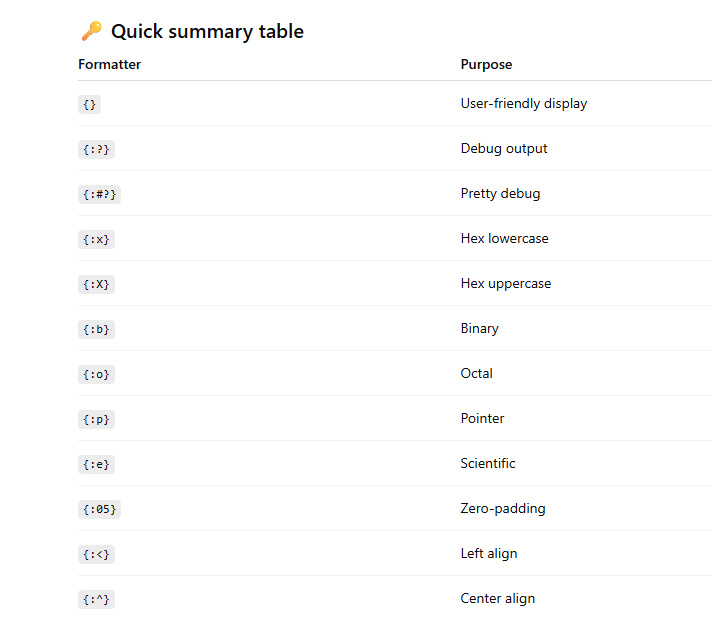
{} — Display formatter
{:?} — Debug formatter
{:#?} — Pretty Debug formatter
{:x} — Lowercase hexadecimal
{:X} — Uppercase hexadecimal
{:b} — Binary format
{:o} — Octal format
{:p} — Pointer address
{:e} / {:E} — Scientific notation
Width & alignment formatting
Padding with zeros
Precision (floats & strings)
Positional arguments
Named arguments
Mixing format styles
Custom Formatting specifier for control flow
MCQs – Rust Formatting Specifiers
Printing is handled by a series of macros defined in std::fmt some of which are:
format!: write formatted text to String
print!: same as format! but the text is printed to the console (io::stdout).
println!: same as print! but a newline is appended.
eprint!: same as print! but the text is printed to the standard error (io::stderr).
eprintln!: same as eprint! but a newline is appended.
{} — Display formatter
Used for user-friendly output
Requires the Display trait.
fn main() {
println!("{}", 10);
println!("{}", "Rust");
}
Output
10
Rust
✔ Clean
✔ No quotes
✔ Best for UI / logs shown to users
Another Example
fn main() {
let x = 5 + /* 90 + */ 5;
println!("Is `x` 10 or 100? x = {}", x);
}
output
Is `x` 10 or 100? x = 10
{:?} — Debug formatter
Used for developer debugging
Requires the Debug trait.
fn main() {
let v = vec![1, 2, 3];
println!("{:?}", v);
}
Output
[1, 2, 3]
✔ Shows internal structure
❌ Not user-friendly
3️⃣
{:#?} — Pretty Debug formatter
Same as Debug, but formatted nicely
fn main() {
let v = vec![1, 2, 3];
println!("{:#?}", v);
}
Output
[
1,
2,
3,
]
✔ Excellent for inspecting complex data
4️⃣
{:x} — Lowercase hexadecimal
fn main() {
println!("{:x}", 255);
}
Output
ff
{:X} — Uppercase hexadecimal
fn main() {
println!("{:X}", 255);
}
Output
FF
{:b} — Binary format
fn main() {
println!("{:b}", 10);
}
Output
1010
{:o} — Octal format
fn main() {
println!("{:o}", 10);
}
Output
12
8️⃣
{:p} — Pointer address
Shows memory address
fn main() {
let x = 10;
println!("{:p}", &x);
}
Output (example)
0x7ffddc3a9c2c
✔ Useful for debugging references & memory
9️⃣
{:e} / {:E} — Scientific notation
fn main() {
println!("{:e}", 1234.56);
println!("{:E}", 1234.56);
}
Output
1.23456e3
1.23456E3
🔟
Width & alignment formatting
Right-aligned (default)
println!("{:5}", 42);
Output:
42
Left-aligned
println!("{:<5}", 42);
Output:
42
Center-aligned
println!("{:^5}", 42);
Output:
42
1️⃣1️⃣ Padding with zeros
fn main() {
println!("{:05}", 42);
}
Output
00042
1️⃣2️⃣ Precision (floats & strings)
Float precision
fn main() {
println!("{:.2}", 3.14159);
}
Output:
3.14
String precision (truncate)
fn main() {
println!("{:.3}", "RustLang");
}
Output:
Rus
1️⃣3️⃣ Positional arguments
fn main() {
println!("{1} is learning {0}", "Rust", "Alice");
}
Output
Alice is learning Rust
1️⃣4️⃣ Named arguments
fn main() {
println!("{name} is {age} years old", name="Bob", age=30);
}
Output
Bob is 30 years old
1️⃣5️⃣ Mixing format styles
fn main() {
println!("{name:?} scored {:04}", name="Alice", 7);
}
Output
"Alice" scored 0007
Some More Example
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Structure(i32);
// Put a `Structure` inside of the structure `Deep`. Make it printable
// also.
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Deep(Structure);
fn main() {
// Printing with `{:?}` is similar to with `{}`.
println!("{:?} months in a year.", 12);
println!("{1:?} {0:?} is the {actor:?} name.",
"Slater",
"Christian",
actor="actor's");
// `Structure` is printable!
println!("Now {:?} will print!", Structure(3));
// The problem with `derive` is there is no control over how
// the results look. What if I want this to just show a `7`?
println!("Now {:?} will print!", Deep(Structure(7)));
}
output
12 months in a year.
"Christian" "Slater" is the "actor's" name.
Now Structure(3) will print!
Now Deep(Structure(7)) will print!
Custom Formatting specifier for control flow
Formatting specifier for control flow for Display formatter
Example 1: Country with population (basic Display)
use std::fmt::{self, Display, Formatter};
struct Country {
name: &'static str,
population_millions: f32,
}
impl Display for Country {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(f, "{} has {:.1} million people", self.name, self.population_millions)
}
}
fn main() {
for country in [
Country { name: "India", population_millions: 1429.0 },
Country { name: "USA", population_millions: 339.0 },
Country { name: "Japan", population_millions: 124.5 },
] {
println!("{}", country);
}
}
🔁 How loop iterates
Array [Country; 3]
Each Country is moved
println!("{}", country) → calls Display::fmt
output
India has 1429.0 million people
USA has 339.0 million people
Japan has 124.5 million people
✅ Example 2: Rectangle with calculated area
use std::fmt::{self, Display, Formatter};
struct Rectangle {
width: u32,
height: u32,
}
impl Display for Rectangle {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
let area = self.width * self.height;
write!(f, "Rectangle {}x{} (area = {})", self.width, self.height, area)
}
}
fn main() {
for rect in [
Rectangle { width: 10, height: 5 },
Rectangle { width: 7, height: 3 },
Rectangle { width: 4, height: 4 },
] {
println!("{}", rect);
}
}
📌 Key idea:
Display can compute values (area) before formatting.
output
Rectangle 10x5 (area = 50)
Rectangle 7x3 (area = 21)
Rectangle 4x4 (area = 16)
✅ Example 3: Temperature with unit conversion
use std::fmt::{self, Display, Formatter};
struct Temperature {
celsius: f32,
}
impl Display for Temperature {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
let fahrenheit = self.celsius * 9.0 / 5.0 + 32.0;
write!(f, "{:.1}°C = {:.1}°F", self.celsius, fahrenheit)
}
}
fn main() {
for temp in [
Temperature { celsius: 0.0 },
Temperature { celsius: 25.0 },
Temperature { celsius: 100.0 },
] {
println!("{}", temp);
}
}
Output
0.0°C = 32.0°F
25.0°C = 77.0°F
100.0°C = 212.0°F
✅ Example 4: Student grades (conditional formatting)
use std::fmt::{self, Display, Formatter};
struct Student {
name: &'static str,
marks: u8,
}
impl Display for Student {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
let result = if self.marks >= 40 { "Pass" } else { "Fail" };
write!(f, "{} scored {} → {}", self.name, self.marks, result)
}
}
fn main() {
for student in [
Student { name: "Amit", marks: 85 },
Student { name: "Riya", marks: 38 },
Student { name: "John", marks: 72 },
] {
println!("{}", student);
}
}
output
Amit scored 85 → Pass
Riya scored 38 → Fail
John scored 72 → Pass
✅ Example 5: Color with HEX output (like your Color struct)
use std::fmt::{self, Display, Formatter};
struct Color {
red: u8,
green: u8,
blue: u8,
}
impl Display for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(
f,
"RGB({}, {}, {}) → #{:02X}{:02X}{:02X}",
self.red, self.green, self.blue,
self.red, self.green, self.blue
)
}
}
fn main() {
for color in [
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 },
Color { red: 0, green: 3, blue: 254 },
Color { red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0 },
] {
println!("{}", color);
}
}
Output
RGB(128, 255, 90) → #80FF5A
RGB(0, 3, 254) → #0003FE
RGB(0, 0, 0) → #000000
use std::fmt::{self, Formatter, Display};
struct City {
name: &'static str,
// Latitude
lat: f32,
// Longitude
lon: f32,
}
impl Display for City {
// `f` is a buffer, and this method must write the formatted string into it.
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
let lat_c = if self.lat >= 0.0 { 'N' } else { 'S' };
let lon_c = if self.lon >= 0.0 { 'E' } else { 'W' };
// `write!` is like `format!`, but it will write the formatted string
// into a buffer (the first argument).
write!(f, "{}: {:.3}°{} {:.3}°{}",
self.name, self.lat.abs(), lat_c, self.lon.abs(), lon_c)
}
}
#[derive(Debug)]
struct Color {
red: u8,
green: u8,
blue: u8,
}
fn main() {
for city in [
City { name: "Dublin", lat: 53.347778, lon: -6.259722 },
City { name: "Oslo", lat: 59.95, lon: 10.75 },
City { name: "Vancouver", lat: 49.25, lon: -123.1 },
] {
println!("{}", city);
}
for color in [
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 },
Color { red: 0, green: 3, blue: 254 },
Color { red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0 },
] {
// Switch this to use {} once you've added an implementation
// for fmt::Display.
println!("{:?}", color);
}
}
output
Dublin: 53.348°N 6.260°W
Oslo: 59.950°N 10.750°E
Vancouver: 49.250°N 123.100°W
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 }
Color { red: 0, green: 3, blue: 254 }
Color { red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0 }
Formatting specifier for control flow for Debug formatter
Full example: Manual Debug implementation for Color
use std::fmt;
struct Color {
red: u8,
green: u8,
blue: u8,
}
impl fmt::Debug for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(
f,
"Color {{ red: {}, green: {}, blue: {} }}",
self.red, self.green, self.blue
)
}
}
fn main() {
for color in [
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 },
Color { red: 0, green: 3, blue: 254 },
Color { red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0 },
] {
println!("{:?}", color);
}
}
Output
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 }
Color { red: 0, green: 3, blue: 254 }
Color { red: 0, green: 0, blue: 0 }
2️⃣ Better & idiomatic way (recommended)
Rust provides debug builders for Debug.
use std::fmt;
struct Color {
red: u8,
green: u8,
blue: u8,
}
impl fmt::Debug for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("Color")
.field("red", &self.red)
.field("green", &self.green)
.field("blue", &self.blue)
.finish()
}
}
📌 Why this is better
Matches Rust’s default Debug style
Handles formatting safely
Works with {:#?} automatically
3️⃣ Pretty Debug printing
println!("{:#?}", color);
Output:
Color {
red: 128,
green: 255,
blue: 90,
}
4️⃣ Custom Debug with extra computed info
impl fmt::Debug for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
let hex = format!(
"#{:02X}{:02X}{:02X}",
self.red, self.green, self.blue
);
f.debug_struct("Color")
.field("red", &self.red)
.field("green", &self.green)
.field("blue", &self.blue)
.field("hex", &hex)
.finish()
}
}
Output:
Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90, hex: "#80FF5A" }
5️⃣ Debug vs Display (side-by-side)
use std::fmt::{self, Display};
struct Color {
red: u8,
green: u8,
blue: u8,
}
impl Display for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
write!(f, "rgb({}, {}, {})", self.red, self.green, self.blue)
}
}
impl fmt::Debug for Color {
fn fmt(&self, f: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result {
f.debug_struct("Color")
.field("red", &self.red)
.field("green", &self.green)
.field("blue", &self.blue)
.finish()
}
}
fn main() {
let c = Color { red: 128, green: 255, blue: 90 };
println!("{}", c); // user-friendly
println!("{:?}", c); // developer-friendly
}
MCQs – Rust Formatting Specifiers
Which formatter is used for user-friendly output in Rust?
A. {:?}
B. {}
C. {:#?}
D. {:p}
✅ Answer: B
📌 Explanation: {} uses the Display trait and is meant for end users.
MCQ 2
What is the output of the following code?
println!("{:?}", "Rust");
A. Rust
B. "Rust"
C. 'Rust'
D.
✅ Answer: B
📌 Debug formatting prints strings with quotes.
MCQ 3
Which formatter produces multi-line structured output?
A. {}
B. {:?}
C. {:#?}
D. {:x}
✅ Answer: C
MCQ 4
What does this code print?
println!("{:b}", 8);
A. 8
B. 1000
C. 01000
D. 0b1000
✅ Answer: B
📌 {:b} prints binary without prefix.
MCQ 5
Which formatter prints a memory address?
A. {:x}
B. {:#?}
C. {:p}
D. {}
✅ Answer: C
MCQ 6
What will be the output?
println!("{:05}", 42);
A. 42
B. 00042
C. 04200
D. 42.000
✅ Answer: B
MCQ 7
Which formatter prints uppercase hexadecimal?
A. {:x}
B. {:X}
C. {:h}
D. {:hex}
✅ Answer: B
MCQ 8
What does this print?
println!("{:.3}", "RustLang");
A. Rust
B. Rus
C. RustLang
D. Run-time error
✅ Answer: B
MCQ 9
Which formatter requires the Debug trait?
A. {}
B. {:?}
C. {:x}
D. {:b}
✅ Answer: B
MCQ 10
What happens if a type does not implement Display and you use {}?
A. Compiles successfully
B. Runtime error
C. Compile-time error
D. Prints empty string
✅ Answer: C
🎯
Interview Questions – Formatting Specifiers
Q1. What is the difference between {} and {:?}?
Answer:
{} uses the Display trait for user-friendly output, while {:?} uses the Debug trait for developer-focused debugging output.
Q2. Why does Rust separate Display and Debug?
Answer:
To prevent accidental exposure of internal data and enforce intentional formatting for users vs developers.
Q3. When should {:#?} be preferred over {:?}?
Answer:
When debugging complex or nested data structures where readability matters.
Q4. What does {:p} display and when is it useful?
Answer:
It prints the memory address of a reference, useful for debugging ownership, borrowing, and pointer behavior.
Q5. Can a type implement Debug but not Display?
Answer:
Yes. Debug is commonly derived automatically, while Display must usually be implemented manually.
Q6. What is the output difference between {:.2} for floats and strings?
Answer:
Floats → controls decimal precision
Strings → truncates length
Q7. Why does {:?} print strings with quotes?
Answer:
Because Debug shows the internal representation of data, including string boundaries.
Q8. What is the benefit of width and alignment specifiers?
Answer:
They allow structured, aligned output—useful in logs, tables, and reports.
Q9. What happens if a field inside a struct does not implement Debug?
Answer:
The struct cannot derive Debug, resulting in a compile-time error.
Q10. How does Rust ensure formatting is type-safe?
Answer:
Each formatter requires a specific trait, and Rust enforces this at compile time.

Top comments (0)