Rust replaces classes with struct, impl, and trait, giving object-oriented behavior with strong compile-time safety and zero runtime overhead.
How Rust Replaces Classes with struct, impl, and trait
How to create objects in Rust and java using program example
How to reuse classes function in java or structs function in rust
Notification system in java and rust
How Rust Replaces Classes with struct, impl, and trait
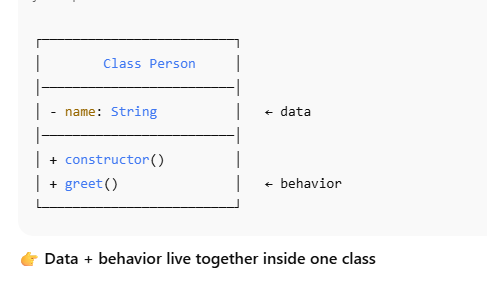
Rust does not support traditional classes or inheritance like Java.
Instead, Rust achieves object-oriented design by separating responsibilities into three clear parts:
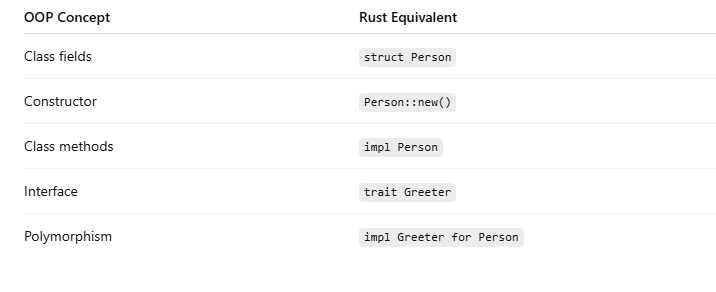
struct→ defines data (state)
impl → defines behavior (methods & constructors)
trait → defines shared behavior (reusability & polymorphism)
This design avoids the problems of deep inheritance while maintaining code reuse, extensibility, and safety.
How to create objects in Rust and java using program example
// Trait = interface / shared behavior
trait Greeter {
fn greet(&self);
}
// Struct = data (like class fields)
struct Person {
name: String,
}
// impl = methods (class behavior)
impl Person {
fn new(name: &str) -> Person {
Person {
name: name.to_string(),
}
}
}
// Implement trait for struct
impl Greeter for Person {
fn greet(&self) {
println!("Hello, my name is {}", self.name);
}
}
fn main() {
// Object creation
let p = Person::new("Ashwani");
// Method call
p.greet();
}
Output
Hello, my name is Ashwani
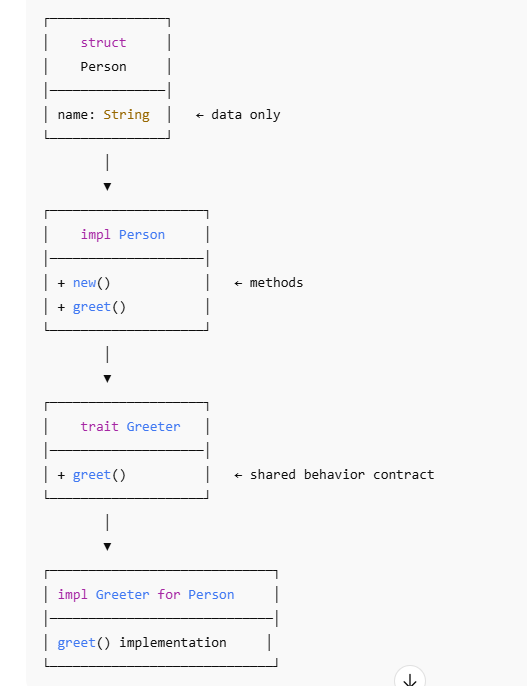
How This Replaces a Class
Conceptual Diagram: Class vs Rust Design
Rust Equivalent (struct + impl + trait)
Runtime Flow (Object Creation & Method Call)
Java (Class + Interface)
// Interface (shared behavior)
interface Greeter {
void greet();
}
// Class (data + behavior)
class Person implements Greeter {
private String name;
// Constructor
Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// Method
public void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("Ashwani");
p.greet();
}
}
Output
Hello, my name is Ashwan
How to reuse classes function in java or structs function in rust
Goal
OrderService will reuse TaxCalculator.calculateTax() by creating its object.
// File: Main.java
class TaxCalculator {
public double calculateTax(double amount) {
return amount * 0.18; // 18% tax
}
}
class OrderService {
private TaxCalculator taxCalculator; // reuse by object
public OrderService() {
this.taxCalculator = new TaxCalculator();
}
public void printBill(double amount) {
double tax = taxCalculator.calculateTax(amount);
double total = amount + tax;
System.out.println("Amount: " + amount);
System.out.println("Tax: " + tax);
System.out.println("Total: " + total);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OrderService service = new OrderService();
service.printBill(1000);
}
}
✅ Output
Amount: 1000.0
Tax: 180.0
Total: 1180.0
✅
Rust: 2 Structs (Reuse by Creating Object)
Goal
OrderService will reuse TaxCalculator::calculate_tax() by creating its object.
// File: main.rs
struct TaxCalculator;
impl TaxCalculator {
fn calculate_tax(&self, amount: f64) -> f64 {
amount * 0.18 // 18% tax
}
}
struct OrderService {
tax_calculator: TaxCalculator, // reuse by object
}
impl OrderService {
fn new() -> Self {
Self { tax_calculator: TaxCalculator }
}
fn print_bill(&self, amount: f64) {
let tax = self.tax_calculator.calculate_tax(amount);
let total = amount + tax;
println!("Amount: {}", amount);
println!("Tax: {}", tax);
println!("Total: {}", total);
}
}
fn main() {
let service = OrderService::new();
service.print_bill(1000.0);
}
✅ Output
Amount: 1000
Tax: 180
Total: 1180
Another Example
Notification system in java and rust
Notification system in rust
Web applications
Microservices
SaaS platforms
Where:
User triggers notification
Notification can be Email / SMS / Push
System doesn’t care how it’s sent
// 1) TRAIT: Shared behavior (like interface)
trait Notifier {
fn send(&self, to: &str, message: &str);
}
// 2) STRUCT: Data for Email "class"
struct EmailNotifier {
from: String,
}
impl EmailNotifier {
// Associated function (constructor style)
fn new(from: &str) -> Self {
Self { from: from.to_string() }
}
}
// Implement trait behavior for EmailNotifier
impl Notifier for EmailNotifier {
fn send(&self, to: &str, message: &str) {
println!("[EMAIL] From: {} -> To: {} | {}", self.from, to, message);
}
}
// 3) STRUCT: Data for SMS "class"
struct SmsNotifier {
sender_id: String,
}
impl SmsNotifier {
fn new(sender_id: &str) -> Self {
Self { sender_id: sender_id.to_string() }
}
}
impl Notifier for SmsNotifier {
fn send(&self, to: &str, message: &str) {
println!("[SMS] SenderID: {} -> To: {} | {}", self.sender_id, to, message);
}
}
// 4) STRUCT: User (like a model class)
struct User {
name: String,
phone: String,
email: String,
}
impl User {
// constructor
fn new(name: &str, phone: &str, email: &str) -> Self {
Self {
name: name.to_string(),
phone: phone.to_string(),
email: email.to_string(),
}
}
// method using &self
fn profile(&self) {
println!("User => name={}, phone={}, email={}", self.name, self.phone, self.email);
}
}
// 5) Function that accepts "any class" implementing Notifier
fn notify_all(user: &User, channels: Vec<Box<dyn Notifier>>) {
for ch in channels {
ch.send(&user.email, &format!("Hello {}, welcome!", user.name));
}
}
fn main() {
// object creation using associated function (constructor style)
let user = User::new("Ashwani", "+91-99999-11111", "ashwani@example.com");
user.profile();
// Polymorphism: different "class objects" in one list
let channels: Vec<Box<dyn Notifier>> = vec![
Box::new(EmailNotifier::new("noreply@myapp.com")),
Box::new(SmsNotifier::new("MOTOSHARE")),
];
notify_all(&user, channels);
}
✅ Output
User => name=Ashwani, phone=+91-99999-11111, email=ashwani@example.com
[EMAIL] From: noreply@myapp.com -> To: ashwani@example.com | Hello Ashwani, welcome!
[SMS] SenderID: MOTOSHARE -> To: ashwani@example.com | Hello Ashwani, welcome!
Notification system in rust
This models a notification system, commonly used in
Java (Class + Interface)
// Interface (shared behavior)
interface Greeter {
void greet();
}
// Class (data + behavior)
class Person implements Greeter {
private String name;
// Constructor
Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// Method
public void greet() {
System.out.println("Hello, my name is " + name);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p = new Person("Ashwani");
p.greet();
}
}
Output
Hello, my name is Ashwani
✅ Rust (struct + impl + trait)
// Trait = interface / shared behavior
trait Greeter {
fn greet(&self);
}
// Struct = data only
struct Person {
name: String,
}
// impl = constructor + methods
impl Person {
fn new(name: &str) -> Person {
Person { name: name.to_string() }
}
}
// Trait implementation = "implements"
impl Greeter for Person {
fn greet(&self) {
println!("Hello, my name is {}", self.name);
}
}
fn main() {
let p = Person::new("Ashwani");
p.greet();
}
Output
Hello, my name is Ashwani
rust-interview-questions-on-functions-objects-class-concept
how-to-create-objects-and-call-functions-in-rust



Top comments (0)