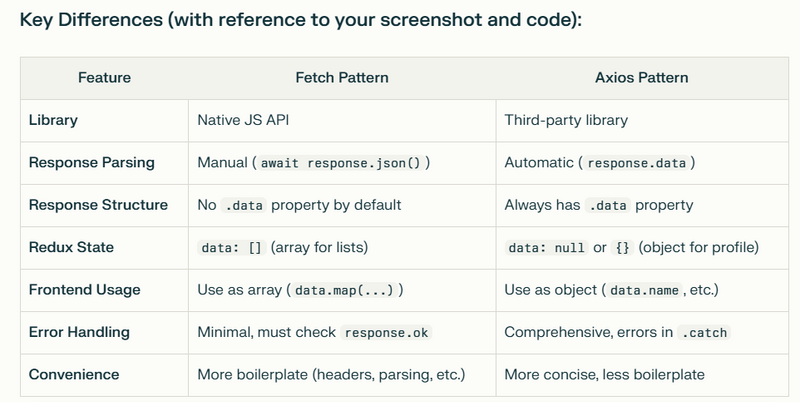
Here’s a clear explanation of the difference between the fetch pattern and the axios pattern in React Native, with reference to your code and the screenshot you provided:
Fetch Pattern
How it works:
fetch is a native JavaScript API for making HTTP requests.
You must manually parse the response using .json().
The response object does not have a .data property by default.
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' },
body: JSON.stringify({ email }),
});
const data = await response.json(); // You must parse it manually
return data;
In Redux Thunk:
if (response && response.data && Array.isArray(response.data)) {
return response.data;
}
Here, you expect response.data to be an array (e.g., a list of vehicles).
In Reducer:
data: [],
You initialize the state as an array.
In Frontend:
const vehiclesState = useSelector(state => state.vehicles || {});
const vehicles = vehiclesState.data || [];
You expect data to be an array and use it as such.
Axios Pattern
How it works:
axios is a third-party library that automatically parses JSON responses.
The response object always has a .data property, which contains the parsed response.
const response = await axios.post(url, { email }, {
headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/json' }
});
return response.data; // Already parsed, no need for .json()
In Redux Thunk:
if (response && response.data) {
return response.data; // You expect an object (e.g., a user profile)
}
Here, you expect response.data to be an object (e.g., a user profile).
In Reducer:
data: null, // or data: {}
You initialize the state as null or an object.
In Frontend:
const { loading, data: profiles, error } = useSelector(state => state.profile);
const profileData = profiles ? profiles : null;
You expect data to be an object and use it as such
==========================SUMMARY==================================
FETCH PATTERN
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
},
});
const data = await response.json();
return data;
after getting respone in createAsyncThunk fun
if (response && response.data && Array.isArray(response.data)) {
return response.data;
in reducers
data: [],
in front end
const vehiclesState = useSelector(state => state.vehicles || {});
const vehicles = vehiclesState.data || [];
=======================================
AXOIS PATTERN
const response = await axios.post(url, {
email, // Send email in the request body
}, {
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
}
});
return response.data; // Return profiles data if success
after getting respone in createAsyncThunk fun
if (response && response.data) {
return response.data; // Return the user profile object
}
in reducers
data: null, // Change from [] to null
in front end
const { loading, data: profiles, error } = useSelector(state => state.profile);
// Extract the first profile from the array
const profileData = profiles ? profiles : null;

Top comments (0)