Rust Interview Questions (Functions, Objects, Class Concept)
Why does Rust not have classes?
How does Rust achieve object-oriented behavior without classes?
What is the role of struct in Rust?
What is the purpose of an impl block?
Difference between an associated function and a method in Rust?
How do you create an object in Rust?
What does &self mean in a method?
What does &mut self mean?
What happens when a method takes self instead of &self?
How is Struct::new() different from struct {} initialization?
Can Rust methods modify object state? How?
How does Rust prevent data races in object methods?
What is method call desugaring in Rust?
How does Rust replace inheritance?
What are traits and how do they relate to classes?
Can one struct have multiple impl blocks?
How do you call a trait method using an object?
What is ownership in relation to object methods?
Difference between Rust structs and Java classes?
Why is Rust’s approach safer than traditional OOP?
20 MCQs (With Answers)
Rust does not support classes because:
A) It is procedural
B) It avoids OOP
C) It separates data and behavior
D) It only supports C-style code
✅ Answer: C
- Which keyword defines data in Rust?
A) class
B) impl
C) struct
D) object
✅ Answer: C
- Which block defines methods for a struct?
A) trait
B) fn
C) mod
D) impl
✅ Answer: D
- What is Struct::new() called?
A) Method
B) Constructor
C) Associated function
D) Trait
✅ Answer: C
- Which method signature allows modification of object?
A) fn f(self)
B) fn f(&self)
C) fn f(&mut self)
D) fn f()
✅ Answer: C
- What does self represent in a method?
A) Copy of object
B) Reference always
C) The calling object
D) Global variable
✅ Answer: C
- Calling obj.method() internally becomes:
A) method(obj)
B) obj::method()
C) Struct::method(&obj)
D) call(obj.method)
✅ Answer: C
- Which Rust feature replaces inheritance?
A) Macros
B) Traits
C) Modules
D) Lifetimes
✅ Answer: B
- Can Rust have constructors?
A) No
B) Yes, via new()
C) Only via macros
D) Only default
✅ Answer: B
- Which is valid object creation?
A) new User()
B) User()
C) User {}
D) class User
✅ Answer: C
- Trait methods are called using:
A) :: only
B) . on object
C) ->
D) call()
✅ Answer: B
- What happens when a method takes self?
A) Borrows object
B) Copies object
C) Consumes object
D) Shares object
✅ Answer: C
13.** Which ensures memory safety in object methods**?
A) GC
B) Ownership system
C) JVM
D) Pointers
✅ Answer: B
- Can a struct have multiple impl blocks?
A) No
B) Yes
C) Only one
D) Only with trait
✅ Answer: B
- Which is NOT part of Rust OOP model?
A) Struct
B) impl
C) Trait
D) Class
✅ Answer: D
- Which allows code reuse without inheritance?
A) Macros
B) Traits
C) Enums
D) Crates
✅ Answer: B
- Rust encourages which design principle?
A) Deep inheritance
B) Global state
C) Composition over inheritance
D) Runtime polymorphism only
✅ Answer: C
- What does &self prevent?
A) Mutation
B) Ownership transfer
C) Copy
D) Drop
✅ Answer: A
- Java class ≈ Rust ?
A) struct only
B) impl only
C) struct + impl
D) trait only
✅ Answer: C
- Main benefit of Rust’s no-class design?
A) More syntax
B) Runtime speed only
C) Compile-time safety + clarity
D) Smaller code
✅ Answer: C
Why does Rust not have classes?
Rust avoids classes to prevent unsafe inheritance, hidden state changes, and runtime errors. Instead, it promotes explicit behavior, composition, and compile-time safety.
2️⃣ How does Rust achieve object-oriented behavior without classes?
Rust uses:
struct → data (state)
impl → behavior (methods)
trait → shared behavior (polymorphism)
Together, these replace traditional classes.
3️⃣ What is the role of struct in Rust?
A struct defines a custom data type that groups related data fields together, similar to instance variables in a class.
4️⃣ What is the purpose of an impl block?
An impl block defines functions and methods associated with a struct, including constructors and business logic.
5️⃣ Difference between an associated function and a method in Rust?
Associated function → called using Struct::function(), does not need an object
Method → called using object.method(), operates on an instance using self
6️⃣ How do you create an object in Rust?
Objects are created by:
Direct struct initialization: User { name: "A".to_string() }
Associated function (constructor style): User::new("A")
7️⃣ What does &self mean in a method?
&self means the method borrows the object immutably, allowing read-only access without modifying or taking ownership.
8️⃣ What does &mut self mean?
&mut self means the method borrows the object mutably, allowing modification of its state.
9️⃣ What happens when a method takes self instead of &self?
The method takes ownership of the object, consuming it. After the call, the object cannot be used again.
🔟 How is Struct::new() different from struct {} initialization?
Struct::new() → controlled, reusable constructor logic
struct {} → direct field assignment without validation
new() is preferred in professional code.
1️⃣1️⃣ Can Rust methods modify object state? How?
Yes, but only if:
The object is declared mut
The method takes &mut self
This ensures safe and explicit mutation.
1️⃣2️⃣ How does Rust prevent data races in object methods?
Rust prevents data races using:
Ownership rules
Borrowing rules (& vs &mut)
Compile-time checks
It disallows multiple mutable references at the same time.
1️⃣3️⃣ What is method call desugaring in Rust?
obj.method() is internally converted to:
Struct::method(&obj)
This is called method call desugaring.
1️⃣4️⃣ How does Rust replace inheritance?
Rust replaces inheritance with:
Traits for shared behavior
Composition instead of parent-child class hierarchies
1️⃣5️⃣ What are traits and how do they relate to classes?
Traits define shared behavior contracts.
They are similar to interfaces, not classes.
Traits enable polymorphism without inheritance.
1️⃣6️⃣ Can one struct have multiple impl blocks?
Yes. A struct can have multiple impl blocks for better code organization.
1️⃣7️⃣ How do you call a trait method using an object?
Once a trait is implemented for a struct, its methods are called like normal methods:
object.trait_method()
1️⃣8️⃣ What is ownership in relation to object methods?
Ownership determines:
Who controls the object
Whether it can be borrowed, mutated, or consumed
Methods respect ownership via self, &self, or &mut self.
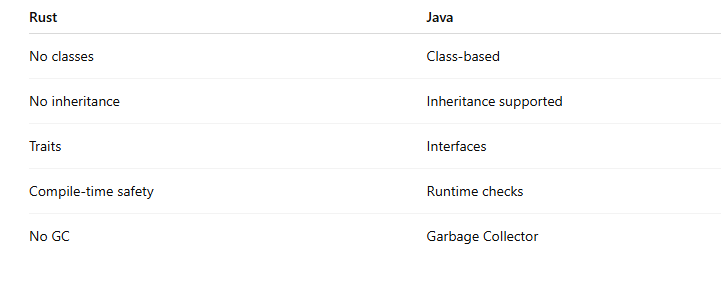
1️⃣9️⃣ Difference between Rust structs and Java classes?
Why is Rust’s approach safer than traditional OOP?
Because Rust:
Prevents null pointers
Prevents data races
Prevents invalid memory access
Enforces safety at compile time
This leads to fewer runtime bugs and more predictable code.
⭐
how-to-create-objects-and-call-functions-in-rust
how-rust-replaces-classes-with-struct-impl-and-trait

Top comments (0)