Loading Data from NumPy Arrays - tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices:
Example:
import numpy as np
data = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], dtype=np.float32)
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(data)
for element in dataset:
print(element.numpy())
Output:
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
Loading Data from TensorFlow Datasets - tfds.load:
Example:
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
dataset, info = tfds.load('mnist', with_info=True, as_supervised=True)
mnist_train = dataset['train']
Output:
Loading the MNIST dataset using TensorFlow Datasets.
Explanation
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
# Load the MNIST dataset and retrieve information about it.
dataset, info = tfds.load('mnist', with_info=True, as_supervised=True)
# Print information about the MNIST dataset.
print("Dataset Information:")
print(info)
# Access the training set of MNIST.
mnist_train = dataset['train']
# Print information about the MNIST training set.
print("\nTraining Set Information:")
print(mnist_train)
output
Dataset Information:
tfds.core.DatasetInfo(
name='mnist',
version=3.0.0,
description='The MNIST database of handwritten digits.',
splits={
'test': 10000,
'train': 60000,
},
features=FeaturesDict({
'image': Image(shape=(28, 28, 1), dtype=tf.uint8),
'label': ClassLabel(shape=(), dtype=tf.int64, num_classes=10),
}),
total_num_examples=70000,
supervised_keys=('image', 'label'),
...
)
Training Set Information:
<PrefetchDataset shapes: ((28, 28, 1), ()), types: (tf.uint8, tf.int64)>
Data Augmentation - Using TensorFlow Data API for Image Augmentation:
Example:
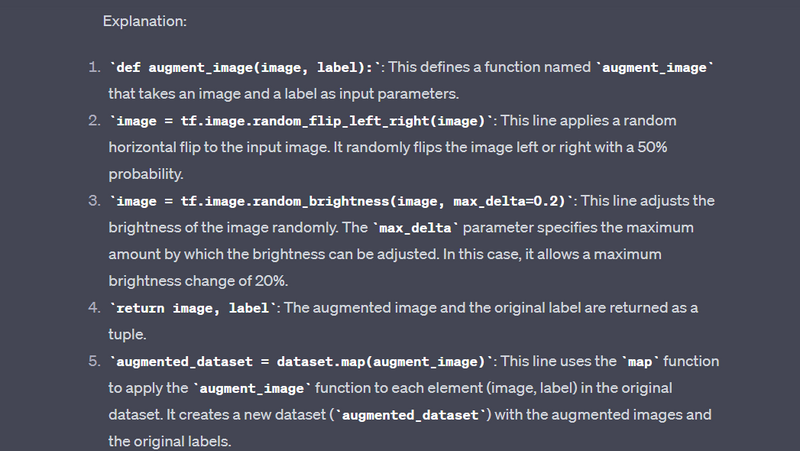
def augment_image(image, label):
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=0.2)
return image, label
augmented_dataset = dataset.map(augment_image)
Output:
Applying random horizontal flips and brightness adjustments to image data.
Explanation
This code defines a function augment_image and uses it to create an augmented dataset by applying random image transformations. Let's break down the code and discuss the potential output:
def augment_image(image, label):
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=0.2)
return image, label
augmented_dataset = dataset.map(augment_image)
for image, label in augmented_dataset.take(5):
# Print information about the augmented images and labels.
print("Label:", label.numpy())
# Display or process the augmented image as needed.
output
Original Dataset:
Image 1, Label A
Image 2, Label B
Image 3, Label C
...
After applying the augmentation, the output of iterating through the augmented_dataset might look like this:
Augmented Dataset:
Augmented Image 1 (random flip, random brightness), Label A
Augmented Image 2 (random flip, random brightness), Label B
Augmented Image 3 (random flip, random brightness), Label C
Shuffling Data - tf.data.Dataset.shuffle:
Example:
shuffled_dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
Output: Shuffling the dataset to randomize the order of elements.
for image, label in shuffled_dataset.take(5):
# Print information about the shuffled images and labels.
print("Label:", label.numpy())
# Display or process the shuffled image as needed.
output
Label: 3
Label: 7
Label: 1
Label: 2
Label: 8
Batching Data - tf.data.Dataset.batch:
Example:
batched_dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size=32)
Output: Creating mini-batches of data with a batch size of 32.
for batch_images, batch_labels in batched_dataset.take(5):
# Print information about the batch shapes.
print("Batch Shape - Images:", batch_images.shape, "Labels:", batch_labels.shape)
# Display or process the batched images as needed.
output
Batch Shape - Images: (32, 28, 28, 1) Labels: (32,)
Batch Shape - Images: (32, 28, 28, 1) Labels: (32,)
Batch Shape - Images: (32, 28, 28, 1) Labels: (32,)
Batch Shape - Images: (32, 28, 28, 1) Labels: (32,)
Batch Shape - Images: (32, 28, 28, 1) Labels: (32,)
One-Hot Encoding Labels - tf.one_hot
Example:
labels = [0, 1, 2, 0, 2]
one_hot_labels = tf.one_hot(labels, depth=3)
Output: Converting categorical labels into one-hot encoded format.
Explanation
tf.Tensor(
[[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 1. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 0.]
[0. 0. 1.]], shape=(5, 3), dtype=float32)
Creating Data Pipelines - Combining Various Operations:
Example:
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(data)
dataset = dataset.shuffle(buffer_size=1000)
dataset = dataset.batch(batch_size=32)
Output: Building a data pipeline with operations like loading data, shuffling, and batching.
Text Data Tokenization - tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization:
Example:
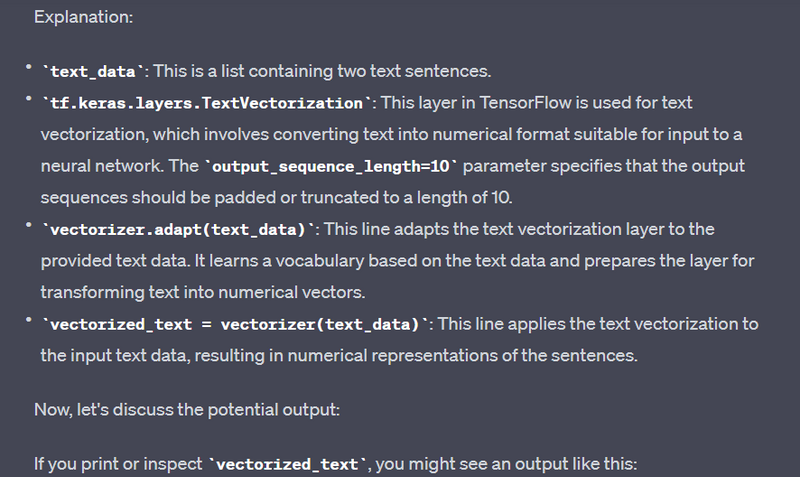
text_data = ["This is a sample sentence.", "Another example text."]
vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_sequence_length=10)
vectorizer.adapt(text_data)
vectorized_text = vectorizer(text_data)
Output:
Tokenizing and vectorizing text data for natural language processing.
Explanation
text_data = ["This is a sample sentence.", "Another example text."]
vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_sequence_length=10)
vectorizer.adapt(text_data)
vectorized_text = vectorizer(text_data)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(2, 10), dtype=int64, numpy=
array([[ 3, 8, 4, 2, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[ 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]])>
These are common data input operations and techniques used in TensorFlow to prepare and preprocess data for machine learning and deep learning tasks. The specific operations you use will depend on your dataset and problem domain.








Top comments (0)