Defination
COMPLETE pytorch TRAINING PIPELINE (FULL CODE BLOCK)
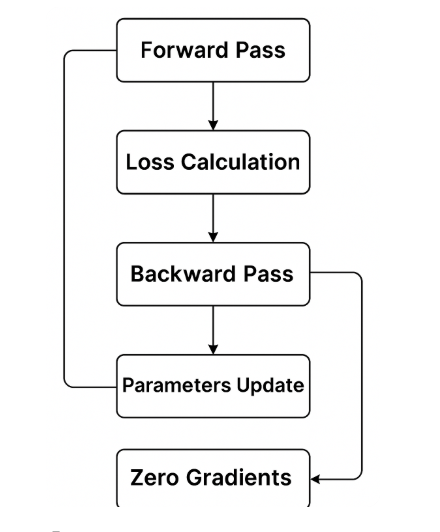
Architecture diagram
COMPLETE KERAS TRAINING PIPELINE (FULL CODE BLOCK)
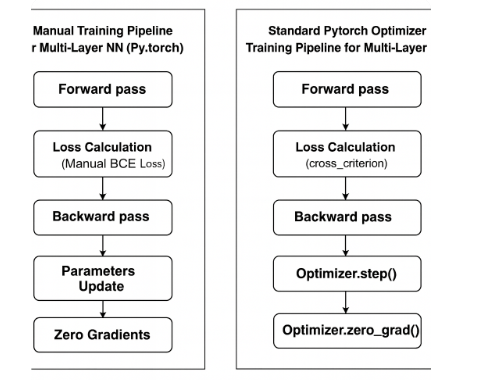
Manual Training Pipeline for Multi-Layer NN
PYTORCH OPTIMIZER Training Pipeline for Multi-Layer NN
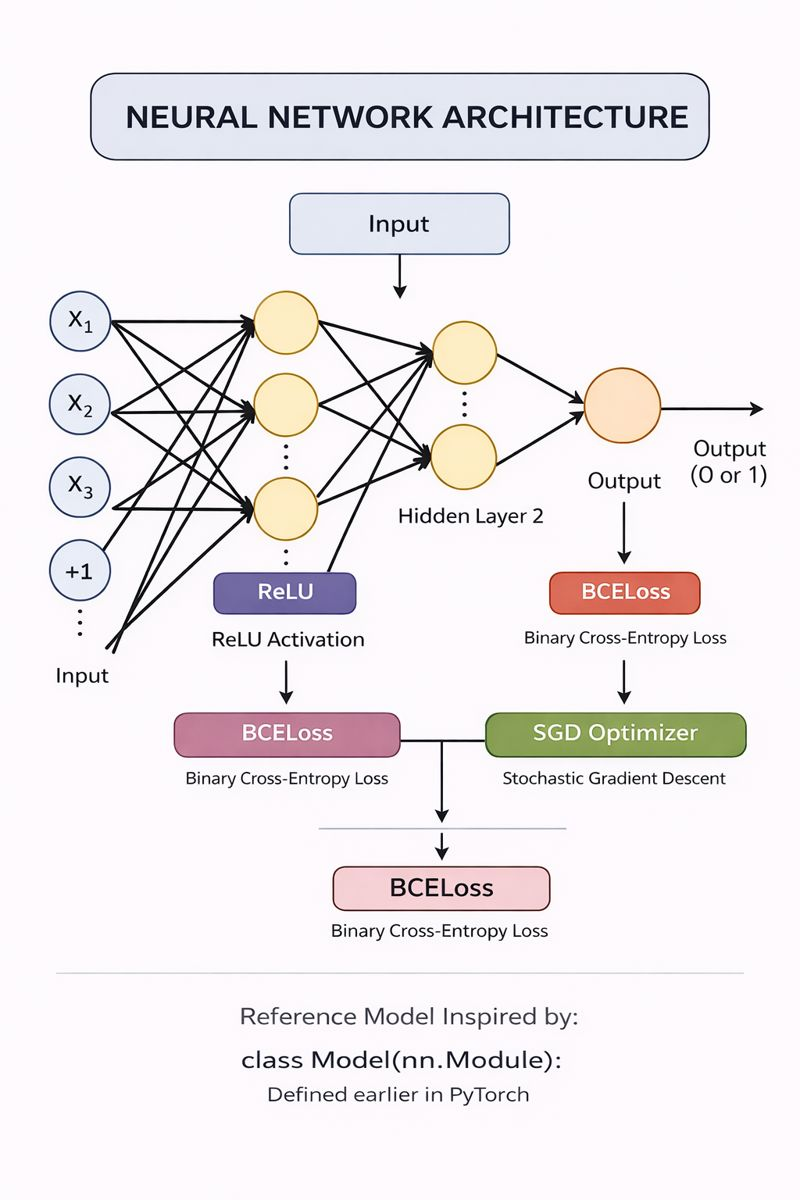
Diagram Manual Training Pipeline (Multi-Layer NN, Manual Update)
Diagram Standard PyTorch Optimizer Training Pipeline
Full code example training pipeline for multilayer with model defined
Different way to define multi-layer neural network models in PyTorch
Training Pipeline in PyTorch — Summary
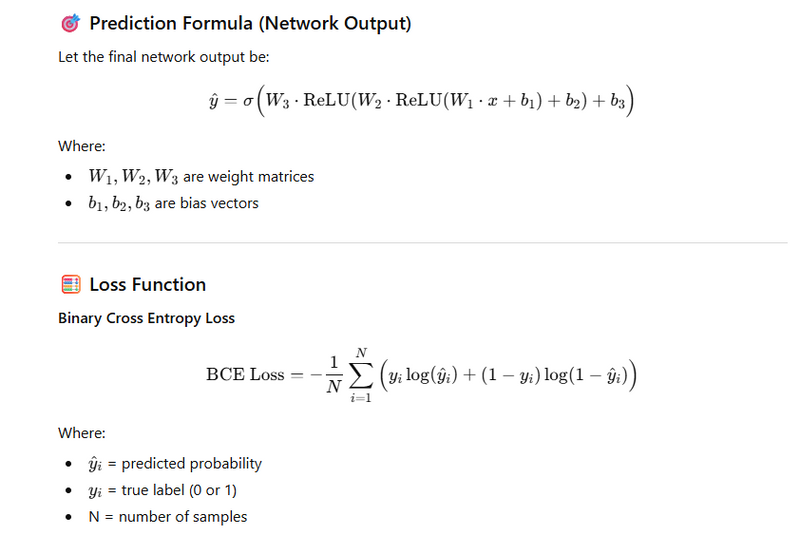
Formula & Notation Cheat Sheet
PyTorch Training Pipeline — Complete Cheat Sheet
Training pipeline
Defination 1
A training pipeline is the repeated cycle of prediction, error measurement, gradient computation, and parameter updates used to train a machine learning model.
Defination 2
A training pipeline is the repeated cycle of prediction, error measurement, gradient computation, and parameter updates used to train a machine learning model.
Defination 3
A training pipeline is a structured sequence of steps through which a machine learning model learns from data. It defines how the model:
Processes input data
Generates predictions
Calculates error (loss)
Computes gradients
Updates its parameters
Repeats the process until the model learns
COMPLETE pytorch TRAINING PIPELINE (FULL CODE BLOCK)
Defining the model
class MySimpleNN():
def __init__(self, X):
self.weights = torch.rand(X.shape[1], 1, dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
self.bias = torch.zeros(1, dtype=torch.float64, requires_grad=True)
def forward(self, X):
z = torch.matmul(X, self.weights) + self.bias
y_pred = torch.sigmoid(z)
return y_pred
def loss_function(self, y_pred, y):
# Clamp predictions to avoid log(0)
epsilon = 1e-7
y_pred = torch.clamp(y_pred, epsilon, 1 - epsilon)
# Calculate loss
loss = -(y_train_tensor * torch.log(y_pred) + (1 - y_train_tensor) * torch.log(1 - y_pred)).mean()
return loss
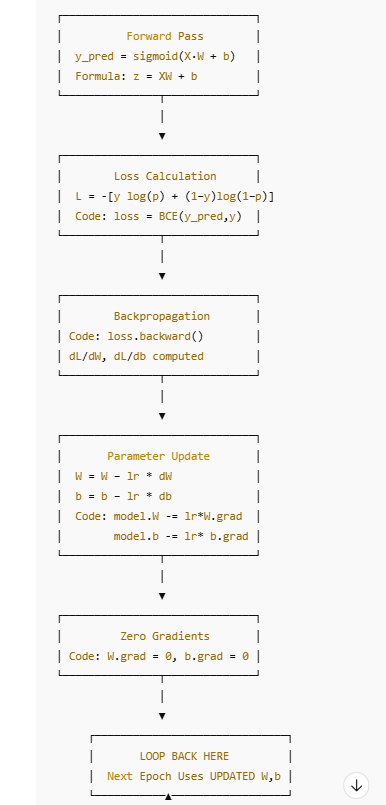
Training Pipeline
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 25
# create model
model = MySimpleNN(X_train_tensor)
# define loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
# forward pass
y_pred = model.forward(X_train_tensor)
# loss calculate
loss = model.loss_function(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# backward pass
loss.backward()
# parameters update
with torch.no_grad():
model.weights -= learning_rate * model.weights.grad
model.bias -= learning_rate * model.bias.grad
# zero gradients
model.weights.grad.zero_()
model.bias.grad.zero_()
# print loss in each epoch
print(f'Epoch: {epoch + 1}, Loss: {loss.item()}')
COMPLETE KERAS TRAINING PIPELINE (FULL CODE BLOCK)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers, Model
# custom model
class MySimpleNN(Model):
def __init__(self, input_dim):
super(MySimpleNN, self).__init__()
self.dense = layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid')
def call(self, inputs):
return self.dense(inputs)
# create model
input_dim = X_train.shape[1]
model = MySimpleNN(input_dim)
# define loss and optimizer
loss_fn = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy()
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
epochs = 100
# training loop
for epoch in range(epochs):
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
# forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train, training=True)
# loss calculation
loss = loss_fn(y_train, y_pred)
# backward pass (compute gradients)
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, model.trainable_variables)
# parameters update
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, model.trainable_variables))
# print loss
print(f'Epoch: {epoch + 1}, Loss: {loss.numpy()}')
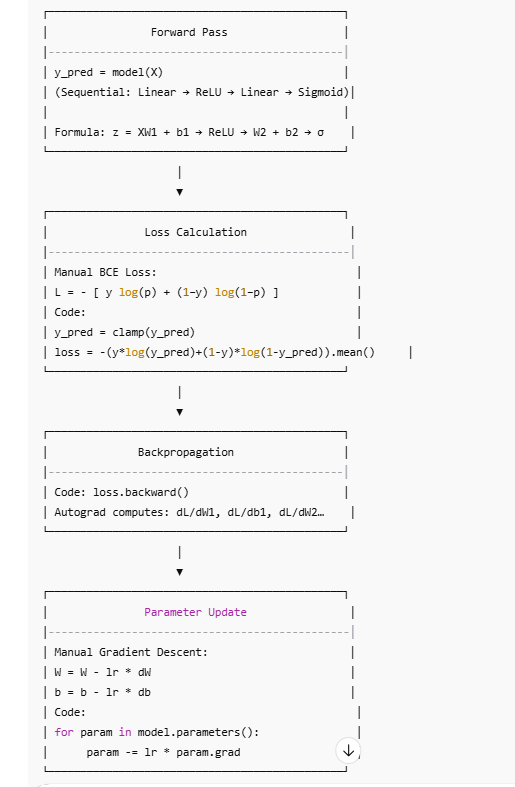
Manual Training Pipeline for Multi-Layer NN
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# Create model
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1])
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 25
# Manual BCE loss function
def bce_loss(y_pred, y_true):
epsilon = 1e-7
y_pred = torch.clamp(y_pred, epsilon, 1 - epsilon)
return -(y_true * torch.log(y_pred) + (1-y_true) * torch.log(1 - y_pred)).mean()
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 1. Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# 2. Loss calculation
loss = bce_loss(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# 3. Backward pass
loss.backward()
# 4. Manual parameter update
with torch.no_grad():
for param in model.parameters():
param -= learning_rate * param.grad
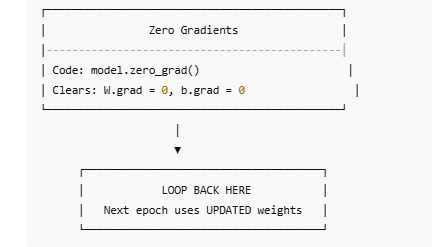
# 5. Zero gradients
model.zero_grad()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}, Loss: {loss.item()}")
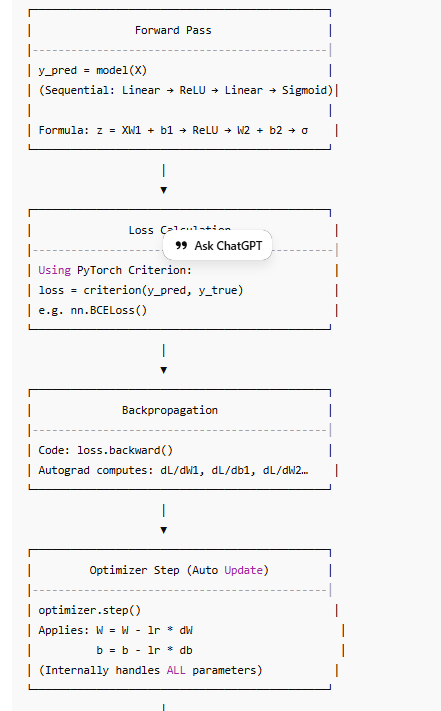
PYTORCH OPTIMIZER Training Pipeline for Multi-Layer NN
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1])
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
epochs = 25
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 1. Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# 2. Loss
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# 3. Backward pass
loss.backward()
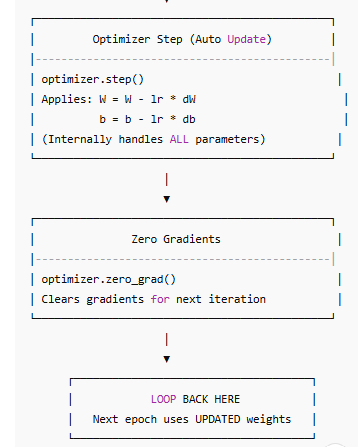
# 4. Update parameters
optimizer.step()
# 5. Zero gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}, Loss: {loss.item()}")
Diagram Manual Training Pipeline (Multi-Layer NN, Manual Update)
Diagram Standard PyTorch Optimizer Training Pipeline
Full code example training pipeline for multilayer with model defined
Without optimizer
DEFINE MULTI-LAYER MODEL
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# -------------------------------
# 2. DEFINE MODEL CLASS
# -------------------------------
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_features, 3), # layer 1
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.Linear(3, 1), # layer 2
nn.Sigmoid() # output activation for binary classification
)
def forward(self, features):
return self.network(features)
PREPARE TRAINING DATA
# -------------------------------
X_train_tensor = X_train_tensor.double()
y_train_tensor = y_train_tensor.double()
CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
# 4. CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1])
LOSS FUNCTION
# -------------------------------
# 5. LOSS FUNCTION
# -------------------------------
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
TRAINING PIPELINE
earning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 25
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# Loss calculation
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# -------------------------------
# MANUAL PARAMETER UPDATE
# -------------------------------
with torch.no_grad():
for param in model.parameters():
param -= learning_rate * param.grad
# -------------------------------
# ZERO GRADIENTS
# -------------------------------
for param in model.parameters():
param.grad.zero_()
# Print progress
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss = {loss.item():.6f}")
# -------------------------------
# 1. IMPORT LIBRARIES
# -------------------------------
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# -------------------------------
# 2. DEFINE MULTI-LAYER MODEL
# -------------------------------
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Linear(num_features, 3, dtype=torch.float64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.l2 = nn.Linear(3, 1, dtype=torch.float64)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
# Ensure gradients enabled
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
def forward(self, X):
out = self.l1(X)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.l2(out)
out = self.sigmoid(out)
return out
# -------------------------------
# 3. PREPARE TRAINING DATA
# -------------------------------
X_train_tensor = X_train_tensor.double()
y_train_tensor = y_train_tensor.double()
# -------------------------------
# 4. CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1])
# -------------------------------
# 5. LOSS FUNCTION
# -------------------------------
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
# -------------------------------
# 6. TRAINING LOOP (NO OPTIMIZER)
# -------------------------------
learning_rate = 0.1
epochs = 25
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# Loss calculation
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# Backward pass
loss.backward()
# -------------------------------
# MANUAL PARAMETER UPDATE
# -------------------------------
with torch.no_grad():
for param in model.parameters():
param -= learning_rate * param.grad
# -------------------------------
# ZERO GRADIENTS
# -------------------------------
for param in model.parameters():
param.grad.zero_()
# Print progress
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss = {loss.item():.6f}")
With optimizer
DEFINE MULTI-LAYER MODEL
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Linear(num_features, 3, dtype=torch.float64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.l2 = nn.Linear(3, 1, dtype=torch.float64)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
# Ensure gradients enabled
for param in self.parameters():
param.requires_grad = True
def forward(self, X):
out = self.l1(X)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.l2(out)
out = self.sigmoid(out)
return out
PREPARE TRAINING DATA
# -------------------------------
X_train_tensor = X_train_tensor.double()
y_train_tensor = y_train_tensor.double()
CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
# 4. CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1])
LOSS FUNCTION and optimizer
# -------------------------------
# 5. LOSS FUNCTION
# -------------------------------
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
TRAINING PIPELINE
epochs = 25
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# Loss calculation
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# Backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad() # reset gradients
loss.backward() # compute gradients
optimizer.step() # update model parameters
# Print progress
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}")
# -------------------------------
# 1. IMPORT LIBRARIES
# -------------------------------
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
# -------------------------------
# 2. DEFINE MODEL CLASS
# -------------------------------
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_features, 3), # layer 1
nn.ReLU(), # activation
nn.Linear(3, 1), # layer 2
nn.Sigmoid() # output activation for binary classification
)
def forward(self, features):
return self.network(features)
# --------------------------------------------------
# 3. PREPARE TRAINING DATA (X_train_tensor, y_train_tensor)
# --------------------------------------------------
# Make sure tensors are float64 because your old model used float64
X_train_tensor = X_train_tensor.double()
y_train_tensor = y_train_tensor.double()
# -------------------------------
# 4. CREATE MODEL INSTANCE
# -------------------------------
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1]).double()
# -------------------------------
# 5. DEFINE LOSS FUNCTION & OPTIMIZER
# -------------------------------
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
# You can also use:
# optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# -------------------------------
# 6. TRAINING PIPELINE
# -------------------------------
epochs = 25
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Forward pass
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
# Loss calculation
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
# Backward pass
optimizer.zero_grad() # reset gradients
loss.backward() # compute gradients
optimizer.step() # update model parameters
# Print progress
print(f"Epoch {epoch + 1}/{epochs}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}")
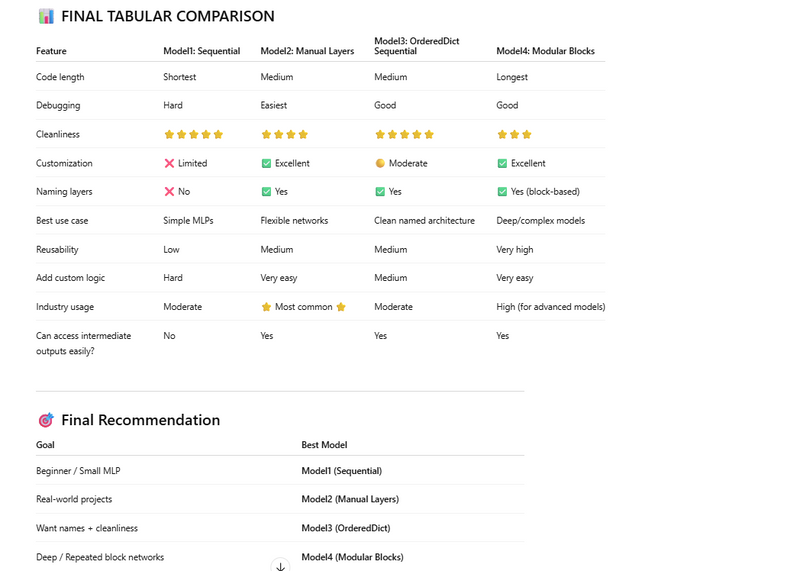
Different way to define multi-layer neural network models in PyTorch
Using nn.Sequential (cleanest & shortest)
Using Explicit Layers (most common in production)
Using OrderedDict inside Sequential
Custom Model With “Blocks”
Training Pipeline in PyTorch — Summary
A training pipeline organizes all steps required to train a model. In PyTorch, a typical pipeline includes:
Step 1: Prepare Dataset
Convert your raw data into tensors:
X_train_tensor = X_train_tensor.double()
y_train_tensor = y_train_tensor.double()
✔ ensures correct dtype matches model’s parameters
Step 2: Create Model Instance
Define your architecture using nn.Module:
model = Model(num_features=X_train_tensor.shape[1]).double()
Step 3: Define Loss Function (Criterion)
Used to measure prediction error:
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
Common losses:
nn.MSELoss() → regression
nn.CrossEntropyLoss() → multi-class classification
nn.BCELoss() / nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() → binary classification
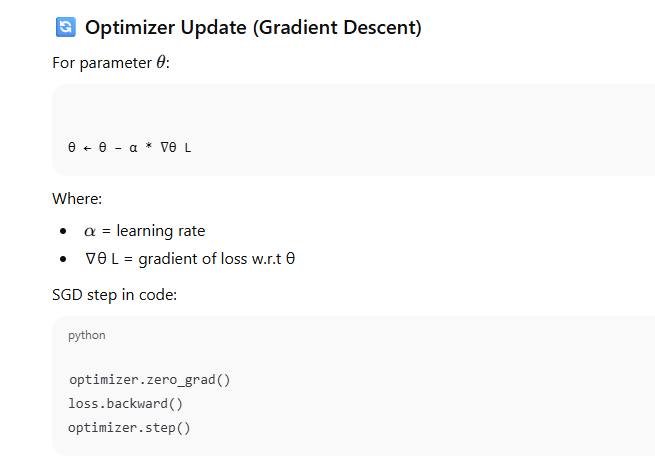
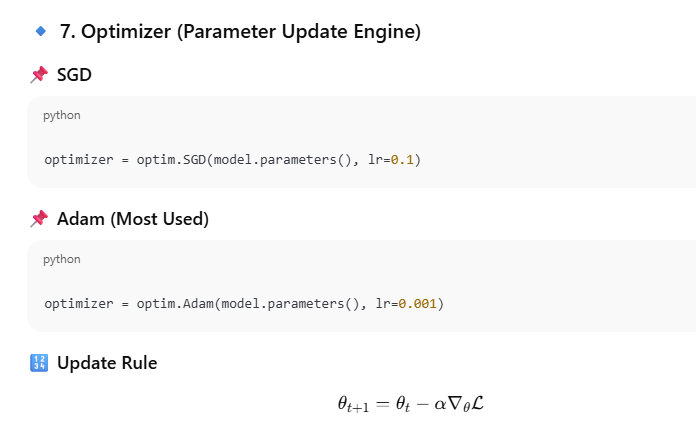
Step 4: Define Optimizer
Optimizer updates model parameters:
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
Other options:
optim.SGD
optim.Adam
optim.RMSprop
Step 5: Training Loop
For each epoch:
✔ Forward pass
✔ Compute loss
✔ Backward pass (gradient computation)
✔ Optimizer update
for epoch in range(epochs):
y_pred = model(X_train_tensor)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_train_tensor)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{epochs}, Loss: {loss.item():.6f}")
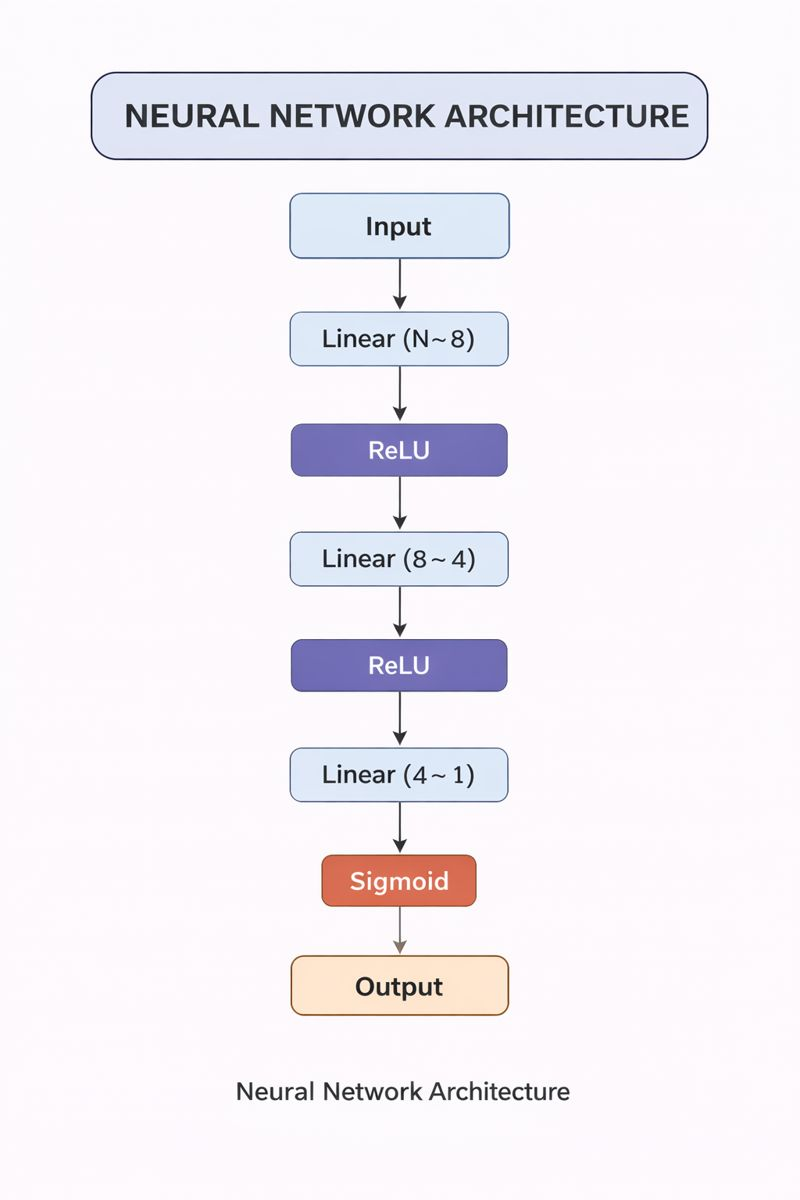
Neural Network Architecture Summary
Your PyTorch model:
class Model1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_features, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)
This is a 3-layer, fully connected feed-forward network:
🧠
Architecture Breakdown
Input → Linear(num_features → 8) → ReLU
→ Linear(8 → 4) → ReLU
→ Linear(4 → 1) → Sigmoid
→ Output
Formula & Notation Cheat Sheet
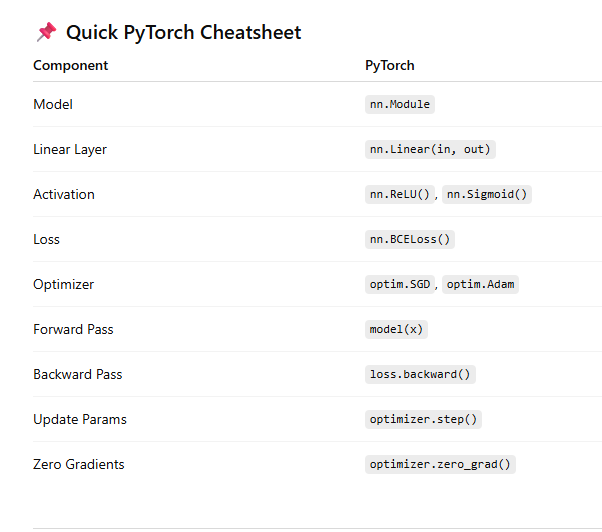
PyTorch Training Pipeline — Complete Cheat Sheet
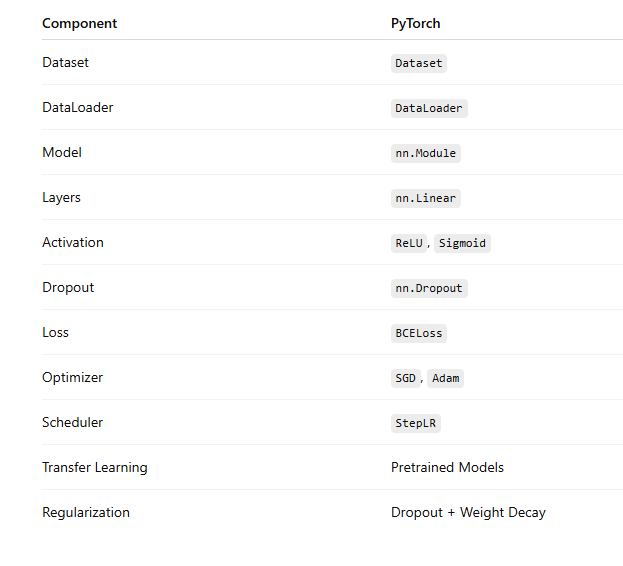
Dataset (Data Preparation Layer)
📌 Purpose
Dataset defines how data is read, transformed, and labeled.
✅ PyTorch Way
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, X, y):
self.X = X
self.y = y
def __len__(self):
return len(self.X)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
return self.X[idx], self.y[idx]
🔢 Mathematical View
DataLoader (Batching + Shuffling)
📌 Purpose
Efficient batching, shuffling, and parallel loading.
✅ PyTorch Way
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=train_dataset,
batch_size=32,
shuffle=True
)
🔢 Formula
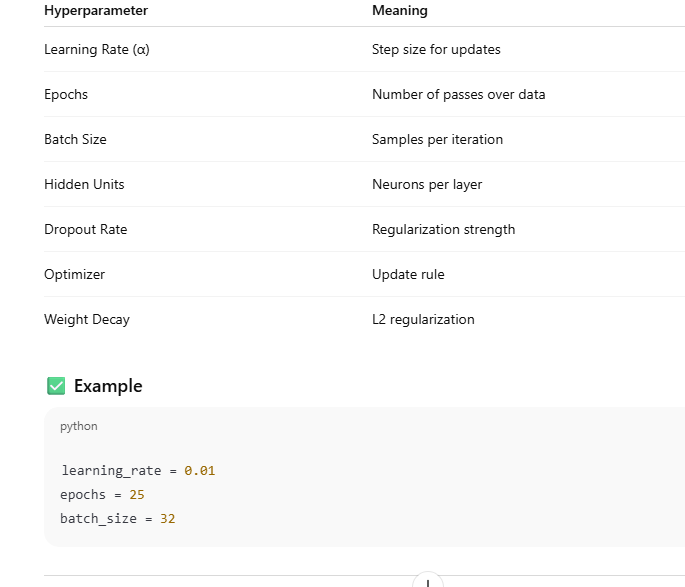
Hyperparameters (Most Important Controls)
📌 Definition
Hyperparameters are set before training and not learned.
🔑 Common Hyperparameters
Neural Network (Optimized Architecture)
📌 Optimized Model with Dropout
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.net = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_features, 64),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5),
nn.Linear(64, 32),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.3),
nn.Linear(32, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.net(x)
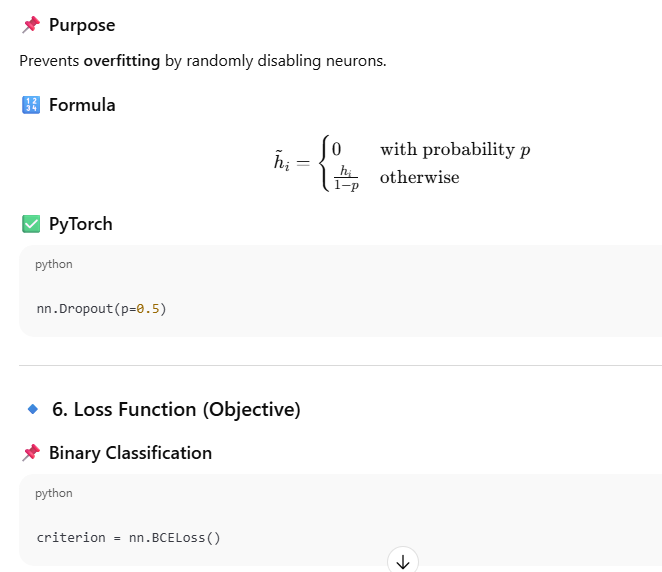
🔹 5. Dropout (Regularization)
Training Loop (End-to-End)
for epoch in range(epochs):
for X_batch, y_batch in train_loader:
y_pred = model(X_batch)
loss = criterion(y_pred, y_batch)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
Transfer Learning (Pretrained Models)
📌 Use Case
Reuse knowledge from large pretrained networks.
✅ Example (Freezing Layers)
for param in pretrained_model.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
📌 Replace Final Layer
pretrained_model.fc = nn.Linear(512, 1)
🔢 Concept
New Task
←
Knowledge from Old Task
New Task←Knowledge from Old Task
Optimized Neural Network Checklist
✔ Batch Normalization
✔ Dropout
✔ Proper Initialization
✔ Adam Optimizer
✔ Learning Rate Scheduling
✅ Scheduler
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(
optimizer, step_size=10, gamma=0.1
)
Convert this into PDF cheat sheet






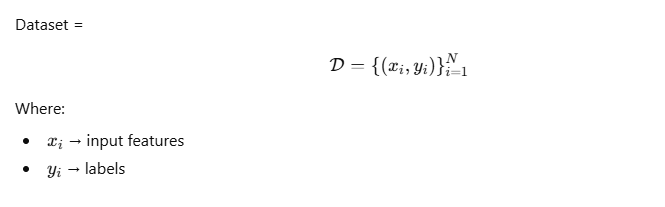
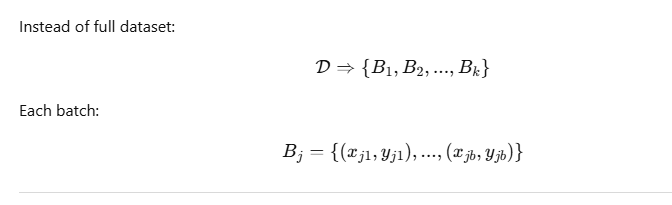

Top comments (0)