How to create batch
create batch and passed to neural network
How to create batch
import tensorflow as tf
# Simulate a dataset of integers from 0 to 99
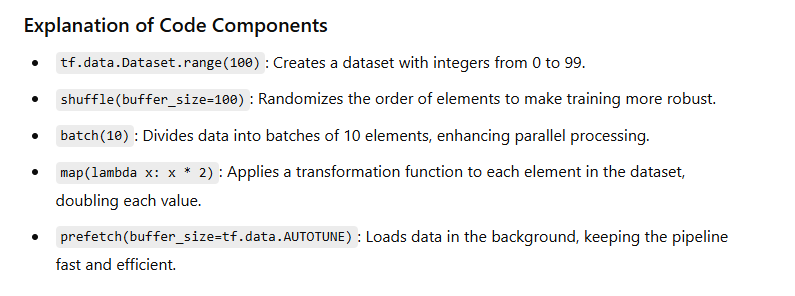
data = tf.data.Dataset.range(100)
# Shuffle, batch, and map transformations
pipeline = (
data
.shuffle(buffer_size=100) # Randomize the data
.batch(10) # Batch in groups of 10
.map(lambda x: x * 2) # Multiply each element by 2
.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE) # Prefetch for efficiency
)
# Print the output from each batch
for batch in pipeline:
print(batch.numpy())
output
[60 36 82 58 76 56 26 74 62 18]
[94 84 22 10 80 66 48 50 2 88]
...
Another Example
import tensorflow as tf
# Example dataset: List of sentences and corresponding labels
sentences = [
"TensorFlow is great for machine learning",
"Natural language processing is fun",
"I love creating deep learning models",
"Transformers have revolutionized NLP",
"TensorFlow Hub provides pre-trained models"
]
labels = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1] # Example binary labels
# Create a tf.data Dataset from sentences and labels
data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((sentences, labels))
# Text vectorization layer to tokenize and convert text to sequences
vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_mode='int', max_tokens=1000)
vectorizer.adapt(sentences) # Fit the vectorizer on the data
# Pipeline: Shuffle, batch, tokenize, and prefetch
pipeline = (
data
.shuffle(buffer_size=5) # Shuffle the sentences
.batch(2) # Batch data in groups of 2
.map(lambda x, y: (vectorizer(x), y)) # Tokenize sentences
.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE) # Prefetch for efficiency
)
# Print the output from each batch
for batch, labels in pipeline:
print("Batch (tokenized):", batch.numpy())
print("Labels:", labels.numpy())
create batch and passed to neural network
We passed pipeline batch during training
model.fit(pipeline, epochs=5)
Text Classification Example
For text classification, we'll use the pipeline and pass batches to a simple neural network. Here, we’ll build a binary classification model using an embedding layer and a few dense layers.
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Example sentences and labels
sentences = [
"TensorFlow is great for machine learning",
"Natural language processing is fun",
"I love creating deep learning models",
"Transformers have revolutionized NLP",
"TensorFlow Hub provides pre-trained models"
]
labels = [1, 0, 1, 0, 1] # Example binary labels
# Create tf.data Dataset and TextVectorization layer
data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((sentences, labels))
vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_mode='int', max_tokens=1000)
vectorizer.adapt(sentences)
# Define the pipeline
pipeline = (
data
.shuffle(buffer_size=5)
.batch(2)
.map(lambda x, y: (vectorizer(x), y))
.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
)
# Define a simple text classification model
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Embedding(input_dim=1000, output_dim=64),
layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D(),
layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') # Sigmoid for binary classification
])
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# Train the model
model.fit(pipeline, epochs=5)
# Evaluate the model (optional)
loss, accuracy = model.evaluate(pipeline)
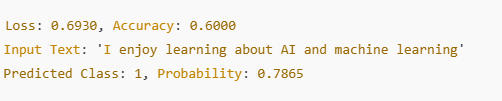
print(f"Loss: {loss}, Accuracy: {accuracy}")
# Function to classify new input text
def classify_text(input_text):
# Process the input text
vectorized_text = vectorizer(tf.constant([input_text])) # Vectorize the input
prediction = model.predict(vectorized_text) # Make prediction
predicted_class = 1 if prediction[0][0] > 0.5 else 0 # Convert probability to class label
return predicted_class, prediction[0][0] # Return class and probability
# Example usage of the classify function
new_sentence = "I enjoy learning about AI and machine learning"
predicted_class, probability = classify_text(new_sentence)
print(f"Input Text: '{new_sentence}'")
print(f"Predicted Class: {predicted_class}, Probability: {probability:.4f}")
Text Summary
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
# Example sentences and corresponding summaries
sentences = [
"TensorFlow is great for machine learning",
"Natural language processing is fun",
"I love creating deep learning models",
"Transformers have revolutionized NLP",
"TensorFlow Hub provides pre-trained models"
]
summaries = [
"ML with TensorFlow",
"Fun with NLP",
"Deep learning models",
"NLP with transformers",
"Pre-trained models on TF Hub"
]
# Create tf.data Dataset and TextVectorization layers
data = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((sentences, summaries))
input_vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_mode='int', max_tokens=1000)
output_vectorizer = tf.keras.layers.TextVectorization(output_mode='int', max_tokens=1000)
input_vectorizer.adapt(sentences)
output_vectorizer.adapt(summaries)
# Define the pipeline
pipeline = (
data
.shuffle(buffer_size=5)
.batch(2)
.map(lambda x, y: (input_vectorizer(x), output_vectorizer(y)))
.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.AUTOTUNE)
)
# Define the sequence-to-sequence model
class Seq2SeqModel(tf.keras.Model):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, units):
super().__init__()
self.encoder_embedding = layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.encoder_gru = layers.GRU(units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
self.decoder_embedding = layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.decoder_gru = layers.GRU(units, return_sequences=True, return_state=True)
self.dense = layers.Dense(vocab_size)
def call(self, inputs, training=False):
encoder_input, decoder_input = inputs
encoder_embedded = self.encoder_embedding(encoder_input)
encoder_output, encoder_state = self.encoder_gru(encoder_embedded)
decoder_embedded = self.decoder_embedding(decoder_input)
decoder_output, _ = self.decoder_gru(decoder_embedded, initial_state=encoder_state)
return self.dense(decoder_output)
vocab_size = 1000
embedding_dim = 64
units = 128
# Instantiate the model
model = Seq2SeqModel(vocab_size, embedding_dim, units)
# Compile the model
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy')
# Prepare the inputs and targets for training (shifted decoder inputs)
def prepare_pipeline(data):
for enc_in, dec_out in data:
dec_in = dec_out[:, :-1] # Decoder input (except last token)
dec_out_shifted = dec_out[:, 1:] # Decoder target (except first token)
yield (enc_in, dec_in), dec_out_shifted
train_data = tf.data.Dataset.from_generator(lambda: prepare_pipeline(pipeline), output_signature=(
(tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None, None), dtype=tf.int32), tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None, None), dtype=tf.int32)),
tf.TensorSpec(shape=(None, None), dtype=tf.int32)
)).batch(2)
# Train the model
model.fit(train_data, epochs=5)
# Function to generate summary for a new sentence
def generate_summary(input_sentence, max_length=10):
# Vectorize input sentence
input_seq = input_vectorizer(tf.constant([input_sentence]))
# Start the decoding process
start_token = output_vectorizer("start")[0] # Assume "start" is the start token
generated_tokens = [start_token]
for _ in range(max_length):
decoder_input = tf.constant([generated_tokens]) # Prepare decoder input
predictions = model.predict((input_seq, decoder_input)) # Get predictions
predicted_token = tf.argmax(predictions[:, -1, :], axis=-1).numpy()[0] # Get the last prediction
if predicted_token == output_vectorizer.vocabulary_size(): # Assuming last index is for end token
break
generated_tokens.append(predicted_token) # Append predicted token
# Convert token indices to words
summary = output_vectorizer.get_vocabulary()[0:output_vectorizer.vocabulary_size()] # Vocabulary
return ' '.join([summary[token] for token in generated_tokens if token < output_vectorizer.vocabulary_size()])
# Example usage of the generate_summary function
new_sentence = "Exploring machine learning with TensorFlow"
predicted_summary = generate_summary(new_sentence)
print(f"Input Sentence: '{new_sentence}'")
print(f"Generated Summary: '{predicted_summary}'")




Top comments (0)