How Agentic AI Generates Images
Agentic AI isn’t a single image model — it’s an autonomous system that coordinates specialized agents to manage each stage of image creation, including data preparation, generation, refinement, and evaluation.
Generation Agent: selects the best architecture (e.g., diffusion models, transformers, or even GANs) for a specific type of image.
Refinement Agent: enhances textures and details via super-resolution or style adjustment.
Evaluation Agent: uses reasoning-based feedback loops to iteratively improve image quality and alignment with creative goals.
These agents communicate and adapt dynamically, enabling text-to-image, image-to-image, and scene synthesis that equals or surpasses GAN visual quality.
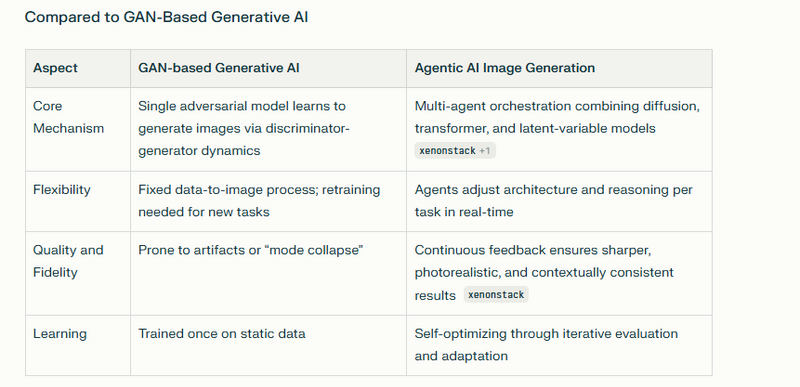
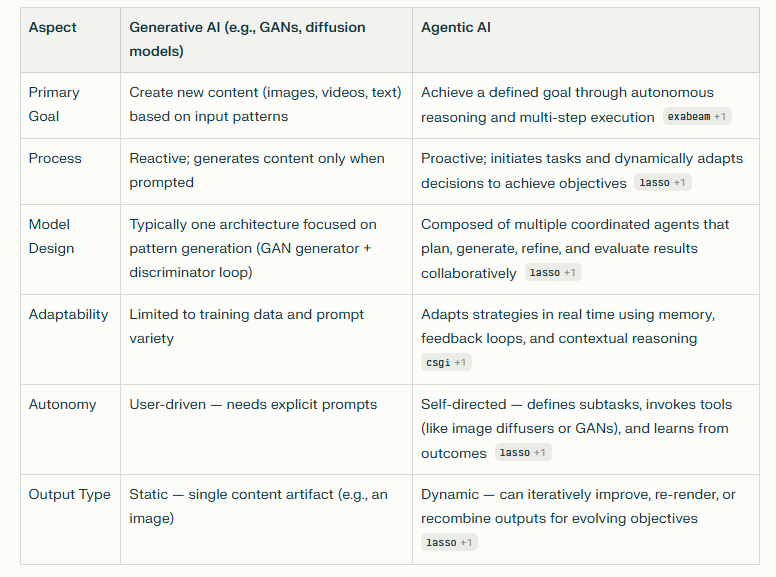
Agentic AI differs from generative image models like GANs primarily in purpose, structure, and autonomy. While generative models such as GANs focus on producing new images in response to human prompts, agentic AI operates at a higher level of intelligence — reasoning, planning, and executing complex image creation workflows autonomously
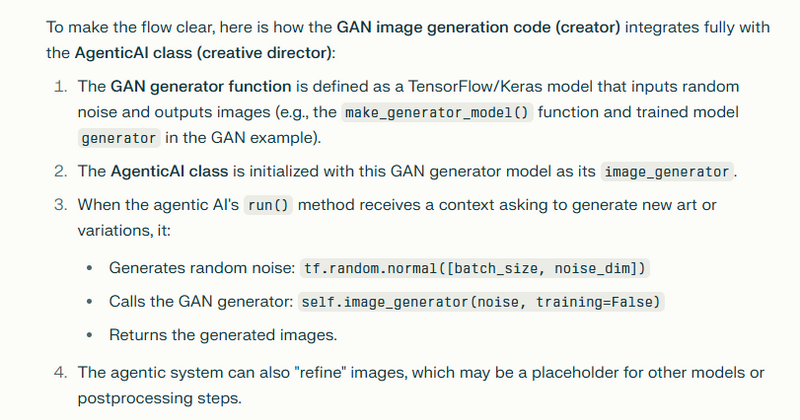
Here is a complete explanation with a code example illustrating the distinction between a GAN-based generative model as a "creator" and an agentic AI system as a "creative director," including Python code for a GAN image generator and a conceptual sketch of an agentic AI orchestrating the generation process.
- GAN-based Generative Model as Creator Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are deep learning models where a generator creates images from random noise, and a discriminator learns to distinguish real images from generated ones. The generator improves over training to produce realistic images.
Below is an example GAN training loop using TensorFlow/Keras that generates images of handwritten digits (like MNIST). This snippet is adapted from a standard DCGAN tutorial:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Define the Generator model
def make_generator_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(7*7*256, use_bias=False, input_shape=(100,)),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Reshape((7, 7, 256)),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(128, (5,5), strides=(1,1), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(64, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False),
layers.BatchNormalization(),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Conv2DTranspose(1, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', use_bias=False, activation='tanh')
])
return model
# Define the Discriminator model
def make_discriminator_model():
model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Conv2D(64, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same', input_shape=[28,28,1]),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Dropout(0.3),
layers.Conv2D(128, (5,5), strides=(2,2), padding='same'),
layers.LeakyReLU(),
layers.Dropout(0.3),
layers.Flatten(),
layers.Dense(1)
])
return model
# Instantiate models
generator = make_generator_model()
discriminator = make_discriminator_model()
# Loss and optimizers
cross_entropy = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
generator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
discriminator_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(1e-4)
# Training step
@tf.function
def train_step(images):
noise = tf.random.normal([batch_size, noise_dim])
with tf.GradientTape() as gen_tape, tf.GradientTape() as disc_tape:
generated_images = generator(noise, training=True)
real_output = discriminator(images, training=True)
fake_output = discriminator(generated_images, training=True)
gen_loss = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(fake_output), fake_output)
disc_loss_real = cross_entropy(tf.ones_like(real_output), real_output)
disc_loss_fake = cross_entropy(tf.zeros_like(fake_output), fake_output)
disc_loss = disc_loss_real + disc_loss_fake
gradients_of_generator = gen_tape.gradient(gen_loss, generator.trainable_variables)
gradients_of_discriminator = disc_tape.gradient(disc_loss, discriminator.trainable_variables)
generator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_generator, generator.trainable_variables))
discriminator_optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients_of_discriminator, discriminator.trainable_variables))
# Visualization function
def generate_and_save_images(model, epoch, test_input):
predictions = model(test_input, training=False)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(4,4))
for i in range(predictions.shape[0]):
plt.subplot(4,4,i+1)
plt.imshow(predictions[i,:,:,0]*127.5 + 127.5, cmap='gray')
plt.axis('off')
plt.suptitle(f'Epoch {epoch}')
plt.show()
# Constants and dataset loading
batch_size = 256
noise_dim = 100
num_examples_to_generate = 16
(train_images, _), _ = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images.reshape(train_images.shape[0],28,28,1).astype('float32')
train_images = (train_images - 127.5) / 127.5
train_dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices(train_images).shuffle(60000).batch(batch_size)
# Training loop
epochs = 50
seed = tf.random.normal([num_examples_to_generate, noise_dim])
for epoch in range(epochs):
for image_batch in train_dataset:
train_step(image_batch)
generate_and_save_images(generator, epoch+1, seed)
This GAN code shows the creator role: given random noise, the generator creates images iteratively improving through feedback from the discriminator.
Agentic AI as Creative Director
An agentic AI system sits above such generative models as a creative director. It is responsible for why, when, and how to use the GAN or any other generative tool. It dynamically orchestrates multiple AI components (agents) to plan, generate, evaluate, and refine outputs through condition-based workflows.
Below is a conceptual Python pseudocode outline demonstrating how an agentic AI might orchestrate image generation using a GAN model and other tools to decide when and how to create or refine images.
# 1. Define or load your trained GAN generator model
generator = make_generator_model()
# (Assuming generator is trained)
# 2. Define Agentic AI class passing generator model
class AgenticAI:
def __init__(self, image_generator):
self.image_generator = image_generator
self.memory = []
self.targets = ["create art", "refine image", "generate variations"]
def decide_task(self, context):
if "refine" in context:
return "refine image"
elif "new" in context:
return "create art"
else:
return "generate variations"
def execute_task(self, task, input_data=None):
if task == "create art":
print("Starting new image generation...")
noise = tf.random.normal([1, 100]) # GAN input noise
img = self.image_generator(noise, training=False)
self.memory.append(img)
return img
elif task == "refine image":
print("Refining existing image...")
refined_img = input_data * 1.1 # Placeholder refinement
self.memory.append(refined_img)
return refined_img
elif task == "generate variations":
print("Generating image variations...")
noise = tf.random.normal([3, 100])
imgs = self.image_generator(noise, training=False)
self.memory.extend(imgs)
return imgs
def run(self, context, input_data=None):
task = self.decide_task(context)
return self.execute_task(task, input_data)
# 3. Use agentic AI with GAN generator
agentic_ai = AgenticAI(generator)
# Agentic AI orchestrates when and how to use GAN for creation/refinement
image1 = agentic_ai.run("generate new art")
image2 = agentic_ai.run("refine image", input_data=image1)
image_set = agentic_ai.run("generate variations")

Top comments (0)