using-nslookup-to-troubleshoot-common
troubleshooting-network-problems-with-command-line-nslookup
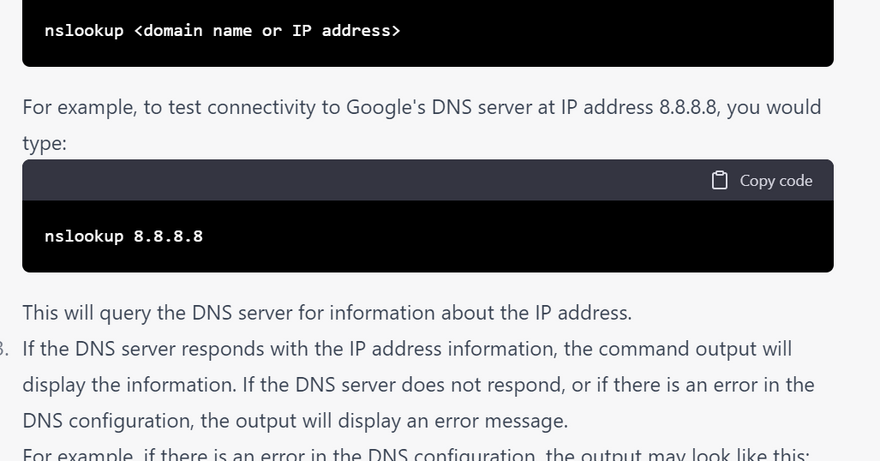
how nslookup solve Testing connectivity error using linux command with example
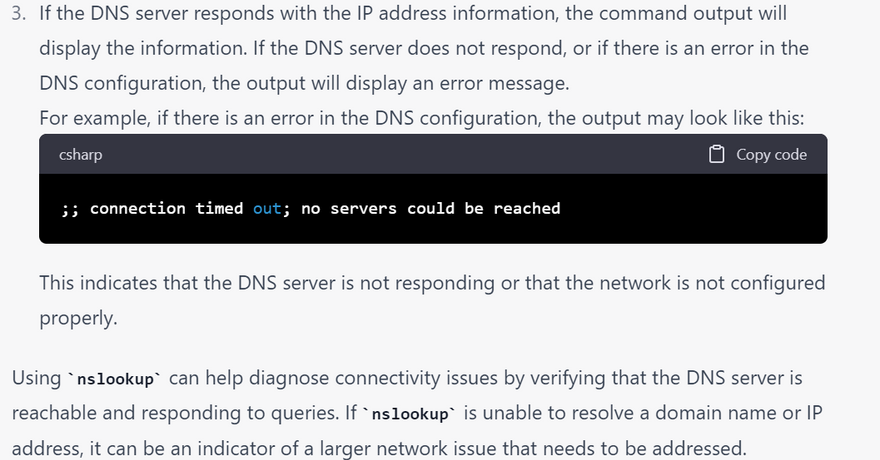
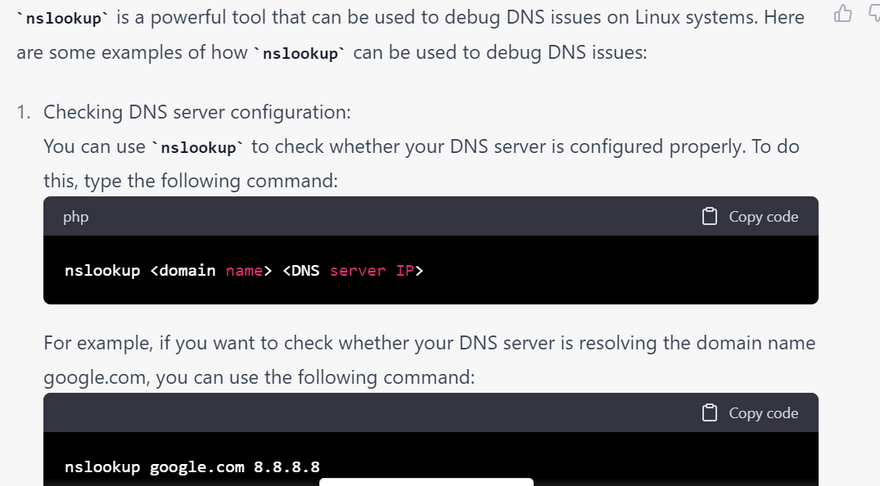
how nslookup solve Debugging DNS issueserror using linux command with example
nslookup is a command-line tool used for troubleshooting networks and DNS-related issues. Here are some ways in which nslookup can be helpful in troubleshooting networks
Checking DNS records: nslookup allows you to query DNS servers to check for the existence of DNS records such as A, AAAA, MX, TXT, and other DNS record types. This can help identify DNS issues such as incorrect DNS entries or missing DNS records.
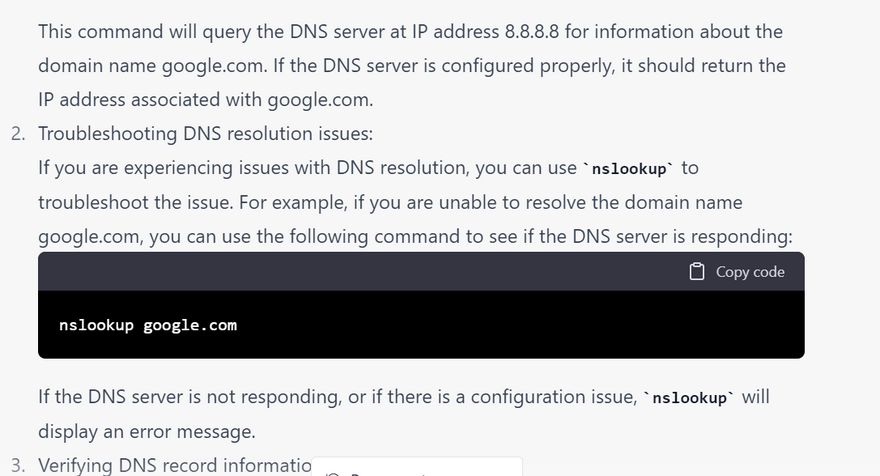
Resolving DNS issues: nslookup can help you identify and resolve DNS issues such as slow DNS resolution or DNS resolution failures. By querying different DNS servers, you can determine whether the issue is with a specific DNS server or with the DNS resolver on your local machine.
Testing connectivity: nslookup can be used to test network connectivity between two hosts by resolving the IP address of a hostname or domain name. This can help identify network issues such as routing problems, firewall blocks, or network connectivity issues.
Debugging DNS issues: nslookup provides verbose output that can help debug DNS issues. By running nslookup with the debug option enabled, you can see detailed information about DNS queries and responses, including the DNS server being used, the query type, and the response time.
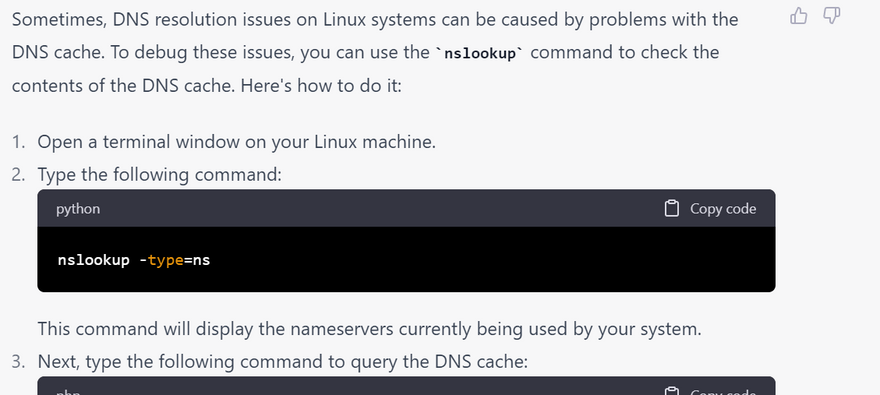
Checking DNS cache: nslookup can help you check the DNS cache on your local machine to see if DNS entries are being cached correctly. This can help identify issues with DNS caching such as stale DNS entries or DNS cache poisoning.
Overall, nslookup is a powerful tool that can be used to troubleshoot network issues and DNS-related problems. By using nslookup in combination with other network troubleshooting tools, you can identify and resolve network issues quickly and efficiently.
Here is a checklist of things to consider when troubleshooting errors with nslookup commands:
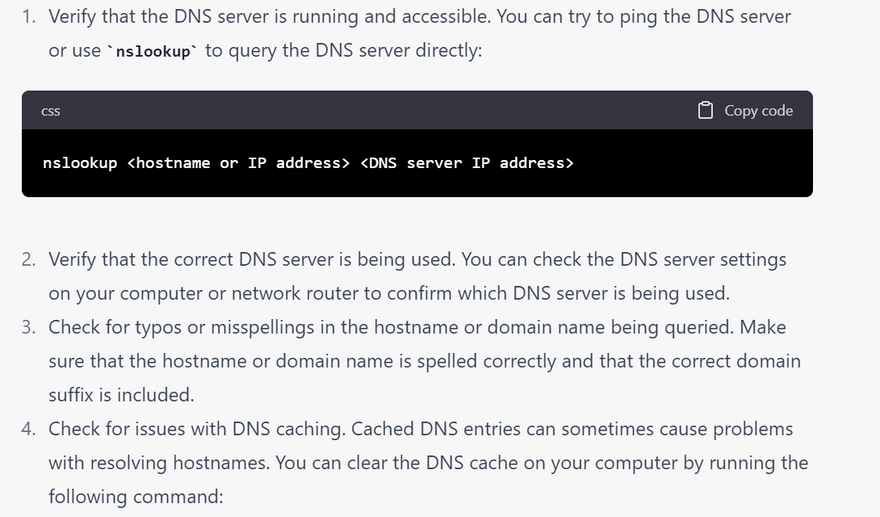
Verify that the DNS server is running and accessible. You can try to ping the DNS server or use nslookup to query the DNS server directly:
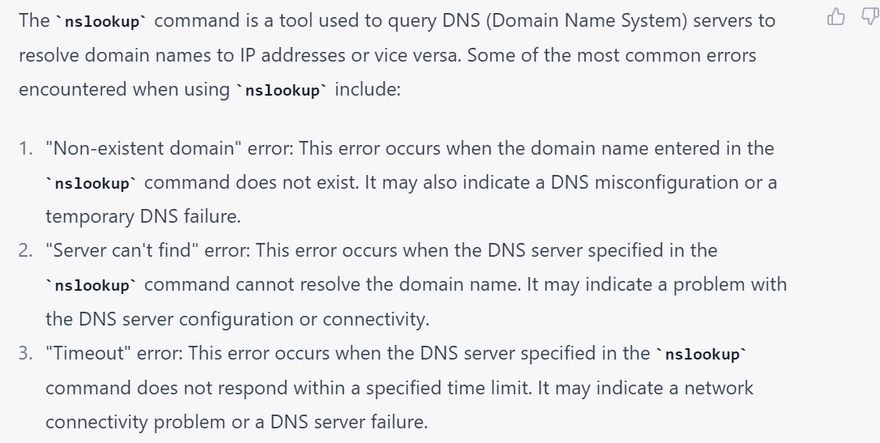
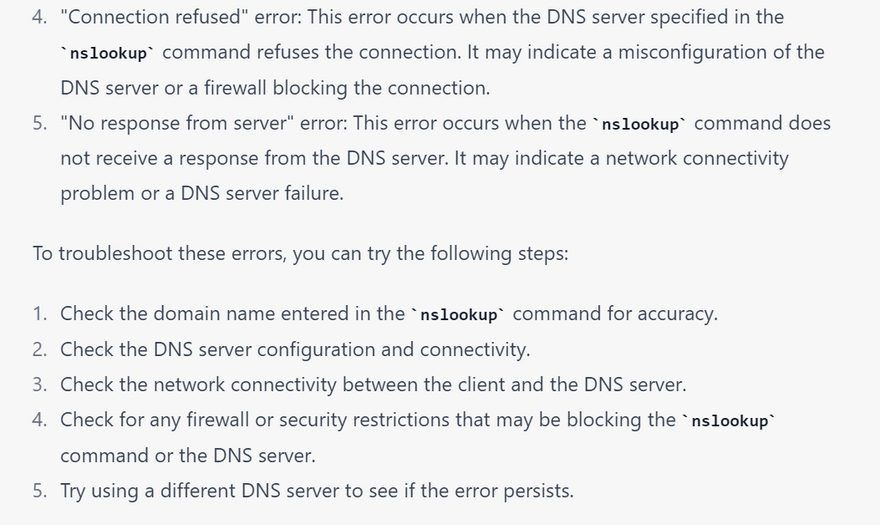
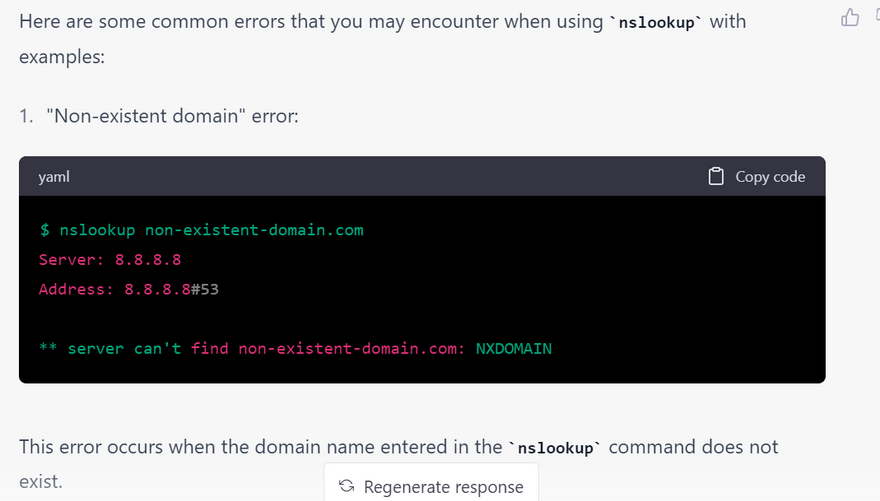
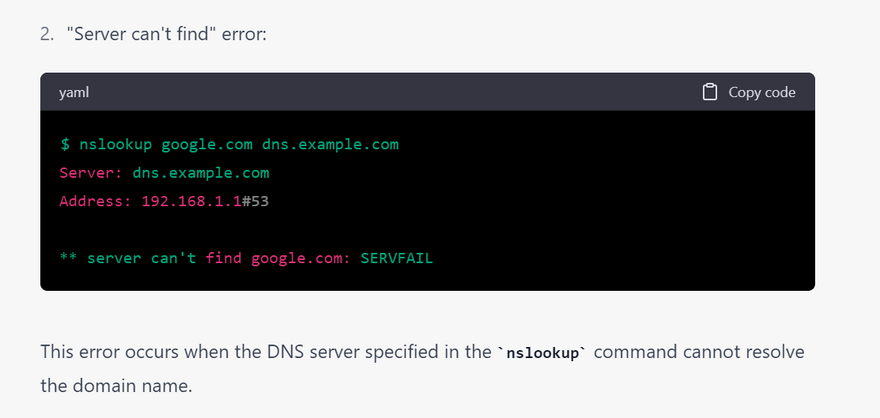
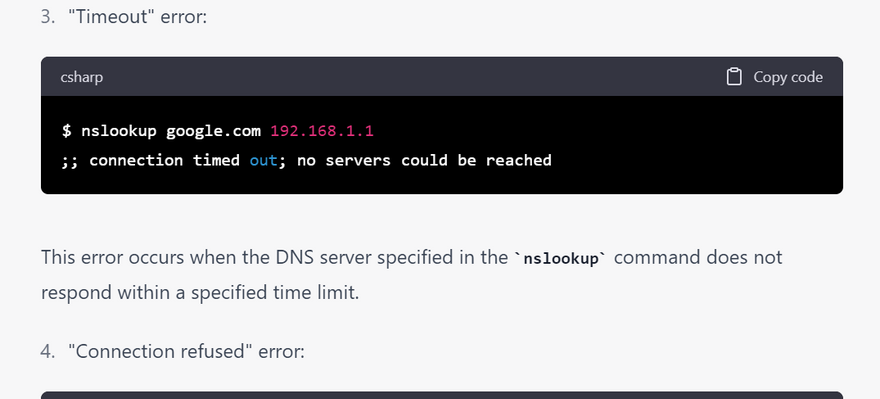
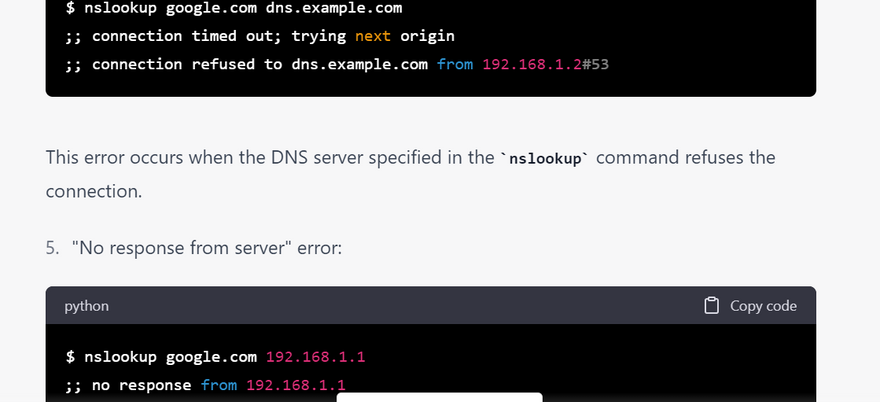
most common error using nslookup
This error occurs when the nslookup command does not receive a response from the DNS server.
Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
f you don’t know what Nslookup is, it’s time to learn and get familiar with it. It is a very useful tool that would save you time troubleshooting DNS problems, such as host name resolution, DNS records, etc., since a lot of network problems are related to DNS. It’s an old school command line that’s been around for many years but is still useful and handy nowadays with even so many advanced networking tools available.
This post is to show you what Nslookup is, how it works, and what we can do with it.
To start Nslookup
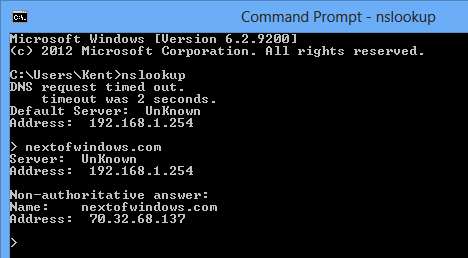
To start, simply type Nslookup in the command prompt window. It shows the host name and IP address of the DNS server configured for your local computer.
Nslookup start - Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
In this case, I have my router configured as default DNS server, therefore the host name shows unknown because it doesn’t have a valid host name associated with it. Because the DNS is set to use my default router, all DNS query will go through it to the external DNS server set up on my Router, which is set by default to my ISP.
Also note that the command displays a command prompt waiting for the further queries after the initial info. If you don’t know what to type, you can type a question mark ? and press enter for all available commands. To exit, type exit.
To look up a host’s IP
To look up an IP address of a host, simply type the host name which could be a domain name if the host you want to check is a website.
nslookup hosts - Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
Nslookup uses my default DNS setting to execute the DNS query to find the IP info of the host. If for some reason the D*NS server you have set up isn’t working properly* because you can’t access internet from any of your browser, it’s time to troubleshoot the problem using a different DNS server.
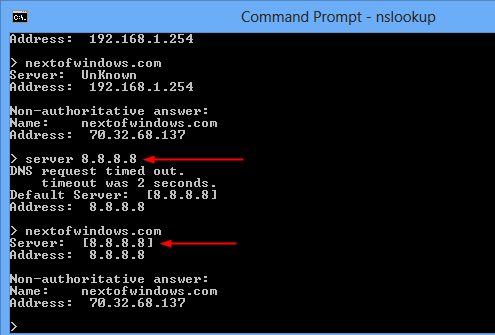
There are 2 public DNS servers that are not only quick but also working almost all the time, Google Public DNS (8.8.8.8 or 8.8.4.4) and Open DNS (208.67.222.222 or 208.67.220.220).
You can switch to any of the public DNS listed above to see if your network problem is indeed something related to DNS. For example, to switch to Google Public DNS, you can type server 8.8.8.8 and press enter. Then type the host name again to look up the IP address of it.
nslookup server to switch dns server - Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
A quick compare between these information would tell you quickly whether your DNS setup on your computer is functioning properly.
To query a specific type of DNS record
The default look-up in Nslookup is to return the IP address for the specified host name or domain, which is basically the “A” records in DNS. But you can look up the other type of DNS information too, such as MX, CNAME, or any other types.
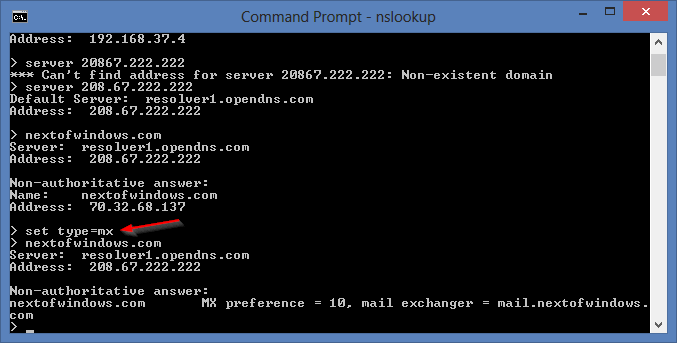
For example, to find what mail server this website uses, run the following command first, and type the host name again.
set type=mx
nslookup set type mx - Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
You can also use the command ls to list the records for the domain but since most of the domain has their zone transfer disabled for security reason, you often get the message “can’t list domain xxx: query failed” that basically returns nothing for you.
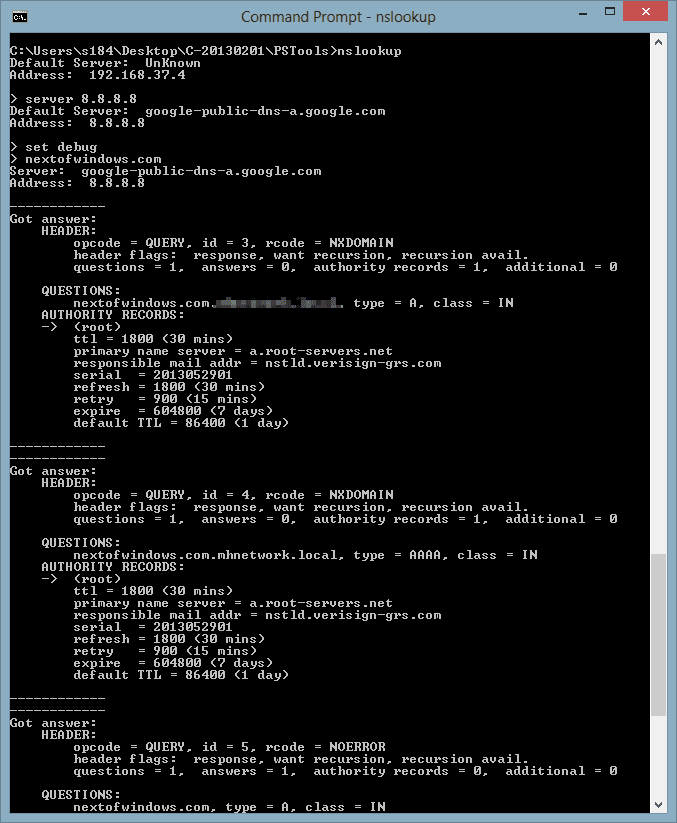
The debug mode
Nslookup also has a debug mode that’s quite helpful. You can turn it on by typing set debug or set d2 which provides more greater detail information. Once the debug mode is on, Nslookup shows up the steps being taken along the way to complete its command, see the example from the screenshot below:
nslookup debug mode on - Troubleshooting Network Problems with Command Line NSLookup
how nslookup solve Testing connectivity error using linux command
how nslookup solve Debugging DNS issueserror using linux command with example
nslookup google.com 8.8.8.8
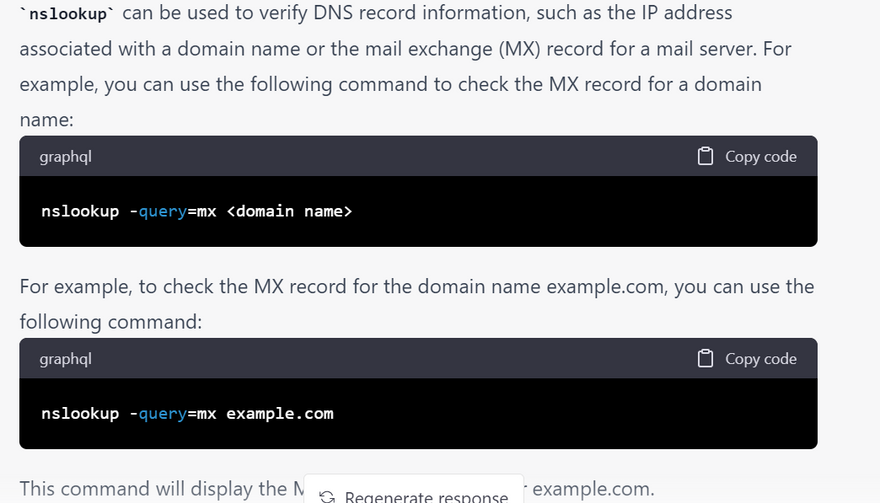
nslookup -query=mx example.com
These are just a few examples of how nslookup can be used to debug DNS issues on Linux systems. By using nslookup to check DNS server configuration, troubleshoot DNS resolution issues, and verify DNS record information, you can quickly diagnose and resolve DNS issues on your Linux system.
how Checking DNS cache solve Debugging DNS issues error using linux command with example
nslookup -type=ns
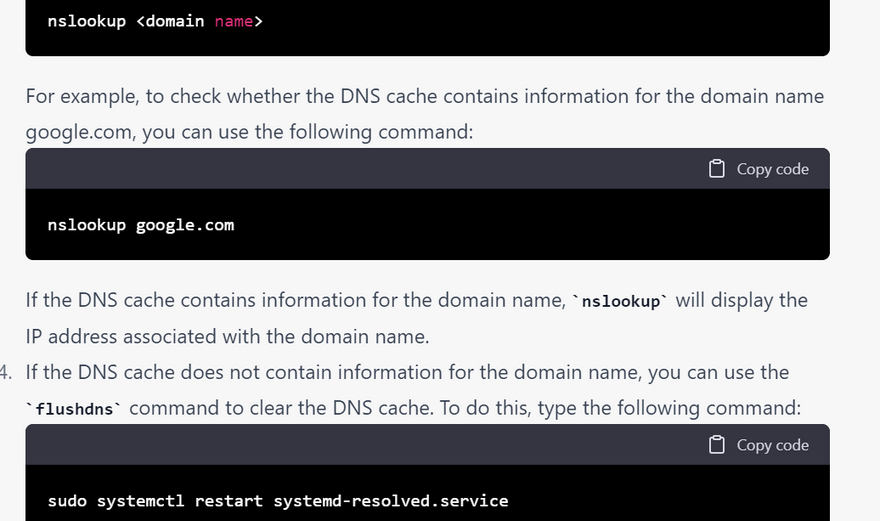
nslookup google.com
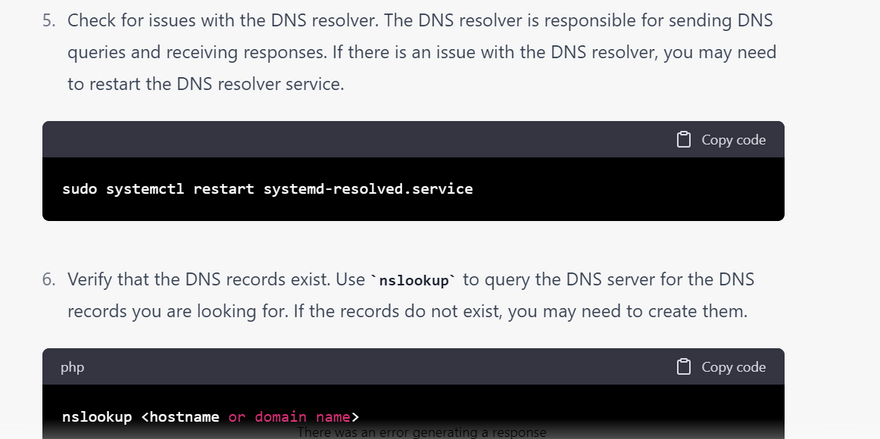
sudo systemctl restart systemd-resolved.service




Top comments (0)