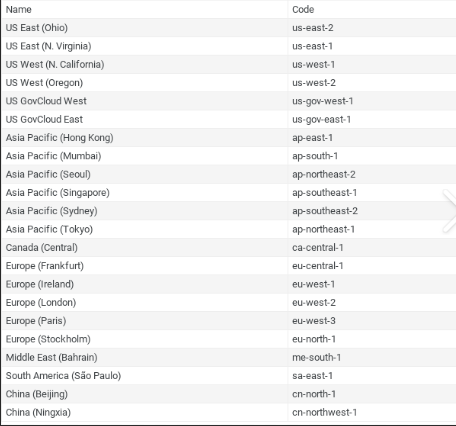
AWS Regions:
AWS Regions are separate geographic areas that AWS uses to house its infrastructure. These are distributed around the world so that customers can choose a region closest to them in order to host their cloud infrastructure there. The closer the region is the better, to reduce network latency as much as possible for your end-us and for fast service.
- Each AWS Region is designed to be isolated from the other AWS Regions. This design achieves the greatest possible fault tolerance and stability.
In general, try to follow these best practices when you choose a region, to ensure top performance and resilience:
-> Proximity: Choose a region closest to your location and your customers’ location to optimize network latency.
-> Services: Try and think about what your most needed services are. Usually, the newest services start on a few main regions then pop up in other regions later.
-> Cost: Certain regions will cost more than others, so use built-in AWS calculators to do rough cost estimates to inform your choices.
-> Service Level Agreement (SLA): Just as with cost, your SLA details will vary by region, so be sure to be aware of what your needs are and if they’re being met.
-> Compliance: You may need to meet regulatory compliance needs such as GDPR by hosting your deployment in a specific — or multiple regions.
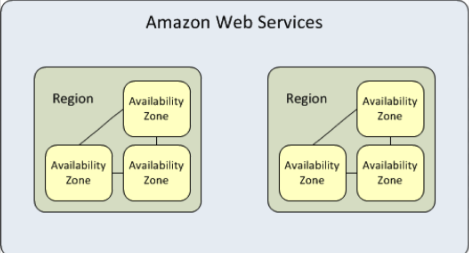
Availablity Zone: An AWS Availability Zone (AZ) is the logical building block that makes up an AWS Region. Each AWS Region has multiple, isolated locations known as Availability Zones. There are currently 69 AZs, which are isolated locations— data centers — within a region.
AWS Availability Zones give you the flexibility to launch production apps and resources that are highly available, resilient/fault-tolerant, and scalable as compared to using a single data center

Top comments (0)