In Dart, List, Set, and Map are three fundamental collection types that allow you to store and manipulate data in different ways. Here, I'll describe the differences between them with examples and provide a comparison table.
List:
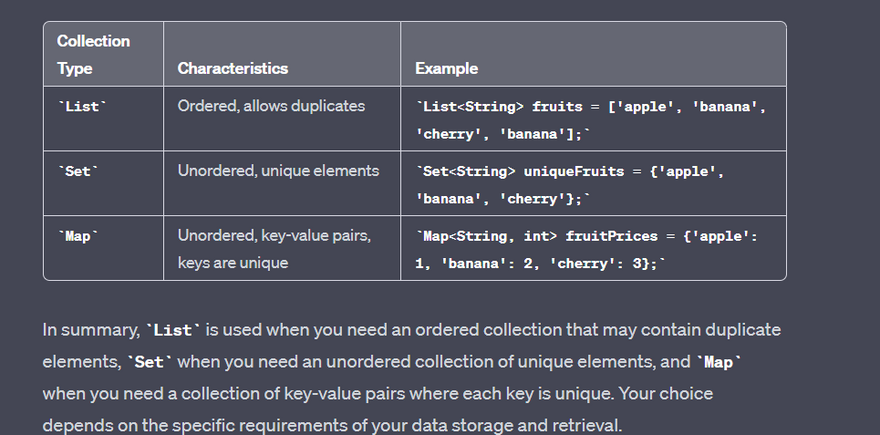
A List is an ordered collection of elements. Elements in a list are indexed, starting from 0, and can have duplicate values.
Example of List:
List<String> fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'banana'];
print(fruits[0]); // Accessing the first element.
print(fruits.length); // Number of elements in the list.
print(fruits.contains('cherry')); // Checking if 'cherry' is in the list.
for (var fruit in fruits) {
print(fruit);
}
Output:
apple
4
true
apple
banana
cherry
banana
Set:
A Set is an unordered collection of unique elements. Sets do not allow duplicate values, and the order of elements is not guaranteed.
Example of Set:
Set<String> uniqueFruits = {'apple', 'banana', 'cherry'};
print(uniqueFruits.contains('cherry')); // Checking if 'cherry' is in the set.
uniqueFruits.add('banana'); // Adding a duplicate value (ignored).
for (var fruit in uniqueFruits) {
print(fruit);
}
Output:
true
apple
banana
cherry
Map:
A Map is a collection of key-value pairs where each key is unique. Maps are unordered, meaning the order of key-value pairs is not guaranteed.
Example of Map:
Map<String, int> fruitPrices = {
'apple': 1,
'banana': 2,
'cherry': 3,
};
print(fruitPrices['banana']); // Accessing the value associated with the key 'banana'.
print(fruitPrices.containsKey('cherry')); // Checking if 'cherry' is a key in the map.
fruitPrices['grape'] = 4; // Adding a new key-value pair.
for (var fruit in fruitPrices.keys) {
print('$fruit: ${fruitPrices[fruit]}');
}
Output:
2
true
apple: 1
banana: 2
cherry: 3
grape: 4
Comparison Table:
Here's a table summarizing the differences between List, Set, and Map collections in Dart:

Top comments (0)