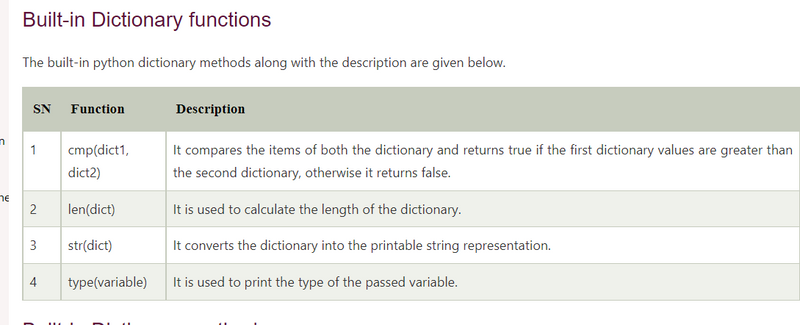
key-value pair format and mutable data-structure
Value can be any type such as list, tuple, integer, etc.
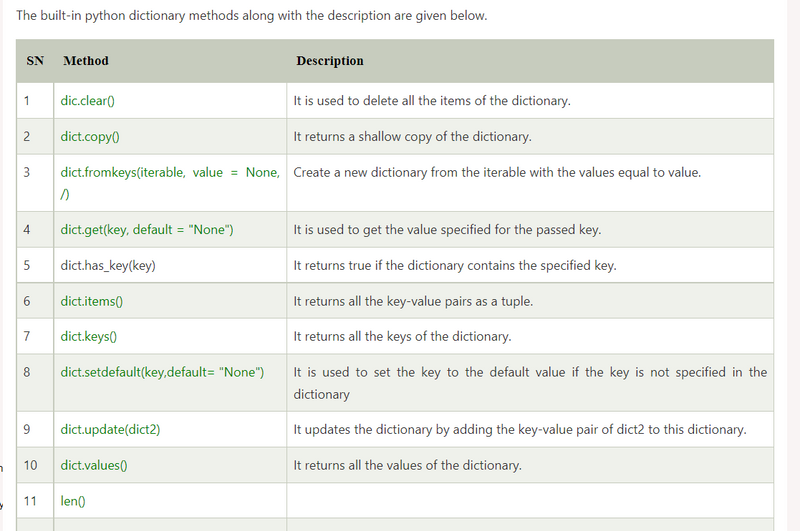
Creating an empty Dictionary using Dict methods
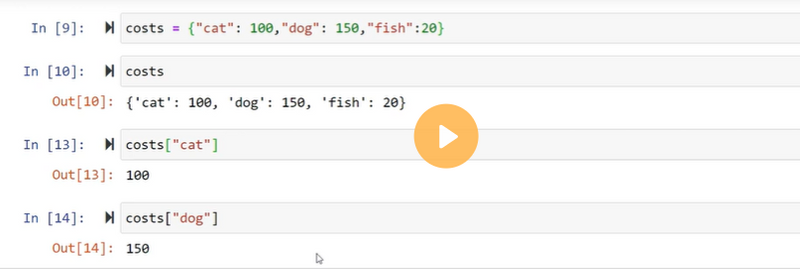
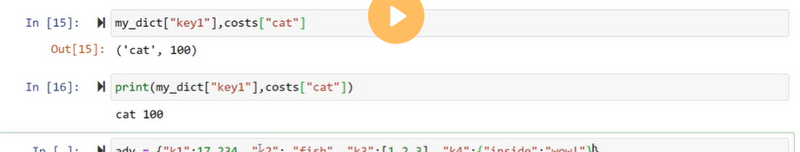
Accessing the dictionary values
print("Name : %s" %Employee["Name"])
Adding dictionary values
Dict[0] = 'Peter'||Dict[key]
Dict['Emp_ages'] = 20, 33, 24
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'JavaTpoint', 'Emp_ages': (20, 33, 24)}
Deleting elements using del keyword
del Employee["Name"]
Deleting elements using pop() method
Iterating Dictionary using for loop
for loop to print all the values of the dictionary
print(Employee[x])
for loop to print the values of the dictionary by using values()
for x in Employee.values():
for loop to print the items of the dictionary by using items()
for x in Employee.items():
o/p=('Name', 'John')
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary
mapping char of string to item to create dictiory with help of list using enumerate
mapping char of string to item to create dictiory with help of list using zip
mapping char of list to item to create dictiory with help of list using enumerate
General Question
Creating a Dictionary using dict method
How to accessing dictionary value
create empty dictionary then Adding elements to dictionary one at a time
Adding set of value in existing dictionary
Deleting elements using del keyword
How to print all key of dictionary using different methods
how to print all value of dictionary using different methods
how to calculate length of dictionary
how to print keys and value of dictionary using dict method
how to Calculate the sum of all values in the shopping_cart dictionary using two way list comprhension and values
total_cost = sum(shopping_cart[item] for item in cart_items)
total_cost = sum(shopping_cart.values())
VERY IMPORTANT QUESTIONS
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary in python
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary in django then display in template file key value pair in table
how to save data in dictionary of dictionaries that come from request after filling form in django and then how to access it
how to save data in dictionary of dictionaries in python
difference between format of list of dictionaries and array of json
difference between format of dictionary of dictionaries and array of json
explain difference between format of dictionary of dictionaries and nested json
how to convert given list to dictionary and store in db in django
Python Dictionary
Python Dictionary is used to store the data in a key-value pair format. The dictionary is the data type in Python, which can simulate the real-life data arrangement where some specific value exists for some particular key. It is the mutable data-structure. The dictionary is defined into element Keys and values.
Keys must be a single element
Value can be any type such as list, tuple, integer, etc.
In other words, we can say that a dictionary is the collection of key-value pairs where the value can be any Python object. In contrast, the keys are the immutable Python object, i.e., Numbers, string, or tuple.
Creating the dictionary
The dictionary can be created by using multiple key-value pairs enclosed with the curly brackets {}, and each key is separated from its value by the colon (:).The syntax to define the dictionary is given below.
Syntax:
Dict = {"Name": "Tom", "Age": 22}
In the above dictionary Dict, The keys Name and Age are the string that is an immutable object.
Let's see an example to create a dictionary and print its content.
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
print(type(Employee))
print("printing Employee data .... ")
print(Employee)
Output
<class 'dict'>
Printing Employee data ....
{'Name': 'John', 'Age': 29, 'salary': 25000, 'Company': 'GOOGLE'}
Python provides the built-in function dict() method which is also used to create dictionary. The empty curly braces {} is used to create empty dictionary.
Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with dict() method
Dict = dict({1: 'Java', 2: 'T', 3:'Point'})
print("\nCreate Dictionary by using dict(): ")
print(Dict)
# Creating a Dictionary
# with each item as a Pair
Dict = dict([(1, 'Devansh'), (2, 'Sharma')])
print("\nDictionary with each item as a pair: ")
print(Dict)
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Create Dictionary by using dict():
{1: 'Java', 2: 'T', 3: 'Point'}
Dictionary with each item as a pair:
{1: 'Devansh', 2: 'Sharma'}
Accessing the dictionary values
We have discussed how the data can be accessed in the list and tuple by using the indexing.
However, the values can be accessed in the dictionary by using the keys as keys are unique in the dictionary.
The dictionary values can be accessed in the following way.
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
print(type(Employee))
print("printing Employee data .... ")
print("Name : %s" %Employee["Name"])
print("Age : %d" %Employee["Age"])
print("Salary : %d" %Employee["salary"])
print("Company : %s" %Employee["Company"])
Output:
<class 'dict'>
printing Employee data ....
Name : John
Age : 29
Salary : 25000
Company : GOOGLE
Python provides us with an alternative to use the get() method to access the dictionary values. It would give the same result as given by the indexing.
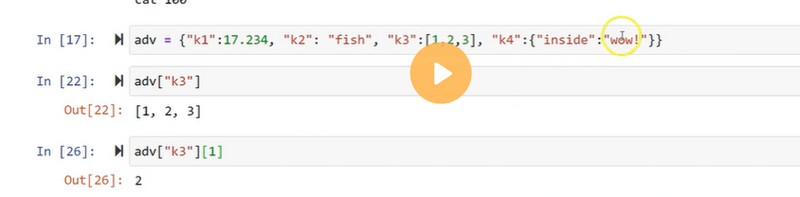
Adding dictionary values
The dictionary is a mutable data type, and its values can be updated by using the specific keys. The value can be updated along with key Dict[key] = value. The update() method is also used to update an existing value.
Note: If the key-value already present in the dictionary, the value gets updated. Otherwise, the new keys added in the dictionary.
Let's see an example to update the dictionary values.
Example - 1:
# Creating an empty Dictionary
Dict = {}
print("Empty Dictionary: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding elements to dictionary one at a time
Dict[0] = 'Peter'
Dict[2] = 'Joseph'
Dict[3] = 'Ricky'
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Adding set of values
# with a single Key
# The Emp_ages doesn't exist to dictionary
Dict['Emp_ages'] = 20, 33, 24
print("\nDictionary after adding 3 elements: ")
print(Dict)
# Updating existing Key's Value
Dict[3] = 'JavaTpoint'
print("\nUpdated key value: ")
print(Dict)
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'Ricky'}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'Ricky', 'Emp_ages': (20, 33, 24)}
Updated key value:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'JavaTpoint', 'Emp_ages': (20, 33, 24)}
Example - 2:
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
print(type(Employee))
print("printing Employee data .... ")
print(Employee)
print("Enter the details of the new employee....");
Employee["Name"] = input("Name: ");
Employee["Age"] = int(input("Age: "));
Employee["salary"] = int(input("Salary: "));
Employee["Company"] = input("Company:");
print("printing the new data");
print(Employee)
Output:
Empty Dictionary:
{}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'Ricky'}
Dictionary after adding 3 elements:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'Ricky', 'Emp_ages': (20, 33, 24)}
Updated key value:
{0: 'Peter', 2: 'Joseph', 3: 'JavaTpoint', 'Emp_ages': (20, 33, 24)}
Deleting elements using del keyword
The items of the dictionary can be deleted by using the del keyword as given below.
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
print(type(Employee))
print("printing Employee data .... ")
print(Employee)
print("Deleting some of the employee data")
del Employee["Name"]
del Employee["Company"]
print("printing the modified information ")
print(Employee)
print("Deleting the dictionary: Employee");
del Employee
print("Lets try to print it again ");
print(Employee)
Output:
<class 'dict'>
printing Employee data ....
{'Name': 'John', 'Age': 29, 'salary': 25000, 'Company': 'GOOGLE'}
Deleting some of the employee data
printing the modified information
{'Age': 29, 'salary': 25000}
Deleting the dictionary: Employee
Lets try to print it again
NameError: name 'Employee' is not defined
The last print statement in the above code, it raised an error because we tried to print the Employee dictionary that already deleted.
Using pop() method
The pop() method accepts the key as an argument and remove the associated value. Consider the following example.
# Creating a Dictionary
Dict = {1: 'JavaTpoint', 2: 'Peter', 3: 'Thomas'}
# Deleting a key
# using pop() method
pop_ele = Dict.pop(3)
print(Dict)
Output:
{1: 'JavaTpoint', 2: 'Peter'}
Python also provides a built-in methods popitem() and clear() method for remove elements from the dictionary. The popitem() removes the arbitrary element from a dictionary, whereas the clear() method removes all elements to the whole dictionary.
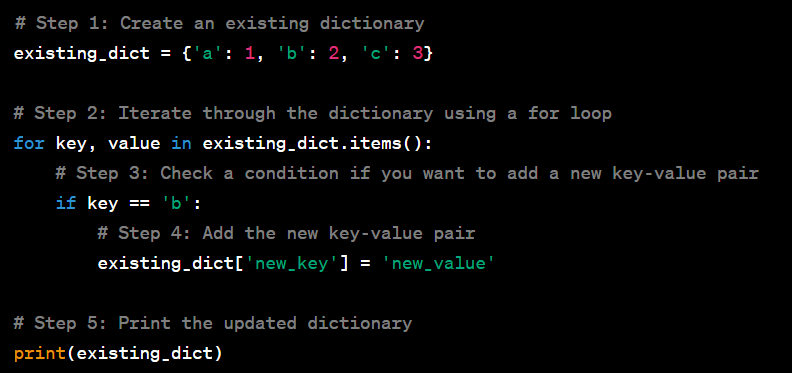
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary
# Iterate over the dictionary
for key, value in my_dict.items():
# Add new key-value pairs or update existing ones
if key == 'key2':
updates[key] = 'new_value'
elif key == 'key3':
updates['new_key'] = 'new_value2'
# Apply updates to the original dictionary
my_dict.update(updates)
# Print the updated dictionary
print(my_dict)
Iterating Dictionary
A dictionary can be iterated using for loop as given below.
Example 1
# for loop to print all the keys of a dictionary
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
for x in Employee:
print(x)
Output:
Name
Age
salary
Company
Example 2
for loop to print all the values of the dictionary
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
for x in Employee:
print(Employee[x])
Output:
John
29
25000
GOOGLE
Example - 3
for loop to print the values of the dictionary by using values() method.
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
for x in Employee.values():
print(x)
Output:
John
29
25000
GOOGLE
Example 4
for loop to print the items of the dictionary by using items() method.
Employee = {"Name": "John", "Age": 29, "salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE"}
for x in Employee.items():
print(x)
Output:
('Name', 'John')
('Age', 29)
('salary', 25000)
('Company', 'GOOGLE')
Properties of Dictionary keys
- In the dictionary, we cannot store multiple values for the same keys. If we pass more than one value for a single key, then the value which is last assigned is considered as the value of the key.
Consider the following example.
Employee={"Name":"John","Age":29,"Salary":25000,"Company":"GOOGLE","Name":"John"}
for x,y in Employee.items():
print(x,y)
Output:
Name John
Age 29
Salary 25000
Company GOOGLE
=========================================================
Dictionary Question
- Create an empty dictionary and add key-value pairs for the names and ages of three people.
- Add a new key-value pair to an existing dictionary representing a student's grade in a subject.
- Given a dictionary of items and their prices, calculate the total cost of a shopping cart.
- Create a dictionary of words and their meanings, and look up the meaning of a specific word.
- Iterate through a dictionary of countries and their capitals and print them out.
- Write a function to merge two dictionaries into one.
- Count the occurrences of each character in a given string and store them in a dictionary.
- Remove a key-value pair from a dictionary and print the updated dictionary.
- Given a list of numbers, create a dictionary with the numbers as keys and their squares as values.
- Create a dictionary that represents a contact list and allows searching for contacts by name.
- Write a function to invert the keys and values of a dictionary.
- Remove duplicate values from a dictionary while keeping the original order.
- Calculate the average score from a dictionary containing student names and their scores.
- Create a dictionary to store information about books (title, author, year), and allow searching by title.
- Write a function to find the key associated with the maximum value in a dictionary.
- Create a dictionary representing a deck of cards and shuffle it randomly.
- Group a list of words by their lengths and store them in a dictionary.
- Create a dictionary to store information about movies (title, director, genre), and allow adding new movies.
- Write a function to find the common keys between two dictionaries.
- Create a dictionary to store words and their synonyms, and allow searching for synonyms.
- Sort a dictionary by its values in ascending order.
- Write a function to flatten a nested dictionary into a single dictionary.
- Create a dictionary of fruits and their quantities. Update the quantity of a specific fruit.
- Check if a key exists in a dictionary and print a corresponding message.
- Calculate the average length of values in a dictionary containing lists of strings.
- Create a dictionary representing a simple phonebook and allow adding, updating, and deleting contacts.
- Find the key associated with the minimum value in a dictionary using a function.
- Create a dictionary of song ratings and titles. Print the titles of the top-rated songs.
- Merge multiple dictionaries into a new dictionary.
- Create a dictionary to store information about cities (name, population, country), and find the most populous city .
# Task 1: Create an empty dictionary and add key-value pairs for the names and ages of three people.
people_dict = {}
people_dict["Alice"] = 25
people_dict["Bob"] = 30
people_dict["Charlie"] = 22
print("Task 1 - Dictionary of People:", people_dict)
# Task 2: Add a new key-value pair to an existing dictionary representing a student's grade in a subject.
student_dict = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 85, "Charlie": 78}
student_dict["David"] = 92
print("Task 2 - Updated Student Dictionary:", student_dict)
# Task 3: Given a dictionary of items and their prices, calculate the total cost of a shopping cart.
shopping_cart = {"apple": 1.0, "banana": 0.5, "cherry": 1.5, "date": 0.75}
cart_items = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
total_cost = sum(shopping_cart[item] for item in cart_items)
print("Task 3 - Total Cost of Shopping Cart:", total_cost)
==========================or====================
shopping_cart = {"apple": 1.0, "banana": 0.5, "cherry": 1.5, "date": 0.75}
cart_items = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
total_cost = 0
for item in cart_items:
total_cost += shopping_cart[item]
print("Total cost:", total_cost)
===========================or============================
shopping_cart = {"apple": 1.0, "banana": 0.5, "cherry": 1.5, "date": 0.75}
# Calculate the sum of all values in the shopping_cart dictionary
total_cost = sum(shopping_cart.values())
# Task 4: Create a dictionary of words and their meanings, and look up the meaning of a specific word.
dictionary = {
"apple": "a round fruit with red or green skin and white flesh",
"banana": "a long curved fruit with yellow skin",
"cherry": "a small, round, red or black fruit with a stone inside",
}
word_to_lookup = "banana"
meaning = dictionary.get(word_to_lookup, "Word not found in dictionary")
print("Task 4 - Meaning of '{}':".format(word_to_lookup), meaning)
# Task 5: Iterate through a dictionary of countries and their capitals and print them out.
countries_dict = {
"USA": "Washington D.C.",
"France": "Paris",
"Germany": "Berlin",
"Japan": "Tokyo",
}
print("Task 5 - Countries and Capitals:")
for country, capital in countries_dict.items():
print("{} - {}".format(country, capital))
# Task 6: Write a function to merge two dictionaries into one.
def merge_dicts(dict1, dict2):
return {**dict1, **dict2}
dict1 = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
dict2 = {"c": 3, "d": 4}
merged_dict = merge_dicts(dict1, dict2)
print("Task 6 - Merged Dictionary:", merged_dict)
# Task 7: Count the occurrences of each character in a given string and store them in a dictionary.
def count_characters(input_string):
char_count = {}
for char in input_string:
if char in char_count:
char_count[char] += 1
else:
char_count[char] = 1
return char_count
text = "hello world"
char_counts = count_characters(text)
print("Task 7 - Character Counts:", char_counts)
# Task 8: Remove a key-value pair from a dictionary and print the updated dictionary.
contact_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
key_to_remove = "Charlie"
if key_to_remove in contact_dict:
del contact_dict[key_to_remove]
print("Task 8 - Updated Contact Dictionary:", contact_dict)
# Task 9: Given a list of numbers, create a dictionary with the numbers as keys and their squares as values.
numbers_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
squares_dict = {num: num ** 2 for num in numbers_list}
print("Task 9 - Dictionary of Numbers and Their Squares:", squares_dict)
# Task 10: Create a dictionary that represents a contact list and allows searching for contacts by name.
contacts_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
name_to_lookup = "Bob"
contact_email = contacts_dict.get(name_to_lookup, "Contact not found")
print("Task 10 - Email for '{}':".format(name_to_lookup), contact_email)
# Task 11: Write a function to invert the keys and values of a dictionary.
def invert_dict(input_dict):
return {value: key for key, value in input_dict.items()}
original_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
inverted_dict = invert_dict(original_dict)
print("Task 11 - Inverted Dictionary:", inverted_dict)
# Task 12: Remove duplicate values from a dictionary while keeping the original order.
from collections import OrderedDict
def remove_duplicates_from_dict(input_dict):
return dict(OrderedDict.fromkeys(input_dict))
duplicates_dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 1, "d": 3, "e": 2}
unique_dict = remove_duplicates_from_dict(duplicates_dict)
print("Task 12 - Dictionary with Duplicate Values Removed:", unique_dict)
# Task 13: Calculate the average score from a dictionary containing student names and their scores.
scores_dict = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 85, "Charlie": 78}
average_score = sum(scores_dict.values()) / len(scores_dict)
print("Task 13 - Average Score of Students:", average_score)
# Task 14: Create a dictionary to store information about books (title, author, year), and allow searching by title.
books_dict = {
"Book1": {"author": "Author1", "year": 2021},
"Book2": {"author": "Author2", "year": 2020},
"Book3": {"author": "Author3", "year": 2019},
}
title_to_lookup = "Book2"
book_info = books_dict.get(title_to_lookup, "Book not found")
print("Task 14 - Information for '{}':".format(title_to_lookup), book_info)
# Task 15: Write a function to find the key associated with the maximum value in a dictionary.
def key_with_max_value(input_dict):
return max(input_dict, key=input_dict.get)
scores_dict = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 85, "Charlie": 78}
key_max_score = key_with_max_value(scores_dict)
print("Task 15 - Student with Maximum Score:", key_max_score)
Output
Task 1 - Dictionary of People: {'Alice': 25, 'Bob': 30, 'Charlie': 22}
Task 2 - Updated Student Dictionary: {'Alice': 90, 'Bob': 85, 'Charlie': 78, 'David': 92}
Task 3 - Total Cost of Shopping Cart: 3.0
Task 4 - Meaning of 'banana': a long curved fruit with yellow skin
Task 5 - Countries and Capitals:
USA - Washington D.C.
France - Paris
Germany - Berlin
Japan - Tokyo
Task 6 - Merged Dictionary: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4}
Task 7 - Character Counts: {'h': 1, 'e': 1, 'l': 3, 'o': 2, ' ': 1, 'w': 1, 'r': 1, 'd': 1}
Task 8 - Updated Contact Dictionary: {'Alice': 'alice@example.com', 'Bob': 'bob@example.com'}
Task 9 - Dictionary of Numbers and Their Squares: {1: 1, 2: 4, 3: 9, 4: 16, 5: 25}
Task 10 - Email for 'Bob': bob@example.com
Task 11 - Inverted Dictionary: {1: 'a', 2: 'b', 3: 'c'}
Task 12 - Dictionary with Duplicate Values Removed: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'd': 3}
Task 13 - Average Score of Students: 84.33333333333333
Task 14 - Information for 'Book2': {'author': 'Author2', 'year': 2020}
Task 15 - Student with Maximum Score: Alice
import random
# Task 1: Create a dictionary representing a deck of cards and shuffle it randomly.
suits = ["Hearts", "Diamonds", "Clubs", "Spades"]
values = ["2", "3", "4", "5", "6", "7", "8", "9", "10", "Jack", "Queen", "King", "Ace"]
deck_of_cards = [{"Suit": suit, "Value": value} for suit in suits for value in values]
random.shuffle(deck_of_cards)
print("Task 1 - Shuffled Deck of Cards (Partial Output):", deck_of_cards[:5])
# Task 2: Group a list of words by their lengths and store them in a dictionary.
words_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
word_length_dict = {}
for word in words_list:
length = len(word)
if length in word_length_dict:
word_length_dict[length].append(word)
else:
word_length_dict[length] = [word]
print("Task 2 - Words Grouped by Length:", word_length_dict)
# Task 3: Create a dictionary to store information about movies (title, director, genre), and allow adding new movies.
movies_dict = {
"Movie1": {"director": "Director1", "genre": "Genre1"},
"Movie2": {"director": "Director2", "genre": "Genre2"},
}
new_movie = {"director": "Director3", "genre": "Genre3"}
movies_dict["Movie3"] = new_movie
print("Task 3 - Updated Movies Dictionary:", movies_dict)
# Task 4: Write a function to find the common keys between two dictionaries.
def find_common_keys(dict1, dict2):
return set(dict1.keys()) & set(dict2.keys())
dict1 = {"a": 1, "b": 2, "c": 3}
dict2 = {"b": 4, "c": 5, "d": 6}
common_keys = find_common_keys(dict1, dict2)
print("Task 4 - Common Keys Between dict1 and dict2:", common_keys)
# Task 5: Create a dictionary to store words and their synonyms, and allow searching for synonyms.
synonyms_dict = {
"happy": ["joyful", "content", "cheerful"],
"sad": ["unhappy", "melancholy", "depressed"],
}
word_to_lookup = "happy"
synonyms = synonyms_dict.get(word_to_lookup, "Synonyms not found")
print("Task 5 - Synonyms for '{}':".format(word_to_lookup), synonyms)
# Task 6: Sort a dictionary by its values in ascending order.
scores_dict = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 85, "Charlie": 78}
sorted_scores = dict(sorted(scores_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
print("Task 6 - Sorted Scores Dictionary:", sorted_scores)
# Task 7: Write a function to flatten a nested dictionary into a single dictionary.
def flatten_dict(input_dict, parent_key='', sep='_'):
flattened_dict = {}
for key, value in input_dict.items():
new_key = f"{parent_key}{sep}{key}" if parent_key else key
if isinstance(value, dict):
flattened_dict.update(flatten_dict(value, new_key, sep=sep))
else:
flattened_dict[new_key] = value
return flattened_dict
nested_dict = {
'a': 1,
'b': {'c': 2, 'd': {'e': 3, 'f': 4}},
'g': 5
}
flattened_dict = flatten_dict(nested_dict)
print("Task 7 - Flattened Dictionary:", flattened_dict)
# Task 8: Create a dictionary of fruits and their quantities. Update the quantity of a specific fruit.
fruit_quantities = {"apple": 10, "banana": 15, "cherry": 5}
fruit_to_update = "banana"
new_quantity = 20
if fruit_to_update in fruit_quantities:
fruit_quantities[fruit_to_update] = new_quantity
print("Task 8 - Updated Fruit Quantities:", fruit_quantities)
# Task 9: Check if a key exists in a dictionary and print a corresponding message.
contact_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
key_to_check = "David"
if key_to_check in contact_dict:
print("Task 9 - Key '{}' exists in the dictionary.".format(key_to_check))
else:
print("Task 9 - Key '{}' does not exist in the dictionary.".format(key_to_check))
# Task 10: Calculate the average length of values in a dictionary containing lists of strings.
list_dict = {"fruits": ["apple", "banana", "cherry"], "colors": ["red", "green", "blue"]}
average_length = sum(len(value) for values in list_dict.values() for value in values) / len(list_dict)
print("Task 10 - Average Length of Values:", average_length)
# Task 11: Create a dictionary representing a simple phonebook and allow adding, updating, and deleting contacts.
phonebook = {"Alice": "123-456-7890", "Bob": "987-654-3210"}
# Adding a contact
phonebook["Charlie"] = "555-555-5555"
# Updating a contact
phonebook["Bob"] = "999-999-9999"
# Deleting a contact
if "Alice" in phonebook:
del phonebook["Alice"]
print("Task 11 - Updated Phonebook:", phonebook)
# Task 12: Find the key associated with the minimum value in a dictionary using a function.
def key_with_min_value(input_dict):
return min(input_dict, key=input_dict.get)
scores_dict = {"Alice": 90, "Bob": 85, "Charlie": 78}
key_min_score = key_with_min_value(scores_dict)
print("Task 12 - Student with Minimum Score:", key_min_score)
# Task 13 (continued): Create a dictionary of song ratings and titles. Print the titles of the top-rated songs.
song_ratings = {"Song1": 5, "Song2": 4, "Song3": 5, "Song4": 3, "Song5": 4}
top_rated_songs = [title for title, rating in song_ratings.items() if rating == 5]
print("Task 13 - Top-Rated Songs:", top_rated_songs)
# Task 14: Merge multiple dictionaries into a new dictionary.
dict1 = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
dict2 = {"c": 3, "d": 4}
dict3 = {"e": 5}
merged_dict = {**dict1, **dict2, **dict3}
print("Task 14 - Merged Dictionary:", merged_dict)
# Task 15: Create a dictionary to store information about cities (name, population, country), and find the most populous city.
cities_dict = {
"City1": {"population": 1000000, "country": "Country1"},
"City2": {"population": 1500000, "country": "Country2"},
"City3": {"population": 800000, "country": "Country1"},
}
most_populous_city = max(cities_dict, key=lambda city: cities_dict[city]["population"])
print("Task 15 - Most Populous City:", most_populous_city)
output
Task 1 - Shuffled Deck of Cards (Partial Output): [{'Suit': 'Clubs', 'Value': '6'}, {'Suit': 'Spades', 'Value': '9'}, {'Suit': 'Spades', 'Value': '2'}, {'Suit': 'Diamonds', 'Value': 'King'}, {'Suit': 'Diamonds', 'Value': '7'}]
Task 2 - Words Grouped by Length: {5: ['apple', 'cherry'], 6: ['banana'], 4: ['date'], 11: ['elderberry']}
Task 3 - Updated Movies Dictionary: {'Movie1': {'director': 'Director1', 'genre': 'Genre1'}, 'Movie2': {'director': 'Director2', 'genre': 'Genre2'}, 'Movie3': {'director': 'Director3', 'genre': 'Genre3'}}
Task 4 - Common Keys Between dict1 and dict2: {'b', 'c'}
Task 5 - Synonyms for 'happy': ['joyful', 'content', 'cheerful']
Task 6 - Sorted Scores Dictionary: {'Charlie': 78, 'Bob': 85, 'Alice': 90}
Task 7 - Flattened Dictionary: {'a': 1, 'b_c': 2, 'b_d_e': 3, 'b_d_f': 4, 'g': 5}
Task 8 - Updated Fruit Quantities: {'apple': 10, 'banana': 20, 'cherry': 5}
Task 9 - Key 'David' does not exist in the dictionary.
Task 10 - Average Length of Values: 5.0
Task 11 - Updated Phonebook: {'Bob': '999-999-9999', 'Charlie': '555-555-5555'}
Task 12 - Student with Minimum Score: Charlie
Task 13 - Top-Rated Songs: ['Song1', 'Song3']
Task 14 - Merged Dictionary: {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': 5}
Task 15 - Most Populous City: City2
Good question with Dictionary
Count the occurrences of each character in a given string and store them in a dictionary.
Given a list of numbers, create a dictionary with the numbers as keys and their squares as values.
Create a dictionary representing a deck of cards and shuffle it randomly.
Group a list of words by their lengths and store them in a dictionary.
sort a dictionary by its values in ascending order.
Write a function to flatten a nested dictionary into a single dictionary.
Create a dictionary of song ratings and titles. Print the titles of the top-rated songs.
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary in python
Output:
Another Example
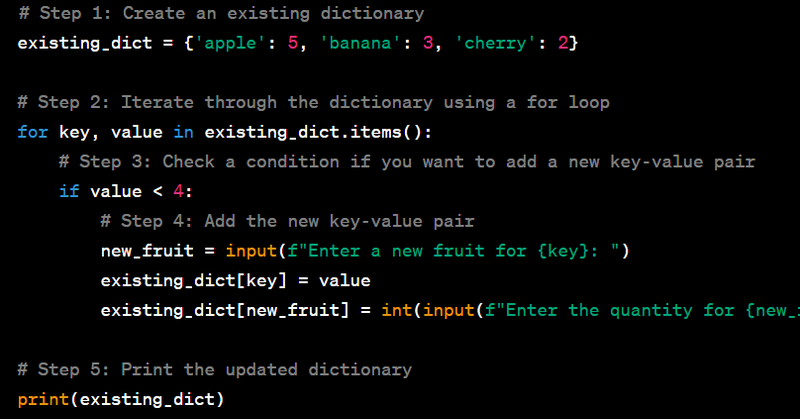
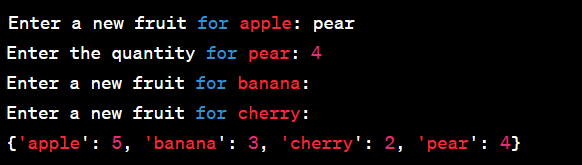
how to add new key value pair in existing dictionary while iterating all element of dictionary in django then display in template file key value pair in table
# views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
def dictionary_table(request):
# Step 1: Create an existing dictionary
existing_dict = {'apple': 5, 'banana': 3, 'cherry': 2}
# Step 2: Iterate through the dictionary and add a new key-value pair
for key, value in existing_dict.items():
if value < 4:
new_fruit = f"new_{key}" # Create a new key
existing_dict[new_fruit] = value + 1 # Add the new key-value pair
# Step 3: Pass the updated dictionary to the template
context = {'fruit_dict': existing_dict}
return render(request, 'myapp/dictionary_table.html', context)
output
<!-- dictionary_table.html -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Dictionary Table</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Fruit Dictionary</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Key</th>
<th>Value</th>
</tr>
{% for key, value in fruit_dict.items %}
<tr>
<td>{{ key }}</td>
<td>{{ value }}</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</table>
</body>
</html>
how to save data in dictionary of dictionaries that come from request after filling form in django and then how to access it
In a Django web application, you can save data from a form submission into a dictionary of dictionaries and access it as follows:
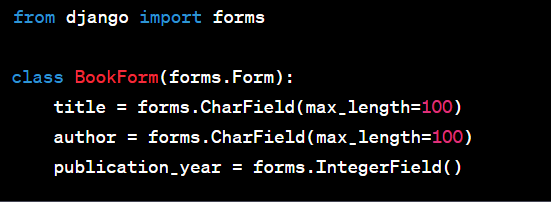
Step 1: Create a Django Form
First, create a Django form that corresponds to the data you want to collect. This should be done in your Django app's forms.py file:
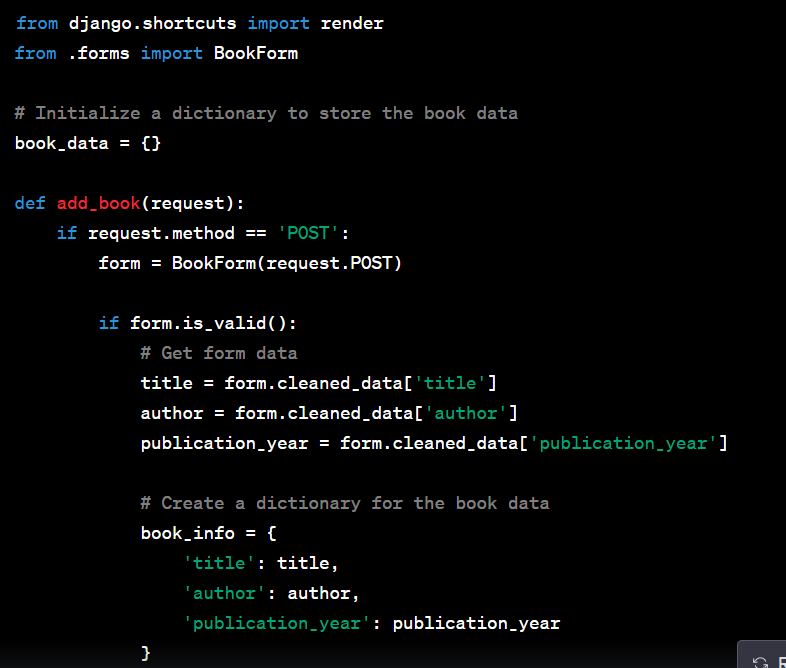
Step 2: Create a Django View: Next, create a Django view that handles the form submission and saves the data in a dictionary of dictionaries. This should be done in your Django app's views.py file
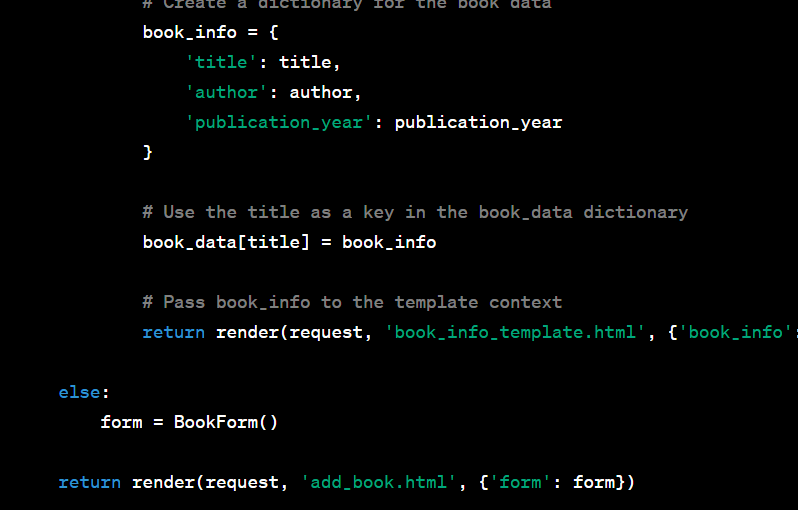
In the example above, we pass the book_info dictionary to the template context using the {'book_info': book_info} dictionary in the render function. We use the 'book_info' key to make book_info available in the template.
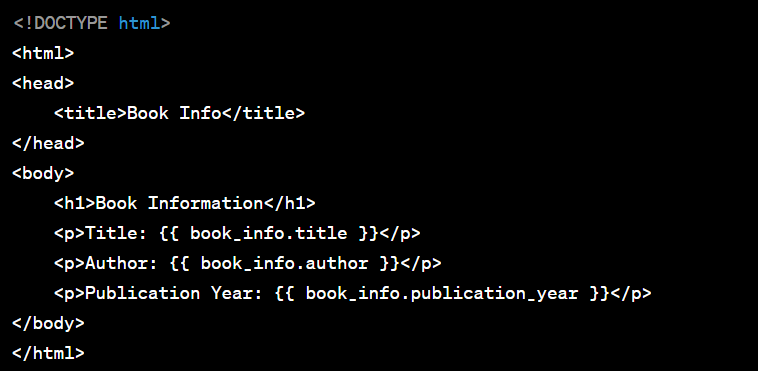
Now, you can access and display book_info in your template file (book_info_template.html) as follows:
how to save data in dictionary of dictionaries in python
# Create an empty dictionary of dictionaries
data = {}
# Add data to the dictionary
data['person1'] = {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York'}
data['person2'] = {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 25, 'city': 'Los Angeles'}
# You can also add more data or update existing data
data['person3'] = {'name': 'Charlie', 'age': 35, 'city': 'Chicago'}
data['person1']['age'] = 31
# Access data from the dictionary
print(data['person1']['name']) # Output: 'Alice'
print(data['person2']['age']) # Output: 25
# Iterate over the dictionary of dictionaries
for key, value in data.items():
print(key, value)
# Output:
# person1 {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 31, 'city': 'New York'}
# person2 {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 25, 'city': 'Los Angeles'}
# person3 {'name': 'Charlie', 'age': 35, 'city': 'Chicago'}
difference between format of list of dictionaries and array of json
BOTH ARE SIMILAR
n Python, a list of dictionaries and an array of JSON objects (JavaScript Object Notation) are similar in that they both allow you to store and organize structured data. However, there are some key differences between the two
Data Serialization Format:
A list of dictionaries is a native data structure in Python. Each element in the list is a Python dictionary with key-value pairs.
An array of JSON objects typically represents data in JSON format, which is a lightweight data interchange format used for data exchange between a server and a web application. JSON objects are similar in structure to Python dictionaries, but they follow JSON syntax.
Syntax Differences:
In a list of dictionaries, the syntax is Python-native. For example:
data = [{'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30}, {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 25}]
In an array of JSON objects, the syntax follows the JSON format. For example:
[
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 25}
]
Data Exchange:
JSON is a commonly used format for data exchange between a server and a web client (e.g., a browser). JSON is designed to be a lightweight, text-based format that is easy for both humans and machines to read and write.
Lists of dictionaries are a more general-purpose data structure in Python, and they can be used for various purposes within Python programs, including data storage, manipulation, and processing.
Data Serialization and Deserialization:
JSON objects can be easily serialized (converted to a string) and deserialized (converted from a string) using built-in functions or libraries in many programming languages.
Lists of dictionaries can also be serialized and deserialized, but the process might require more effort, such as manually converting dictionaries to strings and vice versa.
Supported Types:
JSON supports a limited set of data types, including strings, numbers, booleans, null, objects (JSON objects), and arrays. JSON is primarily used for representing structured data.
Python dictionaries within a list can contain a wider variety of data types, including Python-specific types like tuples and custom objects. They are more flexible in terms of the data they can hold.
difference between format of dictionary of dictionaries and array of json
BOTH ARE DIFFER
A "dictionary of dictionaries" and an "array of JSON objects" are both ways to structure and organize data, but they differ in their representation and use cases. Let's explore the differences with examples:
Dictionary of Dictionaries:
A "dictionary of dictionaries" typically uses Python dictionaries to create a hierarchical or nested structure. Each dictionary contains key-value pairs, and the values can be other dictionaries.
It is often used within Python programs for organizing and managing data in a hierarchical fashion.
Example of a dictionary of dictionaries in Python:
data = {
'person1': {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30},
'person2': {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 25}
}
Array of JSON Objects:
An "array of JSON objects" uses a list or array where each element is a JSON object. JSON objects consist of key-value pairs and are enclosed in curly braces.
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a widely used data interchange format for exchanging data between systems, often used in web development, APIs, and data storage.
Example of an array of JSON objects in JSON format:
[
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 25}
]
Key Differences:
Syntax:
A dictionary of dictionaries uses Python-native dictionary syntax, whereas an array of JSON objects follows the JSON format.
Use Cases:
A dictionary of dictionaries is used within Python programs for data organization and manipulation.
An array of JSON objects is typically used for data interchange between systems and is widely used in web development, APIs, and data storage.
Data Serialization:
JSON objects can be easily serialized (converted to a string) and deserialized (parsed from a string) using built-in functions or libraries in many programming languages. A dictionary of dictionaries may require custom serialization and deserialization.
Explain differencen betweein format of dictionary of dictionaries and nested json
A "dictionary of dictionaries" and "nested JSON" are two different ways to represent structured data hierarchies. Both data structures can be used to organize and represent data with multiple levels of nesting, but they differ in syntax and typical use cases. Here's an explanation of the differences between the two with examples:
Dictionary of Dictionaries:
In Python, a "dictionary of dictionaries" refers to the use of Python dictionaries to create a hierarchical or nested structure. Each dictionary contains key-value pairs, where the values can be other dictionaries.
The structure is typically used in Python programs for organizing and managing data.
Example of a dictionary of dictionaries in Python:
data = {
'person1': {'name': 'Alice', 'age': 30},
'person2': {'name': 'Bob', 'age': 25}
}
Nested JSON:
Nested JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) refers to the use of JSON objects to create a hierarchical or nested structure. In JSON, objects are enclosed in curly braces and can contain other objects (nested objects).
JSON is a widely used format for data interchange between systems and is often used in web development, APIs, and data storage.
Example of nested JSON in JSON format:
{
"person1": {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 30
},
"person2": {
"name": "Bob",
"age": 25
}
}
Key Differences:
Syntax: While the content and structure of the data are similar, the syntax is different. A dictionary of dictionaries uses Python-native dictionary syntax, and nested JSON follows the JSON notation.
Use Cases: A dictionary of dictionaries is used within Python programs for data organization and manipulation. Nested JSON is typically used for data interchange and storage between systems and is commonly used in web development.
Data Serialization: JSON objects can be easily serialized (converted to a string) and deserialized (parsed from a string) using built-in functions or libraries in many programming languages. A dictionary of dictionaries may require custom serialization and deserialization.
how to convert given list to dictionary and store in db in django
# views.py or management command
from .models import WordGroup, Word
words_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
word_length_dict = {}
# Populate the word_length_dict
for word in words_list:
length = len(word)
if length in word_length_dict:
word_length_dict[length].append(word)
else:
word_length_dict[length] = [word]
# Store the data in the database
for length, words in word_length_dict.items():
word_group = WordGroup.objects.create(length=length, words=", ".join(words))
for word in words:
Word.objects.create(word=word, group=word_group)
# Query the data from the database
all_word_groups = WordGroup.objects.all()
for group in all_word_groups:
print(group)
for word in group.word_set.all():
print(f" - {word}")
output:Length: 5, Words: apple, cherry, date
- apple
- cherry
- date Length: 6, Words: banana
- banana Length: 10, Words: elderberry
- elderberry
mapping char of string to item to create dictiory with help of list using enumerate
input_string = "programming"
my_list = ["new", "old", "mine", "ok"]
character_count = {}
# Iterate over the characters and indices using enumerate
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
# Use the index to get the corresponding item from the list
if index < len(my_list):
character_count[char] = my_list[index]
else:
# Handle the case where the list is shorter than the input_string
character_count[char] = None
# Print the result
print(character_count)
output
mapping char of string to item to create dictionary with help of list using zip
input_string = "programming"
my_list = ["new", "old", "mine", "ok"]
character_count = {}
# Use zip to iterate over both the characters in input_string and items in my_list
for char, item in zip(input_string, my_list):
# Map each character to the corresponding item in the list
character_count[char] = item
# Print the result
print(character_count)
output
mapping char of list to item to create dictionary with help of list using enumerate
original_list = ["new", "old", "mine", "ok"]
my_list = ["new", "old", "mine", "ok"]
character_count = {}
# Iterate over the characters and indices using enumerate
for index, char in enumerate(original_list):
# Use the index to get the corresponding item from the list
if index < len(my_list):
character_count[char] = my_list[index]
else:
# Handle the case where the list is shorter than the input_string
character_count[char] = None
# Print the result
print(character_count)
================or=======================
listing=["5","7","50","45","80"]
mine="python"
dictionary={}
for index, data in enumerate(listing):
length=len(mine)
if length > len(dictionary.keys()):
dictionary[data]=mine[index]
print(dictionary)




Top comments (0)