SyntaxError
IndentationError
NameError
TypeError
ValueError
ZeroDivisionError
IndexError
KeyError
FileNotFoundError
AttributeError
PermissionError
FileExistsError
OSError
EOFError
ArithmeticError
FloatingPointError
ImportError
ModuleNotFoundError
MemoryError
RecursionError
GeneratorExit
SystemExit
KeyboardInterrupt
StopIteration
Instance Error
Missing Error
Exception handling in Python is essential for gracefully dealing with errors and exceptions that can occur during program execution. Here are 30 different types of exceptions in Python, along with examples of how to handle them:
SyntaxError:
Explanation: Raised when there's a syntax error in the code.
Example:
def my_function()
pass # Missing colon, raises SyntaxError
my code is
best_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion: 'gini', max_depth: 10, max_leaf_nodes: 9, min_samples_leaf: 2, min_samples_split: 3)
best_clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
SyntaxError: invalid syntax
but i got Cell In[233], line 1
best_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion: 'gini', max_depth: 10, max_leaf_nodes: 9, min_samples_leaf: 2, min_samples_split: 3)
Solution
best_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='gini', max_depth=10, max_leaf_nodes=9, min_samples_leaf=2, min_samples_split=3)
# Train the model with the training data
best_clf.fit(x_train, y_train)
IndentationError:
Explanation: Occurs when there's an indentation-related error.
Example:
if True:
print("Indented incorrectly") # Raises IndentationError
NameError:
Explanation: Raised when a variable or name is not found in the current scope.
Example:
print(undefined_variable) # Raises NameError
TypeError:
Explanation: Occurs when an operation is performed on an inappropriate data type.
Example:
df.shape()
Error
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[13], line 1
----> 1 df.shape()
TypeError: 'tuple' object is not callable
Solution
df.shape
output
(1599, 12)
result = "5" + 5 # Raises TypeError
ValueError:
Explanation: Raised when a built-in operation or function receives an argument of the correct type but with an inappropriate value.
Example:
num = int("abc") # Raises ValueError
my code is
def metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True):
if train:
clf.fit(x_train, y_train) # Ensure that the classifier is fitted
y_pred = clf.predict(x_train)
print("==========train result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
# Other metrics or actions for training data
else:
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print("==========test result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
print("\n \n Test classification report \n" ,classification_report(y_test,pred,digits=2))
Error
ValueError: Classification metrics can't handle a mix of multiclass and continuous targets
Solution
print("\n \n Test classification report \n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred, digits=2))
def metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True):
if train:
clf.fit(x_train, y_train) # Ensure that the classifier is fitted
y_pred = clf.predict(x_train)
print("==========train result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
# Other metrics or actions for training data
else:
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print("==========test result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
print("\n \n Test classification report \n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred, digits=2))
Another Example
my code is
grid_param = {
'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy'],
'max_depth': range(10,15),
'max_sample_leaf':range(2,6),
'min_samples_split': range(3,8),
'max_leaf_nodes':range(5,10),
}
grid_search = GridSearchCV(estimator=clf, param_grid=grid_param, cv=5, n_jobs=-1)
grid_search.fit(x_train, y_train)
Error
ValueError: Invalid parameter 'max_sample_leaf' for estimator DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=10, max_leaf_nodes=5). Valid parameters are: ['ccp_alpha', 'class_weight', 'criterion', 'max_depth', 'max_features', 'max_leaf_nodes', 'min_impurity_decrease', 'min_samples_leaf', 'min_samples_split', 'min_weight_fraction_leaf', 'random_state', 'splitter'].
Solution
grid_param = {
'criterion': ['gini', 'entropy'],
'max_depth': range(10, 15),
'min_samples_leaf': range(2, 6),
'min_samples_split': range(3, 8),
'max_leaf_nodes': range(5, 10),
}
Another Example
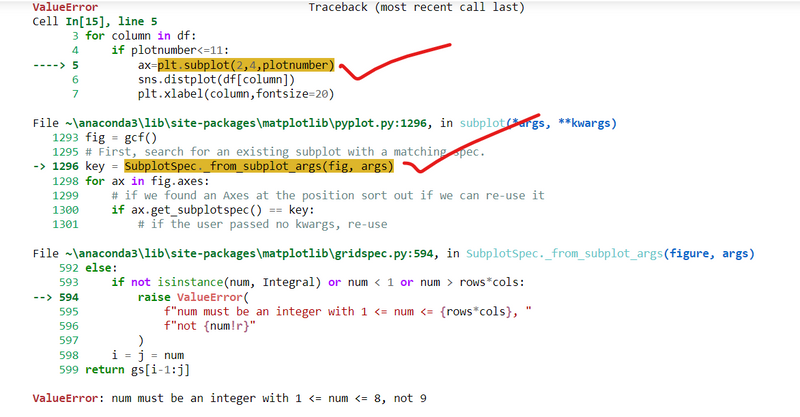
my code is
plt.figure(figsize=(20,15),facecolor='red')
plotnumber=1
for column in df:
if plotnumber<=11:
ax=plt.subplot(2,4,plotnumber)
sns.distplot(df[column])
plt.xlabel(column,fontsize=20)
plotnumber+=1
plt.tight_layout()
Error
solution
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15), facecolor='red')
plotnumber = 1
# Adjust the subplot grid to accommodate more subplots
for column in df:
if plotnumber <= 12:
ax = plt.subplot(3, 4, plotnumber) # Adjusted to a 3x4 grid
sns.distplot(df[column])
plt.xlabel(column, fontsize=20)
plotnumber += 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Solution
ax = plt.subplot(3, 4, plotnumber)
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 15), facecolor='red')
plotnumber = 1
# Adjust the subplot grid to accommodate more subplots
for column in df:
if plotnumber <= 12:
ax = plt.subplot(3, 4, plotnumber) # Adjusted to a 3x4 grid
sns.distplot(df[column])
plt.xlabel(column, fontsize=20)
plotnumber += 1
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Another Example
ValueError: Unknown label type: 'continuous'
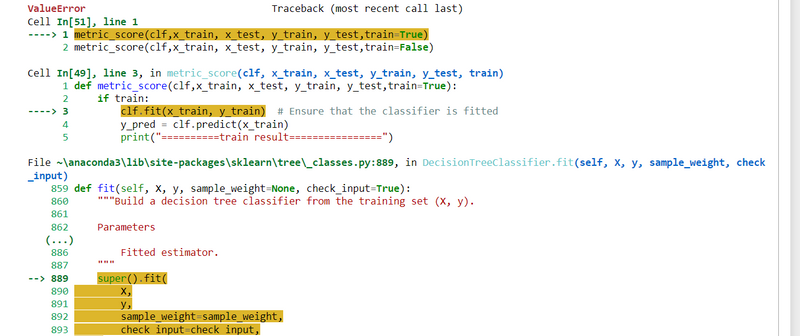
my code is
def metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True):
if train:
clf.fit(x_train, y_train) # Ensure that the classifier is fitted
y_pred = clf.predict(x_train)
print("==========train result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
# Other metrics or actions for training data
else:
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print("==========test result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
print("\n \n Test classification report \n", classification_report(y_test, y_pred, digits=2))
clf=DecisionTreeClassifier()
metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True)
metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=False)
Errors
Solution
indicates that there is an issue with the type of labels (y_train or y_test) you are providing to the fit method of the DecisionTreeClassifier. Decision trees are generally used for classification tasks, and they expect discrete (categorical) labels, not continuous ones.
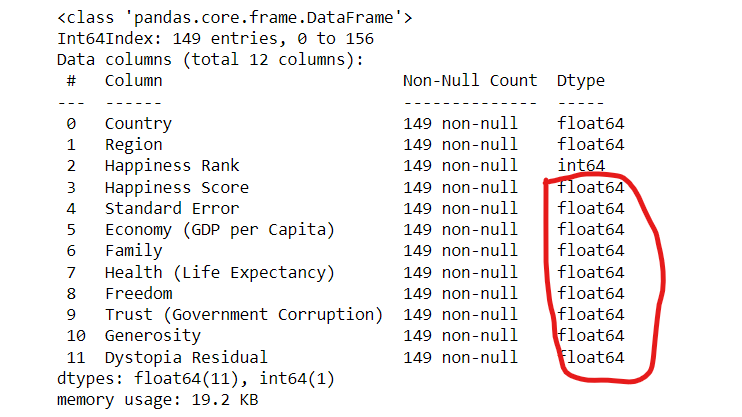
df1.info()
all are float data type it means it is not classification task not regression task continous and descision tree classifier task
Another Example
ValueError: Found input variables with inconsistent numbers of samples: [30, 119]
my code is
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error
import numpy as np
# Assuming x and y are your feature and target variables
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=maxRs)
LR = LinearRegression()
LR.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred_LR = LR.predict(x_test)
pred_train = LR.predict(x_train)
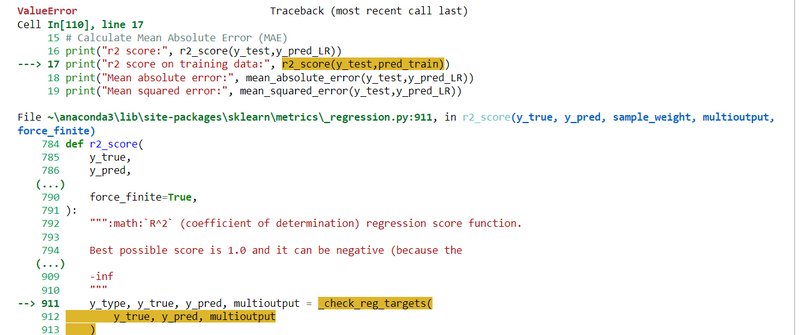
# Calculate Mean Absolute Error (MAE)
print("r2 score:", r2_score(y_test,y_pred_LR))
print("r2 score on training data:", r2_score(y_test,pred_train))
print("Mean absolute error:", mean_absolute_error(y_test,y_pred_LR))
print("Mean squared error:", mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred_LR))
print("Root mean squared error:", np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test,y_pred_LR)))
I got Errors
Solution
print("R-squared score on training data:", r2_score(y_train, pred_train))
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score, mean_absolute_error, mean_squared_error
import numpy as np
# Assuming x and y are your feature and target variables
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=maxRs)
LR = LinearRegression()
LR.fit(x_train, y_train)
# Make predictions
y_pred_LR = LR.predict(x_test)
pred_train = LR.predict(x_train)
# Calculate Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and R-squared scores
print("R-squared score on test data:", r2_score(y_test, y_pred_LR))
print("R-squared score on training data:", r2_score(y_train, pred_train))
print("Mean absolute error:", mean_absolute_error(y_test, y_pred_LR))
print("Mean squared error:", mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR))
print("Root mean squared error:", np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred_LR)))
output
R-squared score on test data: 0.9993695138526167
R-squared score on training data: 0.9988497867914624
Mean absolute error: 0.023082746123624338
Mean squared error: 0.0009927528177423863
Root mean squared error: 0.0315079802231496
Another Example
Another Example
yesterday i run the commands
GB = GradientBoostingRegressor()
GB.fit(x_train, y_train)
predGB = GB.predict(x_test)
print("accuracy_score:", accuracy_score(y_test, predGB))
print("confusion matrix:", confusion_matrix(y_test, predGB))
print("classification_report :", classification_report(y_test, predGB))
i got error
ValueError: Classification metrics can't handle a mix of binary and continuous targets
ValueError raceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[31], line 4
2 GB.fit(x_train, y_train)
3 predGB = GB.predict(x_test)
----> 4 print("accuracy_score:", accuracy_score(y_test, predGB))
5 print("confusion matrix:", confusion_matrix(y_test, predGB))
6 print("classification_report :", classification_report(y_test, predGB))
File ~\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\utils\_param_validation.py:192, in validate_params.<locals>.decorator.<locals>.wrapper(*args, **kwargs)
187 validate_parameter_constraints(
188 parameter_constraints, params, caller_name=func.__qualname__
189 )
191 try:
--> 192 return func(*args, **kwargs)
193 except InvalidParameterError as e:
194 # When the function is just a wrapper around an estimator, we allow
195 # the function to delegate validation to the estimator, but we replace
196 # the name of the estimator by the name of the function in the error
197 # message to avoid confusion.
198 msg = re.sub(
199 r"parameter of \w+ must be",
200 f"parameter of {func.__qualname__} must be",
201 str(e),
202 )
File ~\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\metrics\_classification.py:221, in accuracy_score(y_true, y_pred, normalize, sample_weight)
155 """Accuracy classification score.
156
157 In multilabel classification, this function computes subset accuracy:
(...)
217 0.5
218 """
220 # Compute accuracy for each possible representation
--> 221 y_type, y_true, y_pred = _check_targets(y_true, y_pred)
222 check_consistent_length(y_true, y_pred, sample_weight)
223 if y_type.startswith("multilabel"):
File ~\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\sklearn\metrics\_classification.py:95, in _check_targets(y_true, y_pred)
92 y_type = {"multiclass"}
94 if len(y_type) > 1:
---> 95 raise ValueError(
96 "Classification metrics can't handle a mix of {0} and {1} targets".format(
97 type_true, type_pred
98 )
99 )
101 # We can't have more than one value on y_type => The set is no more needed
102 y_type = y_type.pop()
Solution
replace GradientBoostingRegressor with GradientBoostingClassifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier,GradientBoostingClassifier,AdaBoostClassifier,BaggingClassifier
GB = GradientBoostingClassifier()
GB.fit(x_train, y_train)
predGB = GB.predict(x_test)
print("accuracy_score:", accuracy_score(y_test, predGB))
print("confusion matrix:", confusion_matrix(y_test, predGB))
print("classification_report :", classification_report(y_test, predGB))
Explanation
The error you're encountering indicates that there is a mix of binary and continuous targets, and the accuracy_score function cannot handle such a mix. The issue is likely related to the nature of your target variable (y). It seems that your problem is a regression problem (predicting a continuous variable), but you are using classification metrics.
If you want to evaluate a regression model like GradientBoostingRegressor, you should use regression metrics instead of classification metrics. The common regression metrics include mean squared error (MSE), R-squared, and others.
Here's an example of how you can modify your code:
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
from sklearn.ensemble import GradientBoostingRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Assuming you have defined x and y
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, test_size=0.30, random_state=42)
GB = GradientBoostingRegressor()
GB.fit(x_train, y_train)
predGB = GB.predict(x_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, predGB)
r2 = r2_score(y_test, predGB)
print("Mean Squared Error:", mse)
print("R-squared:", r2)
ZeroDivisionError:
Explanation: Occurs when attempting to divide by zero.
Example:
result = 1 / 0 # Raises ZeroDivisionError
IndexError:
Explanation: Raised when trying to access an element of a list or sequence using an index that is out of bounds.
Example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
element = my_list[5] # Raises IndexError
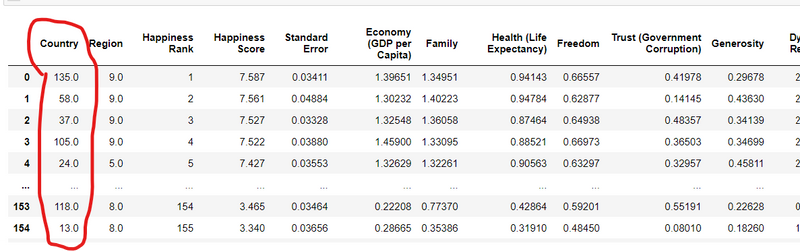
KeyError:
Explanation: Occurs when trying to access a dictionary key that does not exist.
Example:
my_dict = {"key1": "value1"}
value = my_dict["key2"] # Raises KeyError
my code is
my data set
df.set_index('Country', inplace=True)
df
i got error
KeyError: "None of ['Country'] are in the columns"
solution
from sklearn.preprocessing import OrdinalEncoder
OE=OrdinalEncoder()
for i in df.columns:
if df[i].dtypes=="object":
df[i]=OE.fit_transform(df[i].values.reshape(-1,1))
df
df.set_index('Country', inplace=True)
df
FileNotFoundError:
Explanation: Raised when trying to open a file that does not exist.
Example:
with open("nonexistent.txt", "r") as file:
content = file.read() # Raises FileNotFoundError
AttributeError:
Explanation: Occurs when trying to access an attribute or method that does not exist on an object.
Example:
class MyClass:
def __init__(self):
self.value = 42
obj = MyClass()
result = obj.nonexistent_method() # Raises AttributeError
Another Example
fixed_acid=(Q3.fixed_acidity+(1.5*IQR.fixed_acidity))
Errors:
AttributeError Traceback (most recent call last)
Cell In[70], line 1
----> 1 fixed_acid=(Q3.fixed_acidity+(1.5*IQR.fixed_acidity))
File ~\anaconda3\lib\site-packages\pandas\core\generic.py:5902, in NDFrame.__getattr__(self, name)
5895 if (
5896 name not in self._internal_names_set
5897 and name not in self._metadata
5898 and name not in self._accessors
5899 and self._info_axis._can_hold_identifiers_and_holds_name(name)
5900 ):
5901 return self[name]
-> 5902 return object.__getattribute__(self, name)
AttributeError: 'Series' object has no attribute 'fixed_acidity'
Solution
after running commands
print(f"\nThe column headers in the dataset: {df.columns}")
The column headers in the dataset: Index(['fixed acidity', 'volatile acidity', 'citric acid', 'residual sugar',
'chlorides', 'free sulfur dioxide', 'total sulfur dioxide', 'density',
'pH', 'sulphates', 'alcohol', 'quality'],
dtype='object')
fixed_acid=(Q3['fixed acidity']+(1.5*IQR['fixed acidity']))
fixed_acid
output
12.349999999999998
PermissionError:
Explanation: Raised when an operation that requires special permissions is denied.
Example:
with open("/root/sensitive.txt", "w") as file:
file.write("This requires special permissions") # Raises PermissionError
FileExistsError:
Explanation: Occurs when trying to create a f*ile or directory that already exists*.
Example:
import os
os.mkdir("my_directory")
os.mkdir("my_directory") # Raises FileExistsError
OSError:
Explanation: A general exception for I/O-related errors.
Example:
try:
file = open("/root/sensitive.txt", "r")
except OSError as e:
print(f"OSError: {e}")
EOFError:
Explanation: Raised when there is no input to read from a file or the user cancels the input operation.
Example:
try:
user_input = input("Enter something: ")
print(f"You entered: {user_input}")
except EOFError:
print("No input provided")
ArithmeticError:
Explanation: A base class for arithmetic errors.
Example:
try:
result = 1 / 0 # Raises ZeroDivisionError (subclass of ArithmeticError)
except ArithmeticError as e:
print(f"ArithmeticError: {e}")
FloatingPointError:
Explanation: Raised when a floating-point operation fails.
Example:
try:
result = 1.0 / 0.0 # Raises FloatingPointError
except FloatingPointError as e:
print(f"FloatingPointError: {e}")
ImportError:
Explanation: Occurs when an imported module is not found.
Example:
try:
import non_existent_module # Raises ImportError
except ImportError as e:
print(f"ImportError: {e}")
ModuleNotFoundError:
Explanation: Raised when an imported module is not found (Python 3.6+).
Example:
try:
import non_existent_module # Raises ModuleNotFoundError
except ModuleNotFoundError as e:
print(f"ModuleNotFoundError: {e}")
MemoryError:
Explanation: Occurs when there's not enough memory available.
Example:
try:
big_list = [0] * 1000000000 # Raises MemoryError
except MemoryError as e:
print(f"MemoryError: {e}")
RecursionError:
Explanation: Raised when the maximum recursion depth is exceeded.
Example:
def recursive_function(n):
return recursive_function(n - 1) # Raises RecursionError when n is too large
GeneratorExit:
Explanation: Raised when a generator's close() method is called.
Example:
def my_generator():
try:
yield 1
yield 2
except GeneratorExit:
print("Generator closed")
gen = my_generator()
next(gen)
gen.close() # Raises GeneratorExit
SystemExit:
Explanation: Raised when the sys.exit() function is called to exit the program.
Example:
import sys
try:
sys.exit(1)
except SystemExit as e:
print(f"SystemExit: {e}
")
KeyboardInterrupt:
Explanation: Raised when the user interrupts the program (e.g., by pressing Ctrl+C).
Example:
try:
while True:
pass # Infinite loop
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print("Program interrupted by the user")
StopIteration:
Explanation: Raised when there are no more items to be returned by an iterator.
Example:
my_iterator = iter([1, 2, 3])
Instance Error
my code is
def metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True):
if train:
y_pred=clf.predict(x_train)
print("==========train result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_tarin,y_pred)*100:.2f}%")
elif train==False :
pred=clf.predict(x_test)
print("==========test result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)*100:.2f}%")
print("\n \n Test classification report \n" ,classification_report(y_test,pred,digits=2))
clf=DecisionTreeClassifier()
metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True)
metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=False)
I got error
NotFittedError: This DecisionTreeClassifier instance is not fitted yet. Call 'fit' with appropriate arguments before using this estimator.
Solution
y_pred = clf.predict(x_train)
def metric_score(clf,x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test,train=True):
if train:
clf.fit(x_train, y_train) # Ensure that the classifier is fitted
y_pred = clf.predict(x_train)
print("==========train result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_train, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
# Other metrics or actions for training data
else:
y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
print("==========test result================")
print(f"accuracy_score: {accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) * 100:.2f}%")
==========train result================
accuracy_score: 100.00%
==========test result================
accuracy_score: 57.50%
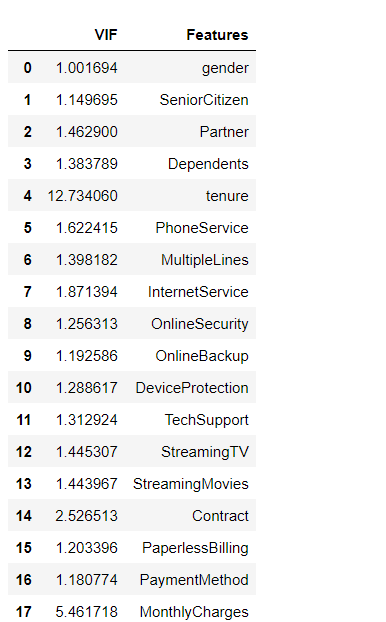
Missing Error
yesterday i run command and i got error
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import variance_inflation_factor
vif = pd.DataFrame()
vif['VIF'] = [variance_inflation_factor(x.values, i) for i in range(len(x.columns))]
vif['Features'] = x.columns
vif
MissingDataError: exog contains inf or nans
Solution
x = x.fillna(x.mean())
from statsmodels.stats.outliers_influence import variance_inflation_factor
vif = pd.DataFrame()
vif['VIF'] = [variance_inflation_factor(x.values, i) for i in range(len(x.columns))]
vif['Features'] = x.columns
vif
Output





Top comments (0)