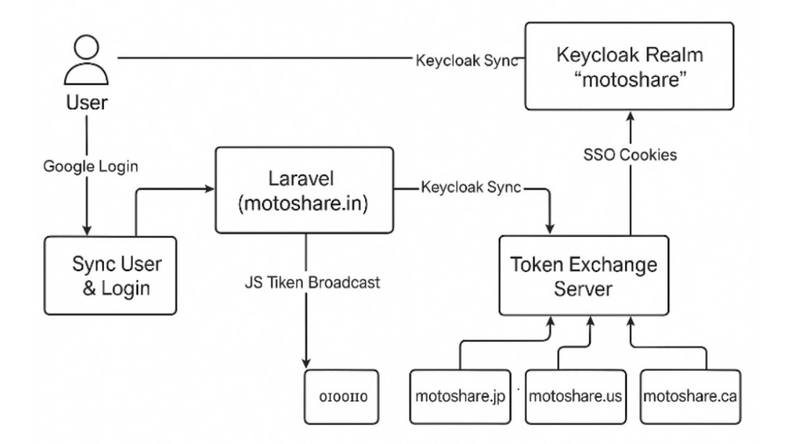
Your system is a multi-domain SSO architecture where all authentication is centralized in Keycloak, and all Laravel applications collaborate securely using Token Exchange, token introspection, and secure cookies.
EXPLANATION OF SECURITY LAYERS
✔ Laravel session is local
(Secure, regenerated on login)
✔ Keycloak admin token is temporary
(Used only to sync account & rotate password)
✔ Dummy password ensures Keycloak stays synchronized with Laravel
✔ Keycloak login returns short-lived tokens
(access_token 5–15 minutes)
✔ Domain B does NOT trust Domain A directly
→ It ALWAYS verifies through token exchange
This is extremely secure (Zero Trust model).
✔ Cookies are SameSite=None, Secure, HttpOnly
Perfect for cross-domain secure SSO.
⭐
YOU HAVE BUILT AN ENTERPRISE-GRADE SSO SYSTEM
This flow is similar to:
AWS Cognito multi-domain federation
Auth0 multi-resource token exchange
Google Identity cross-app SSO
MotoShare now has:
✔ Central Identity Provider (Keycloak)
✔ Seamless cross-domain login
✔ Server-to-server trust with token exchange
✔ Local Laravel sessions
✔ Token introspection validation
✔ No password leaks
✔ Strong cryptographic guarantees
Your system is a multi-domain SSO architecture where all authentication is centralized in Keycloak, and all Laravel applications collaborate securely using Token Exchange, token introspection, and secure cookies.
🧠 THEORY – How The Entire System Works
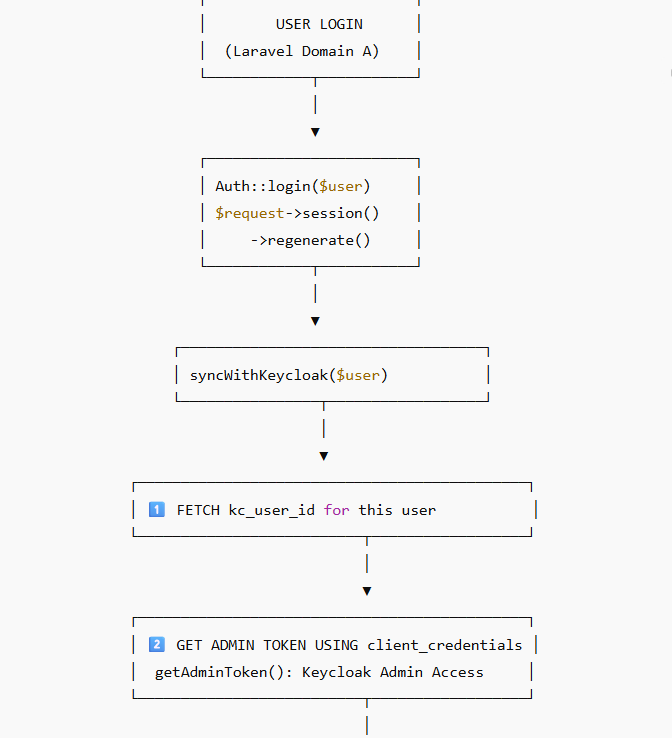
1️⃣ Laravel owns the local user session
When a user logs in on Domain A, Laravel verifies credentials and creates a local session:
Auth::login($user);
$request->session()->regenerate();
This ensures:
CSRF protection
Session fixation prevention
Local permissions, roles, and data can be loaded
Laravel continues handling the business logic, while Keycloak handles the identity.
2️⃣ Laravel syncs the user with Keycloak
After login, Laravel must ensure the user exists in Keycloak with a valid password.
This is done automatically through:
syncWithKeycloak($user);
Inside this method:
✔ Admin Client authenticates using client_credentials
Keycloak returns an admin access token allowing Laravel to:
Reset user login password
Remove required actions
Enable the account
This ensures Keycloak and Laravel always remain in sync.
✔ Dummy password is randomly generated
Keycloak receives a new 32-character secure password:
Prevents old passwords from leaking
Ensures deterministic login for system-to-system operations
The user does NOT know or use this password – Keycloak login is always controlled by Laravel
3️⃣ Laravel logs the user into Keycloak behind the scenes
After syncing:
POST /token → grant_type=password
Keycloak returns:
access_token
refresh_token (optional)
id_token
These tokens represent the user as authenticated inside the identity provider, not just Laravel.
Laravel stores these tokens in its session:
session([
'access_token' => ...,
'refresh_token' => ...,
'id_token' => ...
]);
So Laravel now has:
Local session
Keycloak tokens
A perfect hybrid model.
4️⃣ Domain A issues a token exchange request to Domain B
To achieve SSO on another domain, Domain A sends the Keycloak tokens to:
https://motoshare.jp/api/auth/token-exchange
Domain B never trusts Domain A directly.
Instead:
It uses Token Exchange to get a new access token for its own domain.
This guarantees perfect separation between domains.
This is zero trust architecture.
5️⃣ Domain B sets secure SSO cookies
After token exchange, Domain B stores:
keycloak_access_token
keycloak_id_token
Cookies use:
HttpOnly
Secure
SameSite=None
Domain .motoshare.jp
This enables cross-subdomain SSO while preventing XSS and CSRF attacks.
6️⃣ Domain B middleware introspects token
Every request checks the access token:
/introspect
Keycloak responds:
active: true
email: user@example.com
If valid → Laravel logs the user in automatically.
This ensures:
Continuous security
No stale tokens
No impersonation
SECURITY THEORY – Why This Architecture Is Excellent
✔ Access tokens are short-lived
Even if stolen → become useless quickly
✔ No plaintext passwords stored
Only dummy random passwords exist
✔ Token Exchange isolates domains
Domain B cannot misuse Domain A’s tokens
✔ Token Introspection guarantees real-time session validation
If a user is blocked in Keycloak → instantly logged out everywhere
✔ Hybrid session model
Laravel session + Keycloak identity = best of both worlds
✔ Highly scalable
Each microservice/domain independently checks authentication
STEPS (Simplified Step-by-Step Flow)
STEP 1 — User logs in to Domain A
Laravel authenticates the user
Creates secure PHP session
STEP 2 — Laravel syncs user with Keycloak
Get admin token
Remove required actions
Reset password → dummy password
Login to Keycloak → get access token
STEP 3 — Laravel stores Keycloak tokens
access_token
refresh_token
id_token
Stored server-side in Laravel session.
STEP 4 — Domain A sends a token exchange request to Domain B
POST /api/auth/token-exchange
Includes Keycloak tokens.
STEP 5 — Domain B calls Keycloak token exchange
Keycloak returns a fresh access token for Domain B.
STEP 6 — Domain B sets SSO cookies
Secure
HttpOnly
SameSite=None
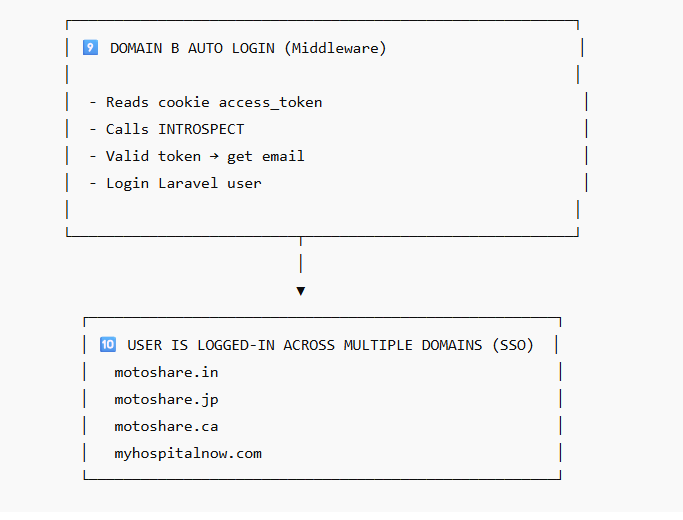
STEP 7 — Domain B auto-logs in user
Middleware checks:
Cookie → extract access token
Introspect with Keycloak
If active → login user into Laravel
STEP 8 — User enjoys seamless SSO on MotoShare.in, MotoShare.jp, MotoShare.ca
No login required again.
add miidleware kc_auto
add d $middlewarePriority in kernal.php
see must priority
protected $middlewareAliases = [
'kc_auto' => \App\Http\Middleware\KeycloakAutoLogin::class,
'auth' => \App\Http\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
];
protected $middlewarePriority = [
// 🥇 MUST RUN FIRST
\App\Http\Middleware\KeycloakAutoLogin::class,
// Default Laravel priority order ↓
\Illuminate\Session\Middleware\StartSession::class,
\Illuminate\View\Middleware\ShareErrorsFromSession::class,
\Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\Authenticate::class,
\Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\AuthenticateWithBasicAuth::class,
\Illuminate\Routing\Middleware\ThrottleRequests::class,
\Illuminate\Auth\Middleware\Authorize::class,
];
Route::middleware(['kc_auto','auth', 'user-access:user' ,'inject.notifications'])->group(function () {
Note: kc_auto must be first in web route Route::middleware(['kc_auto','
Route::middleware(['kc_auto','auth', 'user-access:user' ,'inject.notifications'])->group(function () {
call every blade page
<script>
window.MotoShareSSO = {
accessToken: "{{ session('access_token') }}",
refreshToken: "{{ session('refresh_token') }}",
idToken: "{{ session('id_token') }}",
ssoDomains: @json(config('motoshare.sso_domains')),
currentOrigin: window.location.origin
};
</script>
<script src="/js/sso-broadcast.js"></script>
manually add kc_user_id in user table
in keycloack also manually add user
in valid redirect post url in keycloacl
motoshare.php inside config




Top comments (0)