Cache::remember The Cache::remember method is a high-level abstraction provided by Laravel’s caching system. It integrates seamlessly with Laravel's configuration and can work with multiple caching backends (Redis, Memcached, file, etc.).
Key Characteristics:
- Abstraction Layer: Part of Laravel’s caching layer, which supports multiple cache drivers.
- Auto-Expiration: Automatically handles TTL (time-to-live) and refreshing cached data.
- Convenience: Simplifies cache retrieval and population in a single call.
- Flexibility: Can easily switch between caching backends (Redis, Memcached, etc.) by changing the CACHE_DRIVER in .env . Example:
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Cache;
// Cache the value for 1 hour (3600 seconds)
$value = Cache::remember('key', 3600, function () {
return 'value';
});
// Retrieve the value
$value = Cache::get('key');
Advantages:
Simplifies cache population and retrieval logic.
Backend-agnostic: Can switch caching mechanisms by changing configuration.
Supports cache tagging (grouping of cached items).
Handles expiration and retrieval in a single operation.
Disadvantages:
Limited to operations supported by Laravel's cache abstraction.
May not provide access to Redis-specific advanced features.
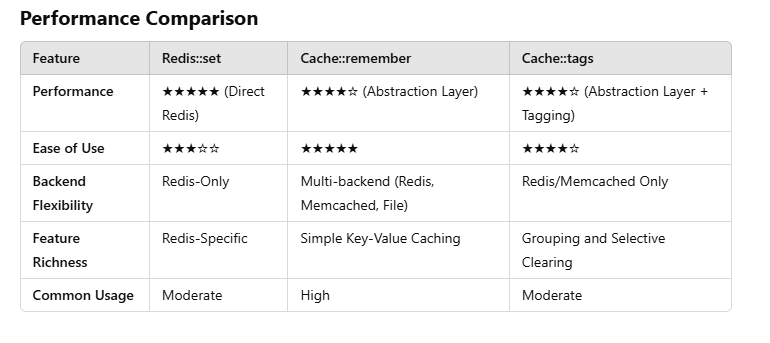
When to Use Which?
Redis::set:
When you need direct access to Redis features, such as advanced data types, manual TTL handling, or atomic operations.
When working with Redis-specific use cases like pub/sub, sorted sets, or lists.
Cache::remember:
When you want a clean, backend-agnostic caching solution for simple key-value pairs.
When you prioritize ease of use and integration with Laravel's ecosystem.
When you want to switch between caching backends easily.

Top comments (0)