Variables (Basics)
Mutability (Changing the Value)
Shadowing (Re-declaring the Variable)
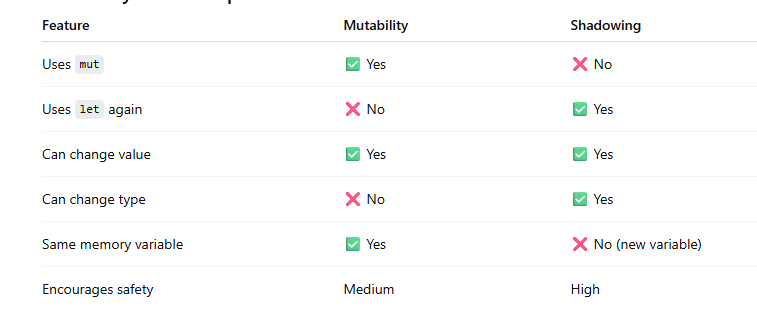
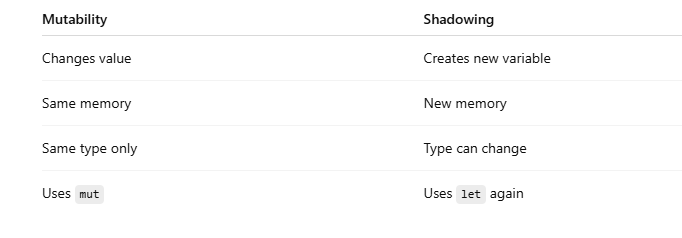
Shadowing vs Mutability (Core Difference)
Programming on scope and shadowing
Side-by-Side Comparison
Practical Example (Why Shadowing is Useful)
Comparison with Other Languages
When to Use What?
Final Summary
Memory diagrams for variable mutability and shadowing
Interview-ready questions and answers on Variables, Mutability, and Shadowing
MCQs – Basics and advanced
Variables (Basics)
A variable is a named storage location used to hold data.
Example (Rust)
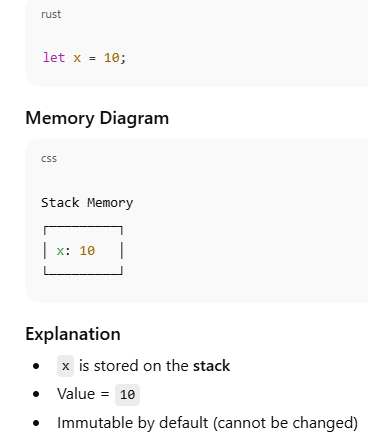
let x = 10;
println!("{}", x);
x stores the value 10
By default, variables in Rust are immutable (cannot be changed)
Mutability (Changing the Value)
What is Mutability?
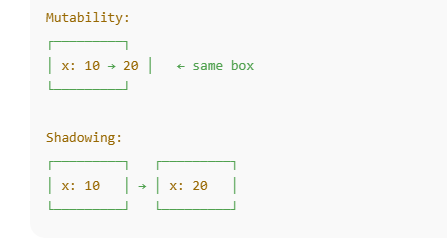
Mutability means the value of a variable can be changed after it is created.
Without Mutability (Error)
let x = 10;
x = 20; // ❌ Error: cannot assign twice to immutable variable
With Mutability (mut)
let mut x = 10;
x = 20; // ✅ Allowed
println!("{}", x);
Key Points
mut allows changing the value
Type cannot change
Same variable, same memory location
Mutability Rules
✔ Value can change
❌ Type cannot change
let mut x = 10;
x = 20; // OK
// x = "hi"; // ❌ Error: type mismatch
Shadowing (Re-declaring the Variable)
What is Shadowing?
Shadowing means declaring a new variable with the same name, which replaces the previous one.
Example (Shadowing)
let x = 10;
let x = x + 5;
println!("{}", x); // 15
The old x is hidden
A new variable is created
The old variable still existed earlier, but is no longer accessible
Shadowing vs Mutability (Core Difference)
Shadowing Allows Type Change
let x = 10;
let x = "hello";
println!("{}", x);
✔ Allowed because this is shadowing, not mutation
Mutability Does NOT Allow Type Change
let mut x = 10;
// x = "hello"; // ❌ Error
Programming on scope and shadowing
What is Scope?
Definition
Scope is the region of the program where a variable is valid and accessible.
Scope is created by { }
When execution leaves the scope, variables inside it are destroyed
Scope is about lifetime & visibility
Example: Scope
fn main() {
let x = 10;
{
let y = 20;
println!("Inside block: x = {}, y = {}", x, y);
}
println!("Outside block: x = {}", x);
}
Output
Inside block: x = 10, y = 20
Outside block: x = 10
Key point
y exists only inside the inner block
Accessing y outside would cause a compile-time error
2️⃣ What is Shadowing?
Definition
Shadowing allows a new variable with the same name to replace an older variable within a scope or a nested scope.
Uses let
Creates a new variable
Old variable still exists but is hidden
Example: Shadowing
fn main() {
let x = 5;
let x = x + 5;
println!("x = {}", x);
}
Output
x = 10
Key point
Second let x shadows the first
No mutation involved
Type can also change
3️⃣ Scope + Shadowing together
fn main() {
let value = 10;
{
let value = value * 2; // shadowing
println!("Inner value: {}", value);
}
println!("Outer value: {}", value);
}
Output
Inner value: 20
Outer value: 10
4️⃣ Shadowing vs Mutation (IMPORTANT)
❌ Mutation (requires mut)
let mut x = 5;
x = x + 1;
✅ Shadowing (no mut)
let x = 5;
let x = x + 1;
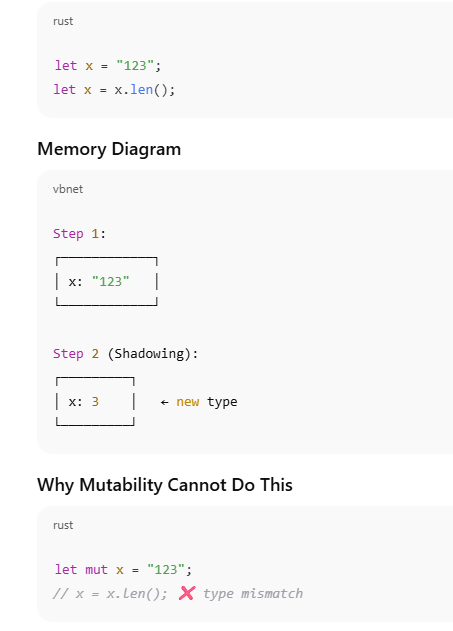
5️⃣ Type change using shadowing
fn main() {
let data = "100";
let data = data.len();
println!("{}", data);
}
Output
3
⚠️ This is not possible with mutation
Shadowing in the same scope
fn main() {
let x = 10;
println!("x = {}", x);
let x = x + 5; // shadows previous x
println!("x after shadowing = {}", x);
}
Output
x = 10
x after shadowing = 15
🔑 Explanation
Second let x creates a new variable
Old x is no longer accessible
2️⃣ Shadowing to change variable type
fn main() {
let value = "100";
println!("value = {}", value);
let value = value.parse::<i32>().unwrap();
println!("value as number = {}", value);
}
Output
value = 100
value as number = 100
🔑 Key Point
Shadowing allows type change
mut cannot change type
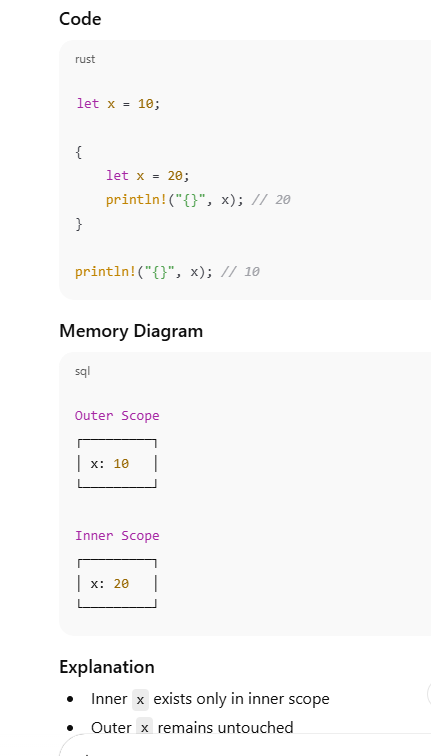
3️⃣ Scope inside a block
fn main() {
let x = 5;
{
let x = 20; // new scope, shadows outer x
println!("inner x = {}", x);
}
println!("outer x = {}", x);
}
Output
inner x = 20
outer x = 5
🔑 Explanation
Inner block has its own scope
Outer x remains unchanged
4️⃣ Shadowing vs mut
fn main() {
let mut count = 1;
count += 1;
println!("mut count = {}", count);
let count = count * 10; // shadowing
println!("shadowed count = {}", count);
}
Output
mut count = 2
shadowed count = 20
🔑 Difference
mut → modifies same variable
let → creates new variable
5️⃣ Function scope vs variable scope
fn main() {
let x = 50;
fn print_x() {
let x = 10; // different scope
println!("x inside function = {}", x);
}
print_x();
println!("x in main = {}", x);
}
Output
x inside function = 10
x in main = 50
🔑 Explanation
Functions create separate scopes
Variables are not shared automatically
Side-by-Side Comparison
Practical Example (Why Shadowing is Useful)
Without Shadowing (Messy)
let spaces_str = " ";
let spaces_len = spaces_str.len();
With Shadowing (Cleaner)
let spaces = " ";
let spaces = spaces.len();
Same name
Clear intent
No extra variable names
Comparison with Other Languages
JavaScript (Mutable by Default)
let x = 10;
x = 20; // OK
x = "hello"; // OK
JavaScript:
Mutable
Type changes allowed
No shadowing safety by default
Python (Mutable Reference)
x = 10
x = 20
x = "hello"
No explicit mutability control
Less compile-time safety
When to Use What?
Use Mutability when:
You truly need to change a value
Same type throughout
Performance-critical updates
Use Shadowing when:
Transforming data step-by-step
Want safer, cleaner code
Type conversion is needed
Final Summary
Variables store data
Mutability allows changing the value
Shadowing replaces a variable with a new one
Shadowing is safer and more flexible
Rust encourages immutability by default to prevent bugs
Memory diagrams for variable mutability and shadowing
Variables – Memory View
Mutability – Same Memory, New Value
Shadowing – New Memory Allocation
Shadowing with Type Change (Power Feature)
Scope-Based Shadowing
Mutability vs Shadowing – Memory Comparison
interview-ready questions and answers on Variables, Mutability, and Shadowing
Beginner Level
What is a variable?
Answer:
A variable is a named memory location used to store data. In Rust, variables are immutable by default to improve safety and prevent accidental changes.
let x = 10;
What does immutability mean?
Answer:
Immutability means the value of a variable cannot be changed after it is assigned.
let x = 10;
// x = 20; ❌ compile-time error
Why are variables immutable by default in Rust?
Answer:
To:
Prevent accidental bugs
Improve thread safety
Make code easier to reason about
Enable compiler optimizations
How do you make a variable mutable?
Answer:
By using the mut keyword.
let mut x = 10;
x = 20;
Intermediate Level
What is mutability?
Answer:
Mutability allows changing the value of a variable without changing its type or memory identity.
let mut x = 5;
x = 8;
What is shadowing?
Answer:
Shadowing occurs when a new variable with the same name is declared, replacing the old one.
let x = 5;
let x = x + 1;
What is the main difference between mutability and shadowing?
Can shadowing change the variable type?
Answer:
Yes.
let x = "123";
let x = x.len(); // now usize
Can a mutable variable change its type?
Answer:
No.
let mut x = 10;
// x = "hello"; ❌ not allowed
Why is shadowing preferred over mut in many cases?
Answer:
Because shadowing:
Encourages immutability
Makes data transformations clearer
Reduces unintended side effects
Allows type conversion
Advanced Level
How does shadowing affect memory?
Answer:
Shadowing allocates a new memory location, while the old variable becomes inaccessible.
let x = 10;
let x = 20; // new variable
Explain scope-based shadowing.
Answer:
A variable declared in an inner scope shadows the outer variable only within that scope.
let x = 10;
{
let x = 20;
}
Is shadowing allowed in the same scope?
Answer:
Yes, Rust allows shadowing in the same scope using let.
How does immutability help with concurrency?
Answer:
Immutable variables:
Can be safely shared across threads
Do not require locks
Prevent data races
When should you use mut instead of shadowing?
Answer:
Use mut when:
The value changes frequently
The type remains the same
Performance is critical (loops, counters)
Practical & Scenario-Based Questions
Give a real-world example where shadowing is useful.
Answer:
Processing user input step-by-step.
let input = " 42 ";
let input = input.trim();
let input = input.parse::<i32>().unwrap();
Give a real-world example where mutability is required.
Answer:
Counters and accumulators.
let mut total = 0;
for i in 1..=5 {
total += i;
}
What happens to the old variable after shadowing?
Answer:
It becomes inaccessible and is cleaned up when it goes out of scope.
Can shadowing cause bugs?
Answer:
Yes, if overused or unclear, it can reduce readability. Proper naming and formatting help avoid confusion.
How does Rust’s approach differ from languages like Java or Python?
Answer:
Rust enforces immutability at compile time
Java/Python allow mutation by default
Rust prevents many runtime bugs before execution
Tricky Interview Questions
Is this code valid? Why?
let x = 5;
let x = x;
Answer:
Yes. The new x shadows the old x using its value.
Is this shadowing or mutation?
let mut x = 10;
x = x + 1;
Answer:
Mutation — same variable, same memory.
Which is safer: shadowing or mutability?
Answer:
Shadowing is generally safer because it avoids unintended state changes.
Part 1: MCQs (With Answers)
MCQs – Basics and advanced
In Rust, variables are immutable by default.
A. True
B. False
✅ Answer: A. True
Which keyword makes a variable mutable in Rust?
A. var
B. mutable
C. mut
D. change
✅ Answer: C. mut
What happens if you try to modify an immutable variable in Rust?
A. Runtime error
B. Program crashes
C. Compile-time error
D. Value is ignored
✅ Answer: C. Compile-time error
Which statement correctly demonstrates shadowing?
A.
let mut x = 10;
x = 20;
B.
let x = 10;
x = 20;
C.
let x = 10;
let x = x + 1;
D.
mut x = 10;
✅ Answer: C
MCQs – Mutability vs Shadowing
Mutability allows:
A. Changing variable type
B. Changing variable value
C. Creating a new variable
D. Changing scope
✅ Answer: B
Shadowing allows:
A. Modifying the same memory
B. Changing value only
C. Changing type and value
D. Runtime mutation
✅ Answer: C
Which of the following is NOT allowed in Rust?
A.
let x = 5;
let x = x + 1;
B.
let mut x = 5;
x = "hello";
C.
let x = "10";
let x = x.len();
D.
let mut x = 5;
x = 10;
✅ Answer: B
Shadowing creates:
A. Same variable, same memory
B. New variable, new memory
C. Runtime mutation
D. Reference alias
✅ Answer: B
Summary
Variables (Basics)
Mutability (Changing the Value)
Shadowing (Re-declaring the Variable)
Shadowing vs Mutability(Shadowing Allows Type Change)
Programming on scope and shadowing
What is Scope?,Shadowing?
Shadowing in the same scope
Comparison with Other Languages
When to Use What?



Top comments (0)