EBS: ELASTIC BLOCK STORAGE
AWS Elastic Block Store (EBS) is Amazon’s block-level storage solution used with the EC2 cloud service to store persistent data. This means that the data is kept on the AWS EBS servers even when the EC2 instances are shut down. EBS offers the same high availability and low-latency performance within the selected availability zone, allowing users to scale storage capacity at low subscription-based pricing model. The data volumes can be dynamically attached, detached and scaled with any EC2 instance, just like a physical block storage drive. As a highly dependable cloud service, the EBS offering guarantees 99.999% availability.
AWS EBS is different from the standard EC2 Instance Store, which merely provides temporary storage available on the physical EC2 host servers. The EC2 Instance Store is useful for temporary data content such as caches, buffers or files that are replicated across the hosted servers. For data that needs to be available persistently, regardless of the operating life of an EC2 instance.
Steps to attach EBS 1 in EC2 instance:
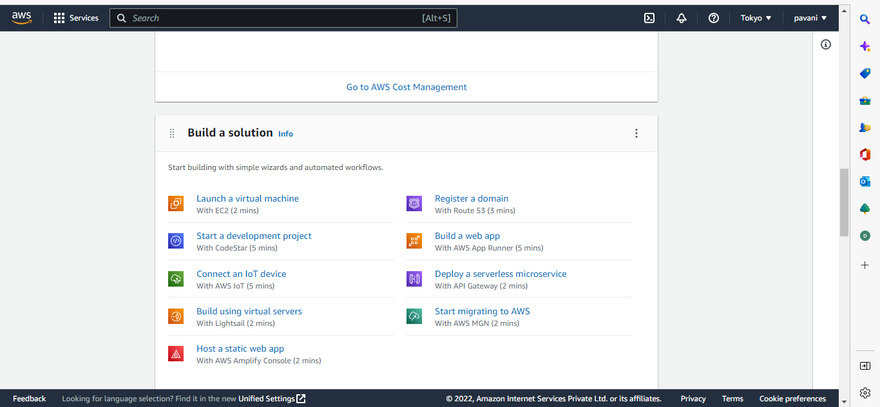
step 1: Go to console home > Build a solution > launch a virtual
machine with EC2
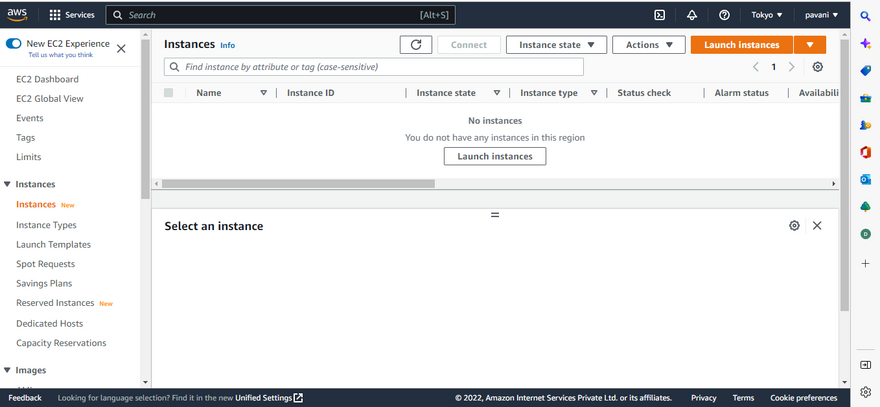
Step 2: Click on launch instance
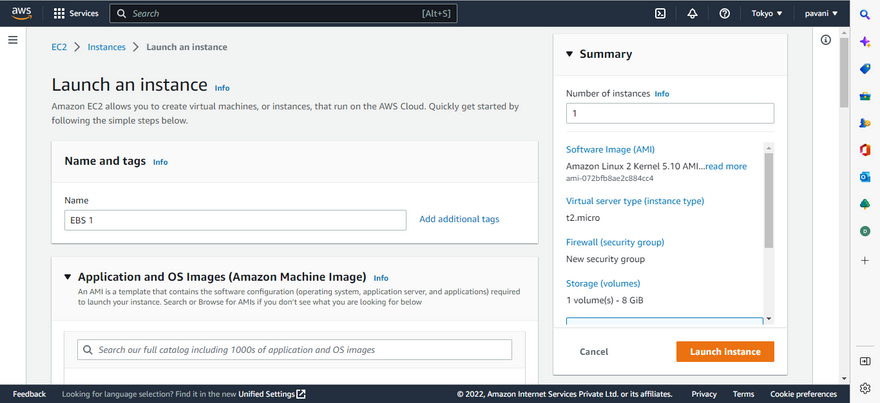
Step 3: Give the EC2 instance name EBS 1
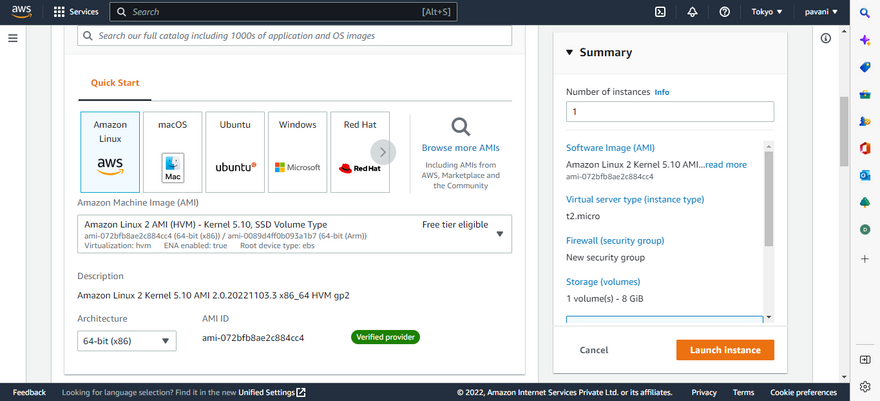
Step 4: Choose the AWS image for EBS1
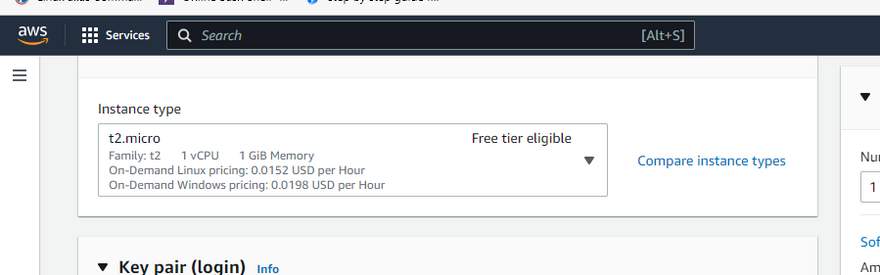
Step 5: Choose an instance type
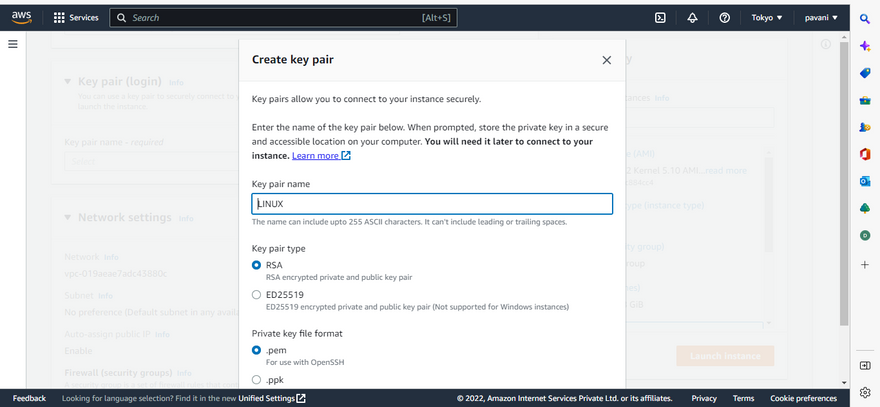
Step 6: Choose the key pair and create the key pair.
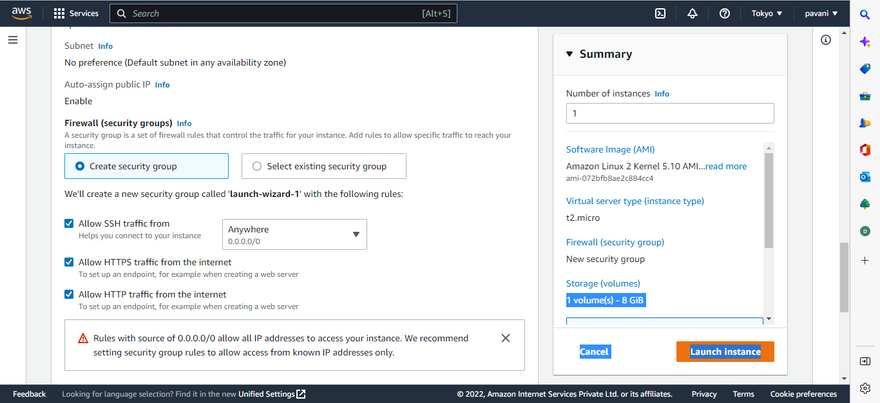
Step 7: Create the security group and open the port as per the requirement
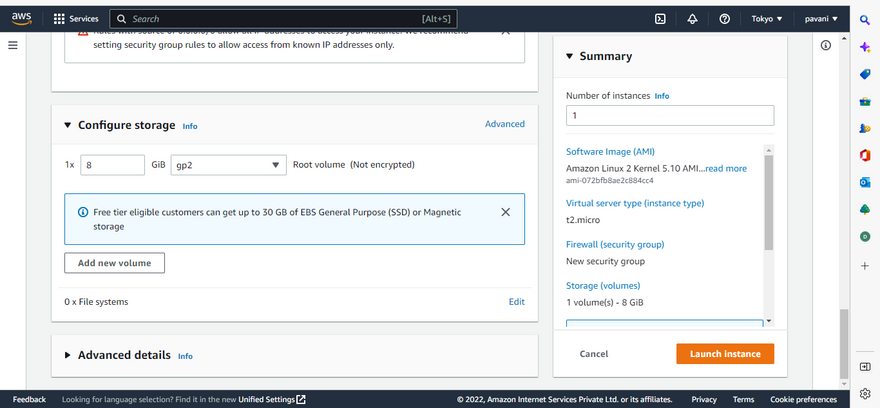
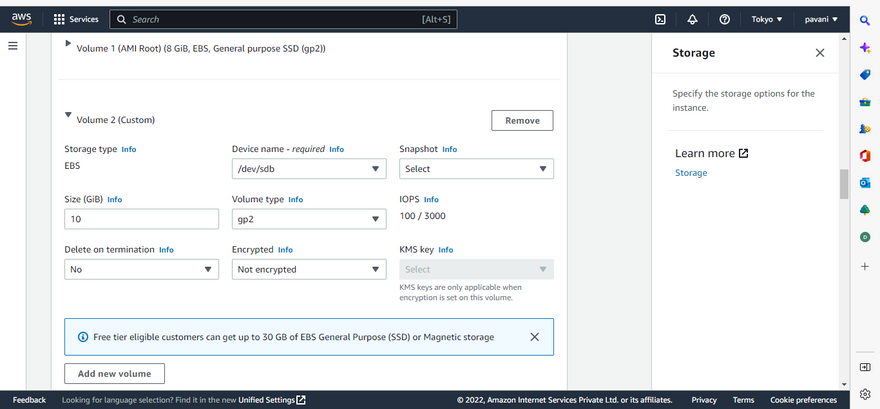
Step 8: click on the add volume for extra EBS1
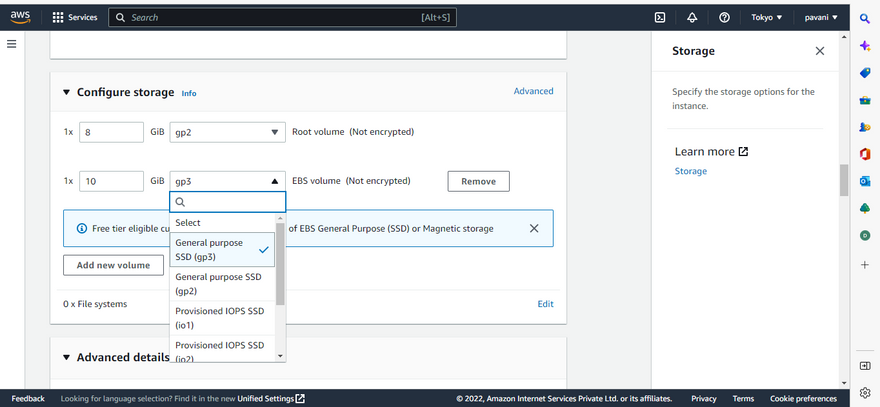
Step 9: Configure EBS Size
Step 10: Select EBS size as per Requirement
the AWS EBS offers the following storage volume options:
General Purpose SSD (gp2): An optimum balance between cost and performance for a variety of IT workloads. Use cases include virtual desktops, apps, dev and test environments, among others.
Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1): The high-performance functionality serves particularly well for mission-critical IT workloads. Suitable use cases include large databases and business apps that require 16,000 IOPS or 250 MiB/s of throughput per volume.
Throughput Optimized HDD (st1): A low cost alternative for large storage volume workloads with high performance throughput requirements. Examples include streaming workloads, big data applications, log processing and data warehousing.
Cold HDD (sc1): An inexpensive alternative for use cases with a requirement to maintain minimal cost for large volume data storage. Examples include workloads that are accessed less frequently.
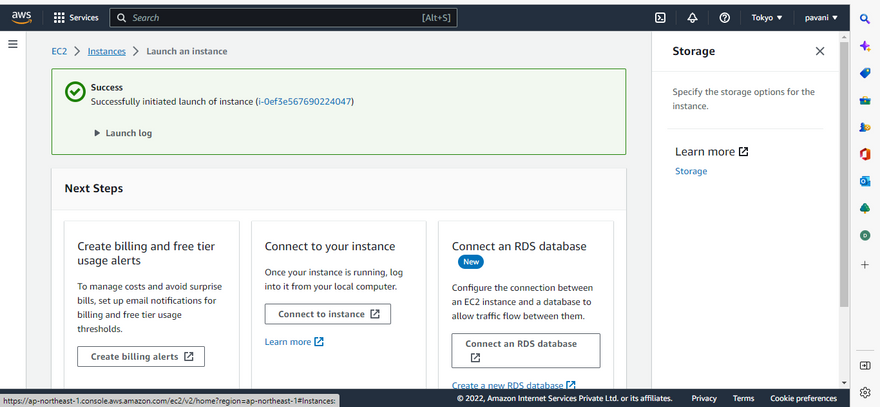
Step 11: Click launch instance button
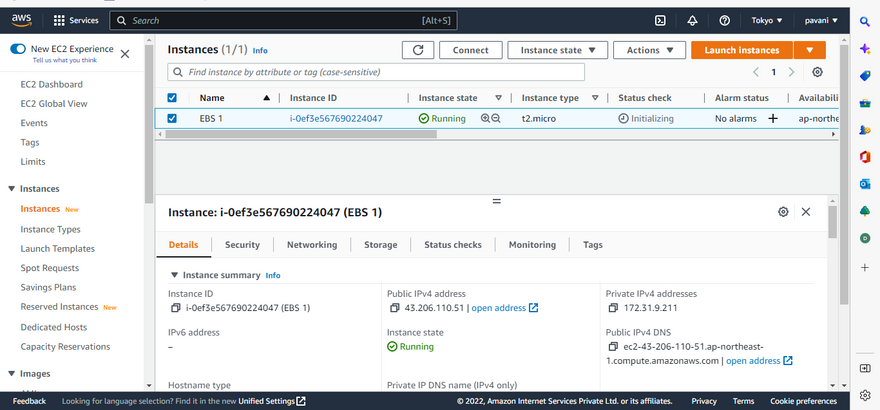
On the Instances screen, we can view the status of the launch. It takes a short time for an instance to launch. When you launch an instance, its initial state is pending. After the instance starts, its state changes to running and it receives a public DNS name

Top comments (0)