laravel-how-to-throw-403-if-the-user-enter-the-id-manually-in-the-route-ask-question-up-vote
laravel-forbidden-you-dont-have-permission-to-access-on-this-server
laravel-error-403
laravel-403-forbidden-error
laravel-9-storage-images-error-403-forbidden
laravel-403-error-for-api-that-previously-worked
Error:
You don't have permission to access the requested object. It is either read-protected or not readable by the server.
If you think this is a server error, please contact the webmaster.
Error 403
dronesnow.in
Solution
goto path==cd /opt/lampp
mv phpmyadmin_bkp phpmyadmin
The HTTP 403 Forbidden client error status response code indicates that the server understands the request, but it refuses to authorize it. This status is similar to 401 (Unauthorized), but indicates that the client must authenticate itself to get the requested response.
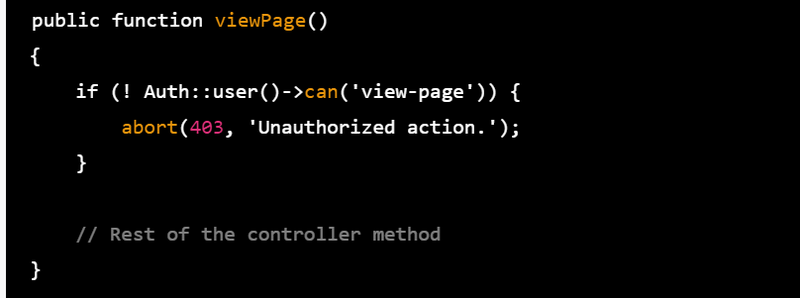
In Laravel, you can return a 403 response in a controller or middleware by using the abort(403) function. For example, in a controller method, you could use the following code to return a 403 response if a user is not authorized to access a certain page:
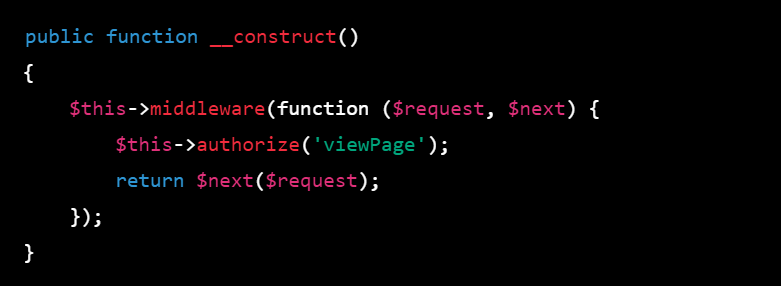
Alternatively, you can use the authorize method in controller constructor or method to check if the user has a specific ability or if the user is authorized to perform a certain action on a resource.
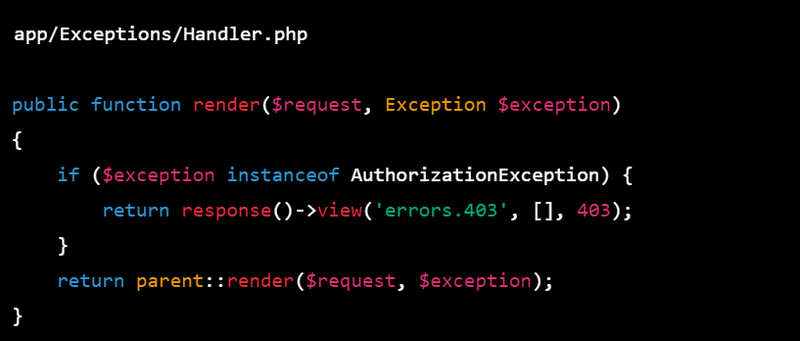
You can also create custom 403 exception handler to handle the 403 exceptions.
Please note that the above example is just one way to implement authorization in a Laravel application, and the specific implementation may vary depending on your application's requirements and architecture.
http://localhost:8000/post/16/edit
ErrorException (E_NOTICE)
Trying to get property 'user_id' of non-object
How to show unauthorised page in this case?
public function edit($id)
{
$post = Post::find($id);
if(Auth::user()->id == $post->user_id){
return view('post-edit',compact('post'));
}else {
return redirect()->route('home');
} }
public function edit($id)
{
$post = Post::find($id);
if (!$post) {
abort(403);
}
if (!Auth::user() || Auth::user()->id != $post->user_id) {
return redirect()->route('home');
}
return view('post-edit',compact('post'));
}
Error: api key endpoint authentication credential is not correct as it is paid version to get twitter follower
specific error message received from the API. This information can help you understand the reason for the 403 Forbidden error.


Top comments (0)