Refer here
Refer here
Refer here
Refer here
what is the use of traceroute command with detail points
what is star mark suggest in traceroute in linux
how to reach the Google host from the local machine
network connectivity problems by identifying where data packets are being lost or delayed along the route
network connectivity problems by identifying where data packets are being lost or delayed along the route
identifying the most efficient route between two nodes
aestrick(*)because of router is overloaded, misconfigured, or simply ignoring the ICMP messages
save route command using traceroute 8.8.8.8 > results.txt
The traceroute command is a network diagnostic tool that is used to identify the route taken by data packets as they travel from one network node to another on the Internet. The primary purpose of the traceroute command is to help network administrators and engineers troubleshoot network connectivity problems by identifying where data packets are being lost or delayed along the route.
Here are some details points about the traceroute command:
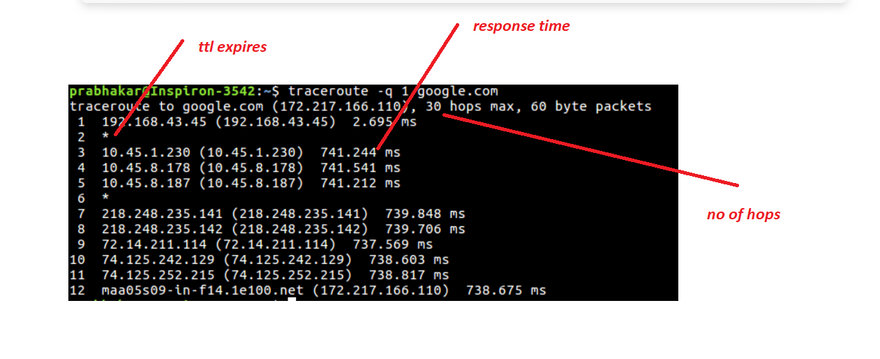
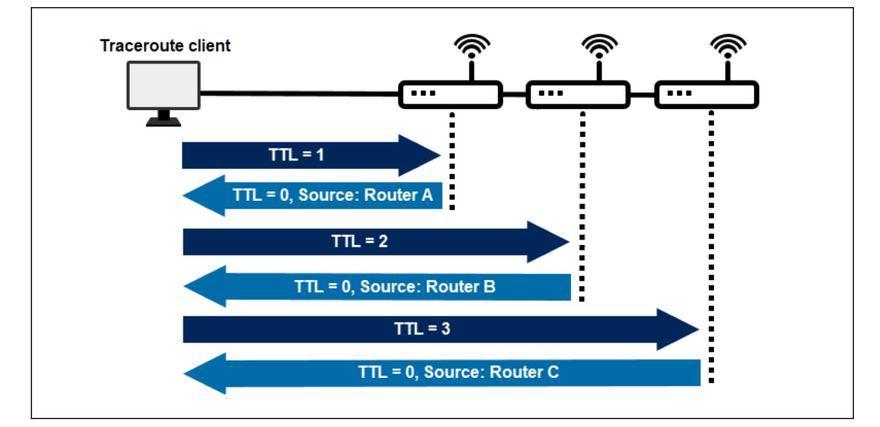
Identify Network Hops: traceroute identifies the network hops between the source and destination by sending a series of ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) packets with increasing Time-to-Live (TTL) values. The TTL value is gradually increased until the destination node is reached, and each hop along the way is identified and displayed in the output.
RTT Metrics: The output of traceroute provides round-trip time (RTT) metrics for each hop along the route. The RTT represents the time it takes for an ICMP packet to travel from the source node to the destination node and back again, and is a useful metric for identifying network latency and congestion issues.
Packet Loss Analysis: traceroute can also be used to identify where data packets are being lost or delayed along the route. If a hop along the route is identified as being slow or unresponsive, it may be an indication of network congestion or a problem with a specific network node.
Path Optimization: traceroute can be used to optimize network paths by identifying the most efficient route between two nodes. By analyzing the output of traceroute, network administrators can identify routes with the least number of hops or the lowest RTT, and use this information to optimize network performance.
Different Platforms: traceroute is available on a variety of platforms, including Linux, Windows, and macOS, and can be used to diagnose network connectivity issues on a wide range of devices.
Overall, the traceroute command is a valuable tool for network administrators and engineers, providing detailed information about network connectivity and performance, as well as aiding in network troubleshooting and optimization.
what is star mark suggest in traceroute in linux
In a traceroute output on Linux, a star (*) is typically used to indicate that a network hop timed out, i.e., the traceroute program didn't receive a response from that particular network node within a certain time frame.
When you run a traceroute command, it sends packets to the destination server with gradually increasing Time to Live (TTL) values. Each intermediate router decrements the TTL value by 1 and if the TTL value reaches 0, it discards the packet and sends an ICMP "Time Exceeded" message back to the sender. The traceroute program then uses these "Time Exceeded" messages to determine the network path and latency to the destination server.
However, if a router or a network node doesn't send back an "Time Exceeded" message within a certain time frame (usually 5 seconds), traceroute will mark that hop with an asterisk (). This could be because the **router is overloaded, misconfigured, or simply ignoring the ICMP messages*. In such cases, the traceroute program cannot determine the exact latency and network path to that node, and hence marks it with an asterisk.
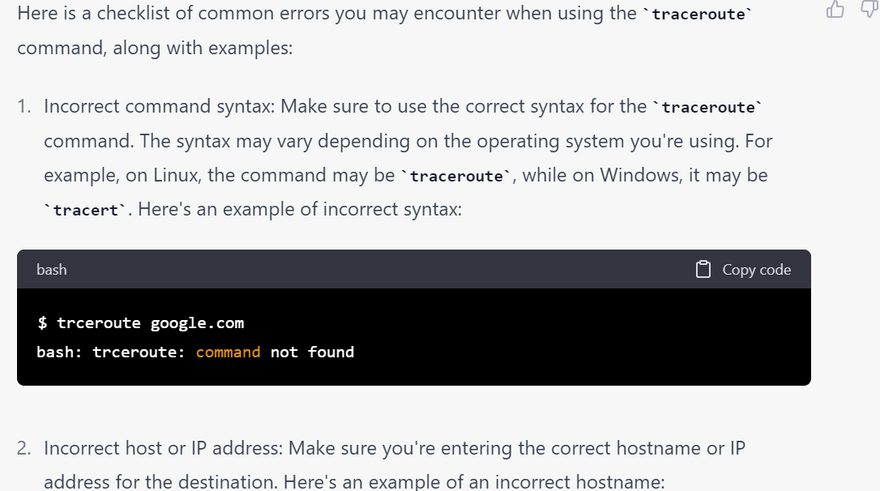
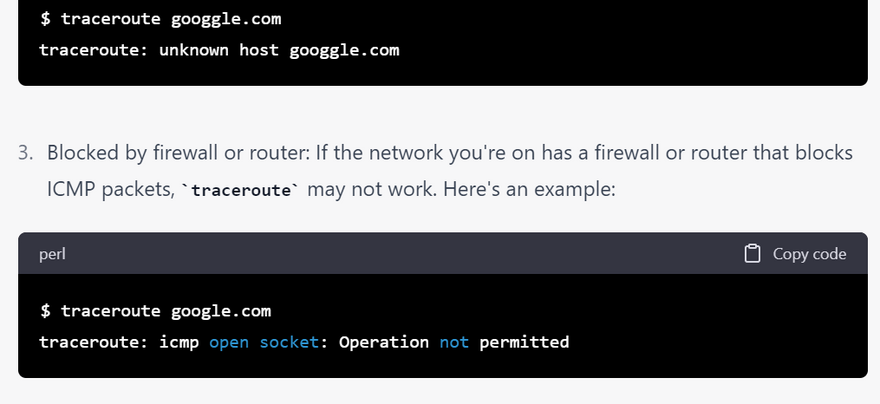
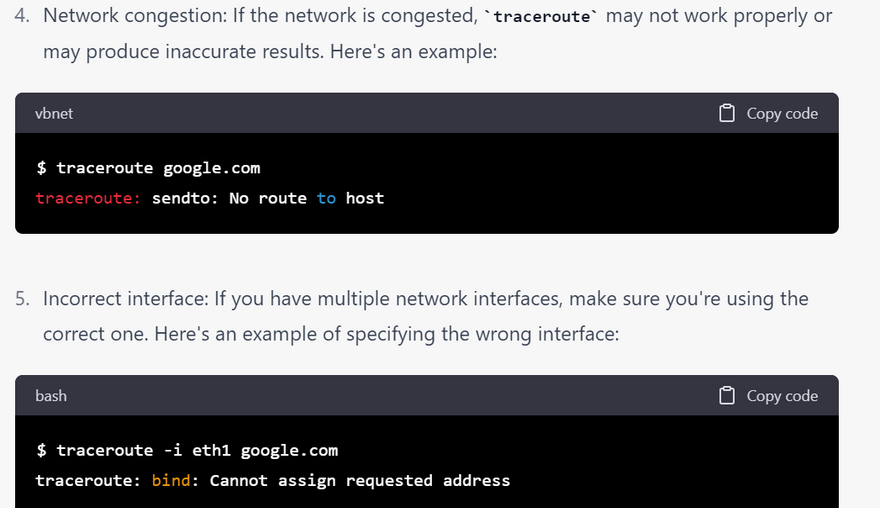
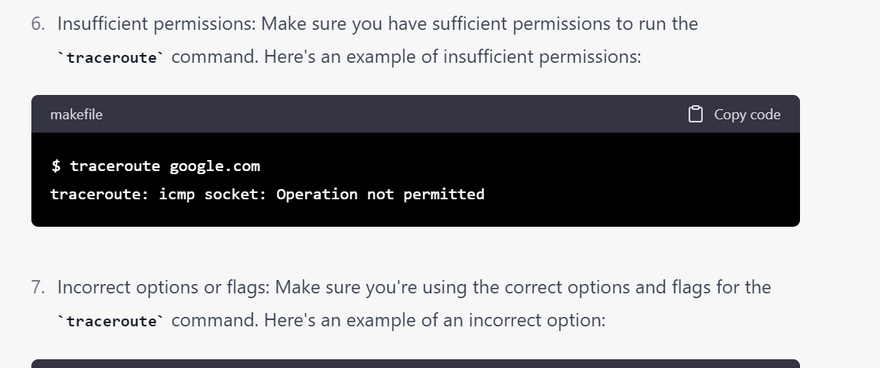
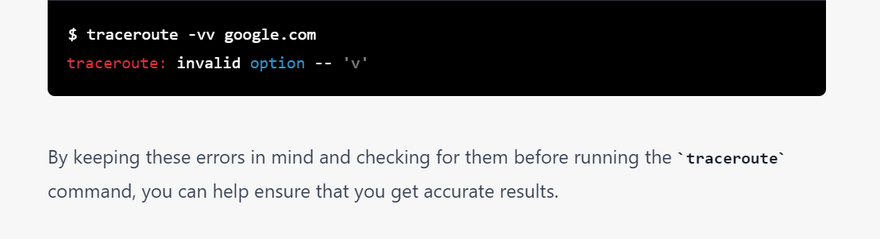
checklist of error for traceroute commands with examples
=========================================================
raceroute acts as a series of ping commands. While ping requests a response from the destination, traceroute gathers the intermediate information as well.
To gather the information available between the source and destination, a traceroute lowers the packet's TTL (time to live) to a minimum (1). When a router receives the information, it decrements the TTL value to 0, indicating it should send information back to the source. The source gathers the intermediate router information, resets the TTL value to 1, and increments it
Advanced Options for Traceroute on Linux
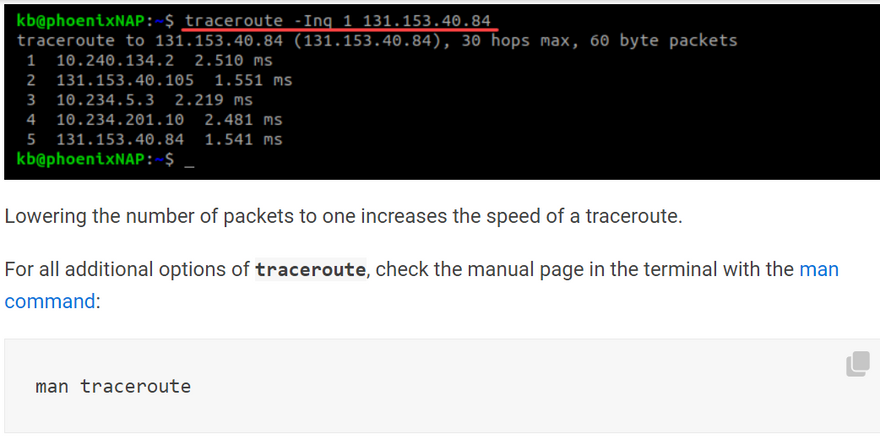
By default, a traceroute sends UDP packets. Add the option -I for ICMP probe packets:
traceroute -I <hostname or IP>
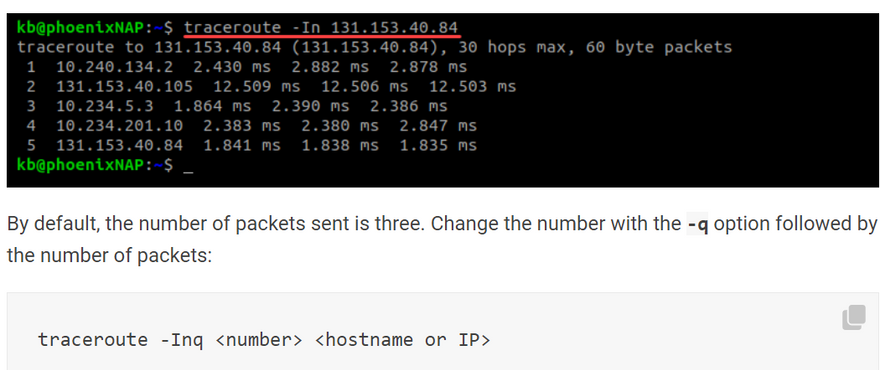
Include the -n option to hide the device names for a cleaner output:
traceroute -In <hostname or IP>
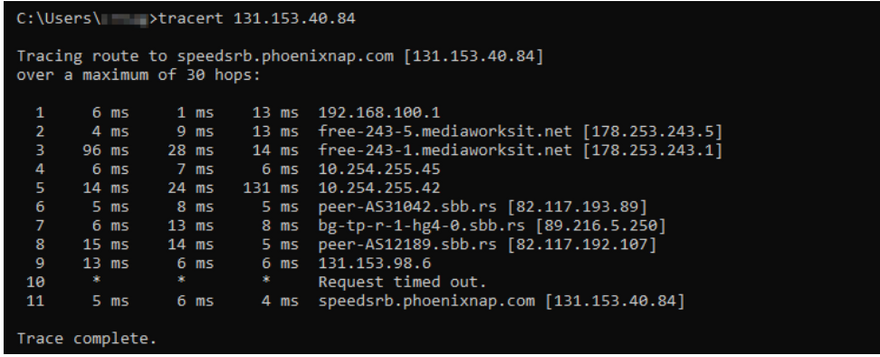
Run a Traceroute in Windows
Traceroute is available for Windows using the shorter name tracert. To run a traceroute on Windows, follow these steps:
Press the Windows key and type CMD.
Press Enter and open the command prompt.
Lastly, run traceroute with:
tracert [options] <hostname or IP>
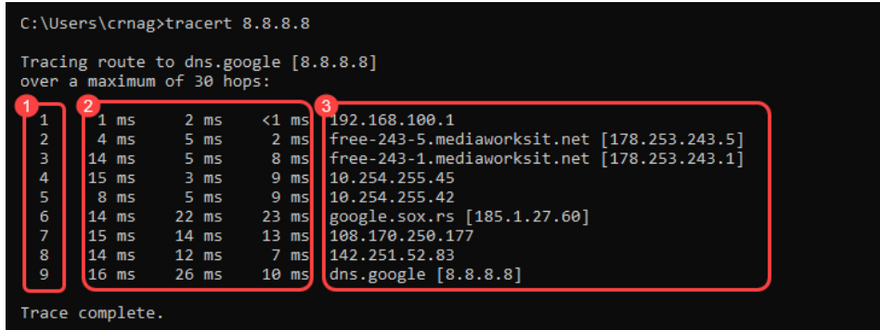
How to Read a Traceroute?
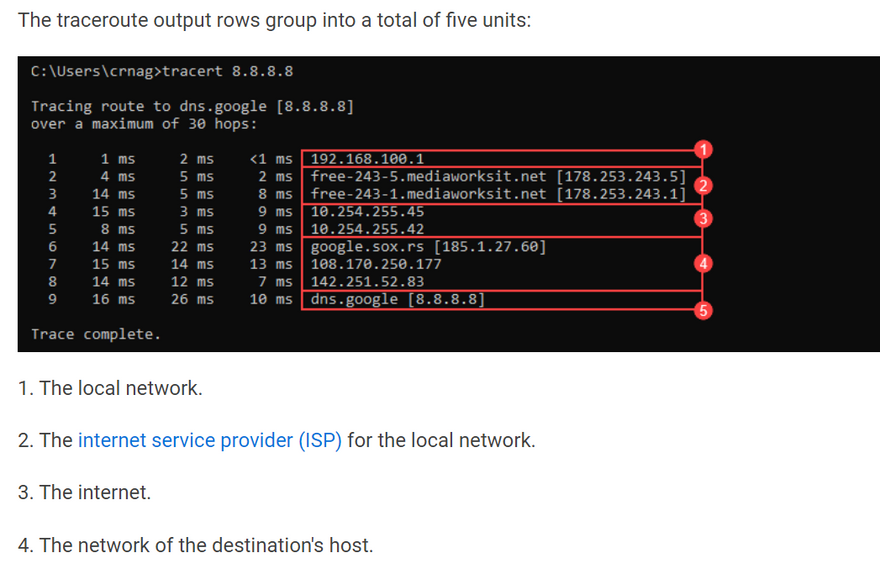
When running a traceroute, the output shows the path packets take when traveling to a destination point. The printed result divides into three general columns:



Top comments (0)