Define Data center
How to create multiple data center
Advantage of multiple data center
Create Highly Available Websites using AWS Infrastructure
Question
How employs a global network of data centers
Each AZ consist of how many data centers
Each region consist of how many AZ*
How AWS automatically replicates data while u store data in amazon s3
How aws gives solution of high availibilty and solve the problem of fault tolerance
how to give solution when web server is hosted in a single AZ and that zone is fails
A data center is a centralized facility or location used to house, manage, and store computer systems, servers, networking equipment, and other associated components for the purpose of collecting, processing, storing, and disseminating data and applications. Data centers play a crucial role in supporting various IT and business functions by providing the necessary infrastructure and resources for computing and data processing.
data center can refer to a network of computing and storage resources that are linked together for the purpose of processing, storing, and managing data. This network may span multiple physical locations.
How to create multiple data center
Amazon Web Services (AWS) employs a global network of data centers, commonly referred to as Availability Zones (AZs), to provide high availability, fault tolerance, and scalability for its services. Each Availability Zone is essentially a separate data center with its own power, cooling, and networking infrastructure. These AZs are interconnected to provide redundancy and ensure that services can continue to operate in the event of failures or disruptions in one location.
Here's how AWS provides multiple data centers through Availability Zones, along with some examples:
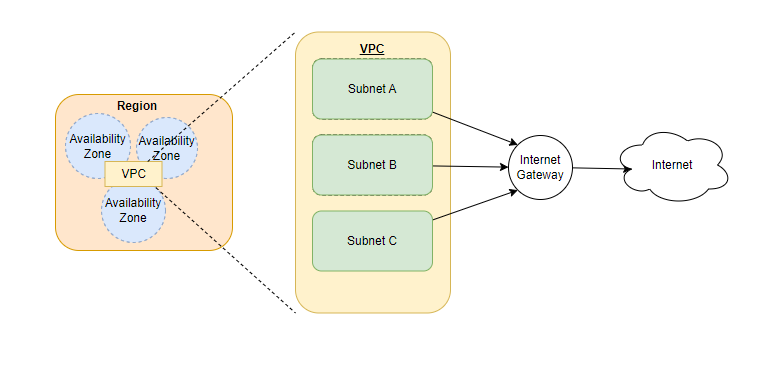
Availability Zones (AZs):
AWS organizes its infrastructure into geographically distinct Availability Zones.
Each AZ typically consists of one or more data centers.
AZs within a region are connected through low-latency links to facilitate synchronous data replication.
Regions:
AWS divides the world into geographic regions, such as us-east-1 (North Virginia), eu-west-1 (Ireland), ap-southeast-2 (Sydney), etc.
Each region consists of multiple Availability Zones.
Regions are designed to be isolated from each other to provide geographic redundancy.
Example: Amazon S3 (Simple Storage Service):
When you store data in Amazon S3, AWS automatically replicates your data across multiple devices within the same AZ.
To enhance durability, S3 also replicates data across multiple AZs within the same region.
For example, if you store an object in the us-east-1 region, AWS may replicate the data across multiple data centers in different Availability Zones within that region.
Example: Amazon EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud):
When you launch EC2 instances, you can choose the specific Availability Zone for each instance or let AWS distribute them across multiple AZs for high availability.
This allows you to design applications that can withstand failures in one or more Availability Zones.
Example: Amazon RDS (Relational Database Service):
When you deploy a relational database using Amazon RDS, you can choose to create a Multi-AZ deployment.
In a Multi-AZ deployment, a standby instance is created in a different AZ, providing failover support for high availability.
Global Services:
Some AWS services operate globally, such as Amazon CloudFront (Content Delivery Network) and Route 53 (Domain Name System).
These services leverage edge locations and points of presence worldwide to deliver low-latency and high-performance content delivery and DNS resolution.
By leveraging multiple Availability Zones and regions, AWS ensures that its infrastructure is resilient to failures, provides low-latency access to services, and allows users to build highly available and fault-tolerant applications. This distributed architecture is a key component of AWS's approach to reliability and scalability.
Advantage of multiple data center
Having multiple data centers, or Availability Zones (AZs), in AWS provides several advantages that contribute to the overall reliability, availability, and fault tolerance of your applications and data. Here are some key advantages:
High Availability:
Multiple data centers allow you to design applications that continue to operate even if one data center experiences issues or failures.
By distributing resources across different AZs within a region, you ensure that your applications remain available even in the face of hardware failures, power outages, or other disruptions.
Fault Tolerance:
AWS AZs are designed to be isolated from each other in terms of power, cooling, and networking.
If one AZ becomes unavailable due to unforeseen circumstances, applications can seamlessly failover to resources in another AZ, reducing the impact of failures on your services.
Disaster Recovery:
Multiple AZs also enable effective disaster recovery strategies. You can replicate your data and applications across different AZs or regions, allowing you to recover quickly in case of a regional outage or disaster.
Increased Performance:
Distributing resources across multiple AZs can improve the performance of your applications by reducing latency. Users can connect to the nearest AZ, leading to faster response times.
Data Durability and Redundancy:
AWS services often replicate data across multiple AZs automatically to enhance durability and redundancy. For example, Amazon S3 stores copies of your objects across multiple AZs within a region.
Scalability:
Multiple data centers support the scalability requirements of your applications. You can easily scale horizontally by adding more resources in different AZs to handle increased workloads.
Compliance and Data Residency:
Having multiple AZs in different geographic locations allows you to meet data residency and compliance requirements. You can store data in specific regions or countries to comply with regulatory guidelines.
Cost Optimization:
AWS provides pricing models that encourage the use of multiple AZs. For example, data transfer between AZs within the same region is often free or comes at a lower cost compared to data transfer across regions.
Flexibility in Resource Placement:
AWS users have the flexibility to choose the specific AZ for their resources. This allows you to optimize resource placement based on factors such as latency, cost, and regulatory requirements.
Global Reach:
For global services like Amazon CloudFront and Amazon Route 53, the use of edge locations and points of presence worldwide ensures low-latency content delivery and efficient DNS resolution for users around the globe.
In summary, the advantages of having multiple data centers in AWS revolve around improving the resilience, availability, and performance of your applications while providing flexibility, scalability, and compliance with various regulatory requirements. This distributed architecture is a fundamental aspect of AWS's approach to providing a reliable and scalable cloud computing platform.
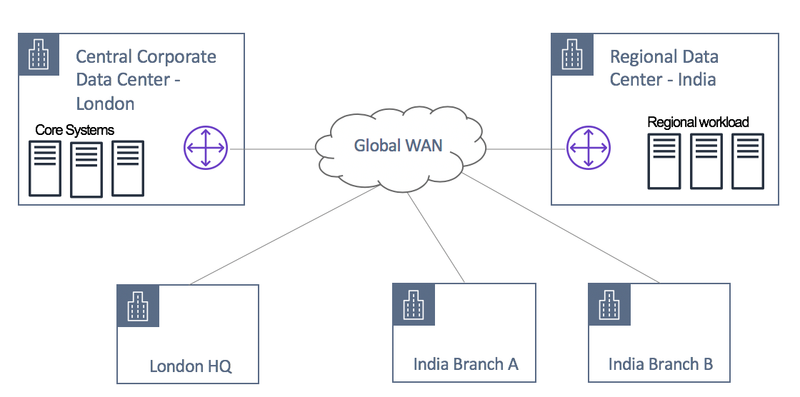
Create Highly Available Websites using AWS Infrastructure
In this age, the transition to e-commerce is happening at a very fast pace. These e-commerce companies, both small and big would like to have to their website up and running 24 hours and 365 days a year not to lose customers and business. For instance, think about amazon.com going down for a couple of hours.
This is where Cloud Computing comes into the picture. Cloud provides agility to build Highly Available (HA) and fault-tolerant applications which was not possible with the on-premise data centers. The Cloud vendors have Data Centers across multiple geographical locations with redundancy to help us build an HA website. The same applies to any of the business-critical applications that need to run all the time. Currently, AWS Global Infrastructure spans 21 geographical Regions with 66 Availability Zones (AZ) with more Regions and AZs to come in the near future. In this article, we will focus on building HA applications in the Cloud.
AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS Global Infrastructure has:
- Regions and Availability Zones (AZ)
- Data Centers in AZs
- Edge Locations Let’s discuss each of these in detail.
Regions & Availability Zones
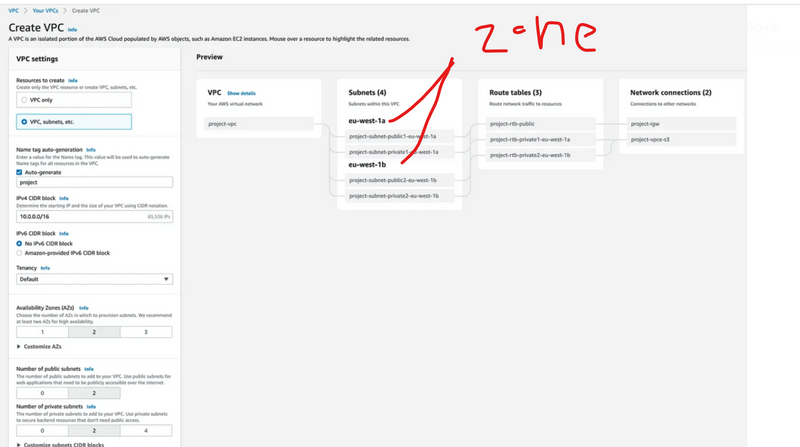
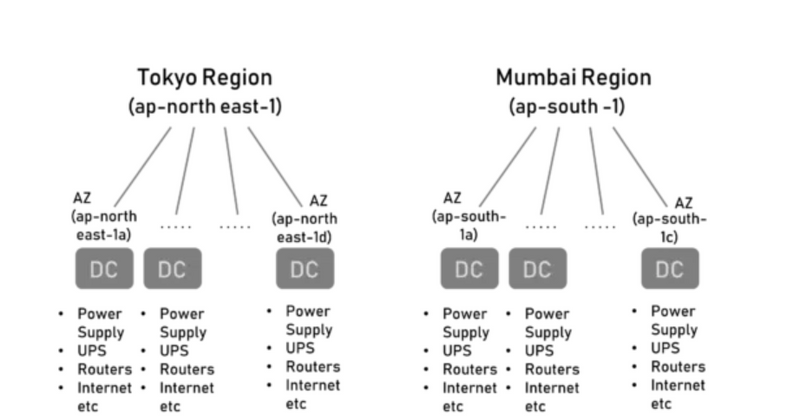
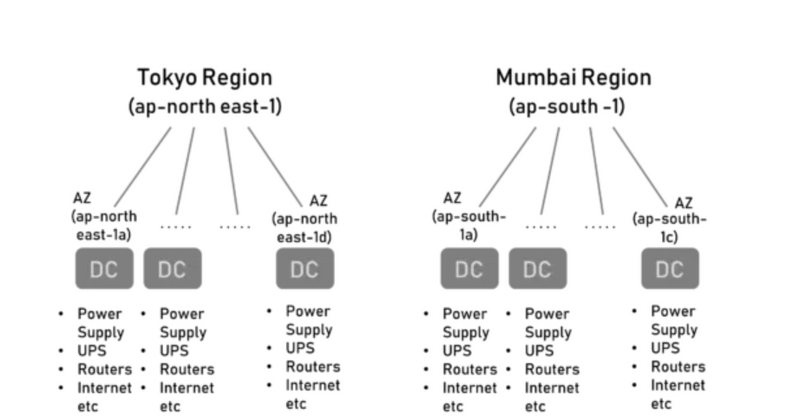
Each Region is a geographical area with more than one isolated location called Availability Zones (AZ). Each AZ can be a combination of one or more Data Centers. For Example, North Virginia is a Region with a code of us-east-1 and has 6 AZ. You can learn more about regions in AWS documentation.
As shown in the above diagram, there are multiple AWS Regions. And each Region has a minimum of two AZs. Each AZ has multiple Data Centers.
Note: Some of the resources in AWS are global, while some are region-specific. When we create an IAM User it is Global and when we create an EC2 Instance it is regional. While creating an EC2 Instance, we got an option to pick the region and which AZ. It is not the same with the IAM User as it is global.
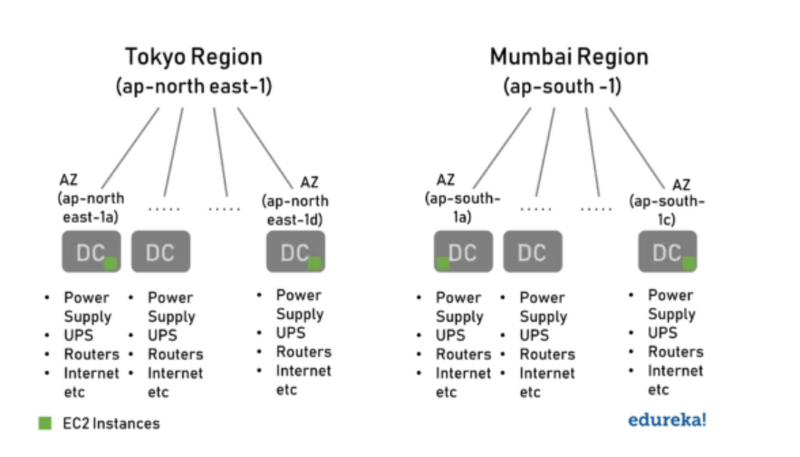
Data Centers in Availability Zones
Amazon is very secretive of the DC locations but that is not the case with AZs.
For Example, the Mumbai AZ ap-south-1a might be in the east of Mumbai and ap-south-1c in the west. This way if there is any natural catastrophe like flood or fire around one of the AZs, it doesn’t affect the other AZs. Also, each of the Data Center (DC) has its own redundancy of Power Supply, UPS, Routers, Internet Connectivity, etc to avoid any Single-Point-Of-Failure. There is no common infrastructure between two DCs and the DCs are connected by high-speed internet connectivity for low latency.
While creating a resource, AWS provides us an option to pick the Region and the AZs, but not the DC within it. The following factors are used for picking an AWS Region.
- Pricing (North Virginia Region is the oldest and the cheapest Region)
- Security and compliance requirement
- User/customer location
- Service availability
- Latency Note: For the sake of learning AWS, North Virginia is best as it is one the cheapest AWS Region and usually is the first one to support any new AWS feature for us to try it out.
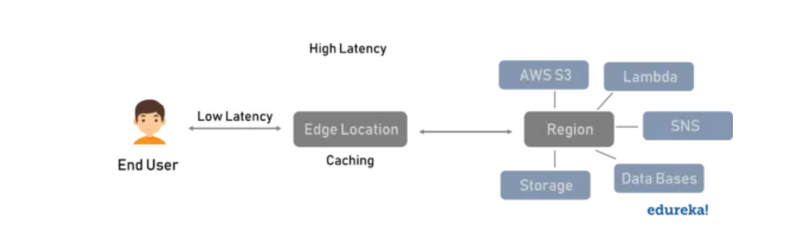
Edge Locations
In AWS Global Infrastructure, the Edge Locations used for caching the static and streaming data. Currently, there is a global network of 187 Points of Presence (176 Edge Locations and 11 Regional Edge Caches) in 69 cities across 30 countries. When compared to the AZs, the number of edge locations is almost triple and close to the end-user. This makes the Edge Locations a ripe candidate for caching data, while the regions are for hosting web servers, databases and so on.
These Edge Locations provide lower latency when compared to the Regions. When a request is made by the user, the Edge Location checks if the data is there locally and if not then gets the data from the appropriate Region, stores it locally and then passes it on to the user.
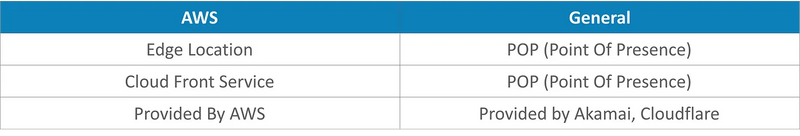
Edge Locations is an AWS term provided by the AWS CloudFront Service. An AWS Edge Location is called PoP (Points of Presence) in general term. A similar service is provided by Content Distribution Network (CDN) providers like Akamai, Cloudflare, etc. These CDN providers cache the data like streaming video during a live match to provide a better experience to the end-user. Below is the table comparing the AWS and the general terminology.
Creating a Highly Available Application using the AWS Global Infrastructure
AWS Global Infrastructure provides a set of Regions, AZs and Edge Locations to create a Highly Available and Fault Tolerant application.
Example
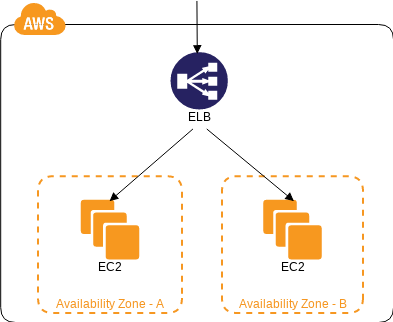
If a web server is hosted in a single AZ, any problem with that AZ will make the website unavailable. To get around this the webserver can be deployed in multiple AZs within the same region as shown below. Similarly, any problem with a region which will also make the website unavailable. To make the website even more available, we can have the webserver across multiple regions, this way the availability of the website is not dependent on the availability of a single region.
HA website and applications are created by using redundancy, but the problem with redundancy is that it comes at a cost. We need to run the same website at multiple locations. Also, the same web server can be deployed in some other Cloud like GCP or Azure. Here we are running the same web server in different Clouds and so the configuration is called Multi-Cloud Configuration. Google Anthos helps in building hybrid and Multi-Cloud applications using Kubernetes.
When we have the webserver across multiple locations, how does the traffic gets distribute among them? We can’t simply keep them sitting idle. This is where the AWS Elastic Load Balancers come into play. The AWS ELB takes the request from the end-user and distributes the same across multiple web servers.


Top comments (0)