Introduction
When building custom authentication flows in Keycloak (like phone login, WhatsApp/SMS login, partner/renter logic), we often need to:
Set dynamic variables
Store data based on conditions
Reuse stored data in the next step
Avoid trusting client-side input
This blog explains how to store dynamic variables conditionally using AuthenticationSession in Keycloak (Keycloak 26 compatible).
🎯 Problem Statement
Let’s say:
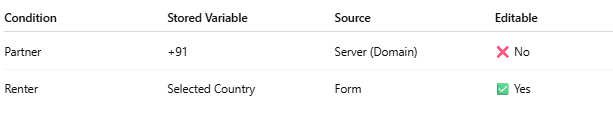
If user type = partner, country must be fixed (e.g., +91 India)
If user type = renter, country comes from dropdown
Country must be stored securely and reused in action()
We cannot trust:
formData.getFirst("country");
Because users can manipulate browser values.
So how do we store dynamic variables securely based on condition?
🧠 Theory – How Keycloak Flow Works
Every custom authenticator has two important methods:
1️⃣ authenticate()
Runs first
Prepares UI
Sets session data
2️⃣ action()
Runs after form submission
Reads data
Validates and processes
To store dynamic data across steps, Keycloak provides:
AuthenticationSessionModel
You can store values using:
session.setAuthNote("KEY", "VALUE");
And retrieve later using:
session.getAuthNote("KEY");
This is the correct enterprise approach.
🔐 Why Use AuthNotes?
Because:
It is server-side
Cannot be modified from browser
Exists only during authentication flow
Automatically cleared after login completes
Perfect for temporary dynamic variables.
🛠
Step-by-Step Coding Example
✅ STEP 1 — Define Dynamic Keys
At top of your class:
private static final String NOTE_USER_TYPE = "USER_TYPE";
private static final String NOTE_COUNTRY_DIAL = "PHONE_COUNTRY_DIAL";
private static final String NOTE_COUNTRY_NAME = "PHONE_COUNTRY_NAME";
✅ STEP 2 — Set Dynamic Variables Conditionally (authenticate())
@Override
public void authenticate(AuthenticationFlowContext context) {
AuthenticationSessionModel session = context.getAuthenticationSession();
String userType = session.getAuthNote(NOTE_USER_TYPE);
CountryFetcher fetcher = new CountryFetcher();
if ("partner".equalsIgnoreCase(userType)) {
List<Map<String,String>> countries =
fetcher.buildSingleCountryFromDomain(context);
if (countries != null && !countries.isEmpty()) {
String dial = countries.get(0).get("dial_code"); // +91
String name = countries.get(0).get("name"); // India
// 🔥 Store dynamically
session.setAuthNote(NOTE_COUNTRY_DIAL, dial);
session.setAuthNote(NOTE_COUNTRY_NAME, name);
}
} else {
// renter logic (do not set fixed country)
session.removeAuthNote(NOTE_COUNTRY_DIAL);
session.removeAuthNote(NOTE_COUNTRY_NAME);
}
context.success();
}
✅ STEP 3 — Retrieve Stored Variable (action())
@Override
public void action(AuthenticationFlowContext context) {
AuthenticationSessionModel session = context.getAuthenticationSession();
MultivaluedMap<String,String> formData =
context.getHttpRequest().getDecodedFormParameters();
String userType = session.getAuthNote(NOTE_USER_TYPE);
String country;
if ("partner".equalsIgnoreCase(userType)) {
// 🔐 Always use server-side value
country = session.getAuthNote(NOTE_COUNTRY_DIAL);
} else {
// renter can choose from form
country = formData.getFirst("country");
}
System.out.println("Final country used = " + country);
}
Conditional Storage Logic Diagram
Storing Dynamic Multiple Variables
You can also store JSON dynamically:
session.setAuthNote("DYNAMIC_SCHEMA", schemaJson);
And retrieve later:
String schema = session.getAuthNote("DYNAMIC_SCHEMA");
This is useful for:
Dynamic forms
Multi-step flows
OTP verification state
Registration enhancements

Top comments (0)