Fixing “Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost'” in MySQL: Creating a New User, Grant Roles, and Password Best Practices
Introduction
While working with MySQL or MariaDB on Linux, many developers and system administrators encounter the following error:
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
This error is confusing, especially when the root password is correct. However, this behavior is intentional in modern Linux systems and is actually designed for security.
In this blog, we will clearly explain:
Why this error occurs
Why creating a new database user is the correct solution
How to create a new user step by step
The role of GRANT permissions
Real command examples with expected output
Password reset and password security best practices
Understanding the Root Access Denied Error
The Error
Access denied for user 'root'@'localhost' (using password: YES)
Why This Happens
On most Linux systems:
MySQL root user uses unix_socket authentication
Password login for root is disabled
Root login works only via the OS root user
This means:
mysql -u root -p
❌ fails even with the correct password
But:
sudo mysql
✅ works without a password
This is by design, not a bug.
Why You Should NOT Fix Root Password Login
Trying to “fix” root login by forcing password authentication is:
❌ insecure
❌ risky in production
❌ against best practices
Instead, the correct approach is to create a separate database admin user.
Step 1: Log in Using Socket Authentication
First, access MySQL as root via the Linux system:
sudo mysql
Expected Output
MariaDB [(none)]>
You now have full admin access.
Step 2: Create a New Admin User (Solution)
This new user will:
Use password authentication
Replace root for daily DB operations
Avoid access denied errors permanently
Command
CREATE USER 'dbadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'StrongAdmin@123';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON *.* TO 'dbadmin'@'localhost' WITH GRANT OPTION;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;
Step 3: Verify the New User Works
mysql -u dbadmin -p
Enter password:
StrongAdmin@123
Expected Output
MariaDB [(none)]>
✅ Root access problem solved without touching root.
Why GRANT Is Important (Role of GRANT Explained)
The GRANT command defines what a user can do.
Example
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON traccar.* TO 'traccar'@'localhost';
This means:
User can read/write only the traccar database
Cannot access other databases
Cannot create users
Cannot break the server
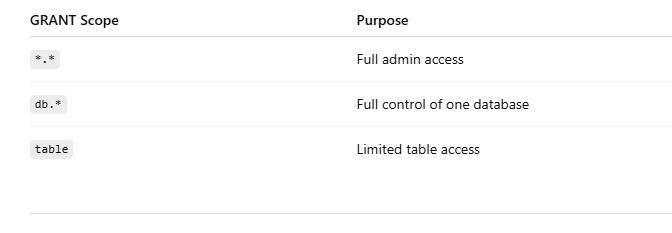
Common GRANT Levels
Step 4: Create Application-Specific User (Best Practice)
Applications should never use root.
Example: Creating App User
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS traccar
CHARACTER SET utf8mb4
COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
CREATE USER 'traccar'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'cotocus@123';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON traccar.* TO 'traccar'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Step 5: Confirm Application User Access
mysql -u traccar -p -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 traccar
Password:
cotocus@123
Expected Output
MariaDB [traccar]>
When Should You Create a New User?
You should create a new user when:
Root login fails with access denied
Running applications (Java, Laravel, Traccar, etc.)
Deploying production systems
Multiple apps share one database server
Following security compliance rules
Password Reset (If Needed)
If you forgot a user password:
ALTER USER 'traccar'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'NewStrongPass@123';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Second Block: traccar (Application-Specific User)
Code
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS traccar
CHARACTER SET utf8mb4
COLLATE utf8mb4_unicode_ci;
DROP USER IF EXISTS 'traccar'@'localhost';
CREATE USER 'traccar'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'cotocus@123';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON traccar.* TO 'traccar'@'localhost';
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
EXIT;

Top comments (0)