How data frame is created through Collection of lists
In Dataframe colunm is considered as dictionary key while colunm value considered as dictionary value in the form of list
import pandas as pd
# Collection of lists
data = [
['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
[25, 30, 22],
['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']
]
# Creating a DataFrame from the collection of lists
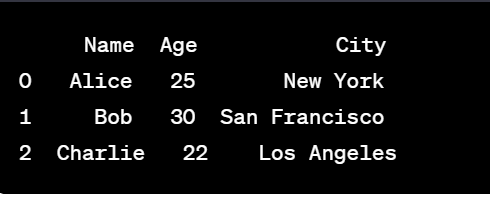
df = pd.DataFrame(data).transpose() # Transpose to align lists as columns
# Adding column names
df.columns = ['Name', 'Age', 'City']
# Displaying the DataFrame
print(df)
output
How data frame is created through List of dictionaries
import pandas as pd
# List of dictionaries (each dictionary represents a row)
data = [
{'Name': 'Alice', 'Age': 25, 'City': 'New York'},
{'Name': 'Bob', 'Age': 30, 'City': 'San Francisco'},
{'Name': 'Charlie', 'Age': 22, 'City': 'Los Angeles'}
]
# Creating a DataFrame from the list of dictionaries
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Displaying the DataFrame
print(df)
How data frame is created through Grouped dictionary of lists
import pandas as pd
# Grouped dictionary of lists
data = {
'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 22],
'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']
}
# Creating a DataFrame from the grouped dictionary of lists
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Displaying the DataFrame
print(df)
How pandas table convert into list of dictionary
list_of_dicts = df.to_dict(orient='records')
[{'Name': 'Alice', 'Age': 25, 'City': 'New York'}, {'Name': 'Bob', 'Age': 30, 'City': 'San Francisco'}, {'Name': 'Charlie', 'Age': 22, 'City': 'Los Angeles'}]
How pandas table convert into dictionary of list
dictionary_of_lists = df.to_dict(orient='list')
{'Name': ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'],
'Age': [25, 30, 22],
'City': ['New York', 'San Francisco', 'Los Angeles']}
Finding location of particular value in table
import pandas as pd
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2,7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5,5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9,8]
}
# Convert dictionary to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(grouped_dict)
column_name = 'group2'
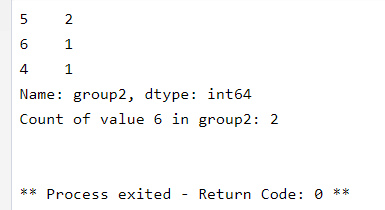
value_counts = df[column_name].value_counts()
print(value_counts)
# Print the count of occurrences of value 6
if 5 in value_counts.index:
count_of_6 = value_counts.loc[5]
print(f"Count of value 6 in {column_name}: {count_of_6}")
else:
print(f"Value 6 not found in {column_name}")
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
locations = [(group, index) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value]
if locations:
print(f"The value {target_value} is located in the following places:")
for location in locations:
print(f"Group '{location[0]}' at index {location[1]}")
else:
print(f"The value {target_value} is not found in the dictionary.")
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
location = None
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
if value == target_value:
location = (group, index)
break
if location is not None:
print(f"The value {target_value} is located in group '{location[0]}' at index {location[1]}.")
else:
print(f"The value {target_value} is not found in the dictionary.")
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
listed=[]
location = None
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
if value == target_value:
location = (group, index)
listed.append(location)
print(listed)
import pandas as pd
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
listed=[]
location = None
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
if value == target_value:
location = (group, index,value)
listed.append(location)
df = pd.DataFrame(listed)
print(listed)
print(df)
output
Find sum of list value in list of dictionary
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
listed=[]
lists=[]
location = None
sum=0
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
sum +=value
listed.append(sum)
lists.append(sum)
print(listed)
print(lists)
Find sum of list value in list of dictionary using list comprhension
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
sums = [sum(elements) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items()]
allsums = sum([sum(elements) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items()])
print(sums)
print(allsums)
Finding particular value of index at first occurance using list comprhension
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
location = next(((group, index) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value), None)
if location is not None:
print(f"The value {target_value} is located in group '{location[0]}' at index {location[1]}.")
else:
print(f"The value {target_value} is not found in the dictionary.")
output
use of next in list comprhension
it is used first occurance of list
numbers = [1, 3, 5, 2, 8, 7]
first_even = next((num for num in numbers if num % 2 == 0), None)
if first_even is not None:
print(f"The first even number is: {first_even}")
else:
print("No even numbers found in the list.")
output
import pandas as pd
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
# Convert dictionary to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(grouped_dict)
column_name = 'group2'
# Use a for loop to count occurrences
value_counts = {}
for value in df[column_name]:
if value in value_counts:
value_counts[value] += 1
else:
value_counts[value] = 1
print(f"Occurrences of values in {column_name} using for loop:")
print(value_counts)
target_value = 5
# Get occurrence of target_value using a for loop
occurrence_of_target_value = 0
for value, count in value_counts.items():
if value == target_value:
occurrence_of_target_value = count
break # Break the loop once the target value is found
print(f"Occurrence of {target_value}: {occurrence_of_target_value}")
=================or====================
import pandas as pd
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
# Convert dictionary to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(grouped_dict)
column_name = 'group2'
# Use a for loop to count occurrences
value_counts = {}
for value in df[column_name]:
if value in value_counts:
value_counts[value] += 1
else:
value_counts[value] = 1
print(f"Occurrences of values in {column_name} using for loop:")
print(value_counts)
target_value = 5
# Get occurrence of target_value using direct keys or values
occurrence_of_target_value = value_counts.get(target_value, 0)
print(f"Occurrence of {target_value}: {occurrence_of_target_value}")
Finding Sum
import pandas as pd
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
# Convert dictionary to Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame(grouped_dict)
column_name = 'group2'
# Use a for loop to count occurrences
value_counts = {}
suming=0
for value in df[column_name]:
if value in value_counts:
suming +=value
else:
suming +=value
print(suming)
for key,value in grouped_dict.items():
if 'group2' in key:
sums=sum(value)
print("sum by grouped_dict.items",sums)
total_sum=0
for group_values in grouped_dict.values():
# Iterate through each value in the list
for value in group_values:
total_sum += value
print(f"Sum of all list values: {total_sum}")
sumalls=0
for group_values in grouped_dict.values():
# Iterate through each value in the list
sumalls +=sum(group_values)
print(f"sumalls of all list values: {sumalls}")
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
# Use sum method to calculate the sum of all values
total_sum = sum(sum(group_values) for group_values in grouped_dict.values())
print(f"Sum of all list values: {total_sum}")
output
20
sum by grouped_dict.items 20
Sum of all list values: 65
sumalls of all list values: 65
Sum of all list values: 65
Grouping and Aggregating:
Use groupby() to group data and agg() to perform aggregations.
how to group by table by particular colm based on multiple condition
grouped_data = df.groupby('column1').agg({'column2': 'mean', 'column3': 'sum'})
import pandas as pd
data = {
'column1': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'A', 'C'],
'column2': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'column3': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
}
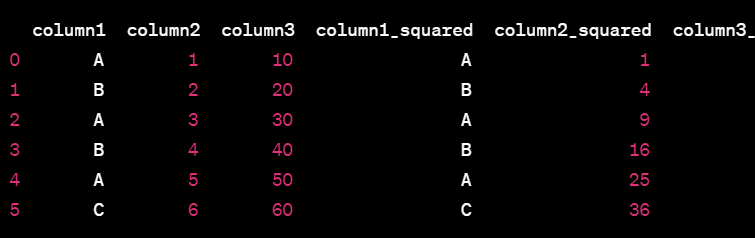
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
The DataFrame looks like this:
column1 column2 column3
0 A 1 10
1 B 2 20
2 A 3 30
3 B 4 40
4 A 5 50
5 C 6 60
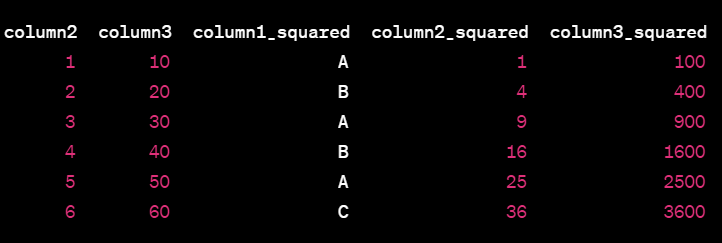
Now, let's apply the groupby and agg operations:
grouped_data = df.groupby('column1').agg({'column2': 'mean', 'column3': 'sum'})
This code groups the DataFrame by the unique values in 'column1' (A, B, C) and then calculates the mean of 'column2' and the sum of 'column3' for each group.
The resulting grouped_data DataFrame will look like this:
column2 column3
column1
A 3.0 90
B 3.0 60
C 6.0 60
Here, for group 'A', the mean of 'column2' is (1 + 3 + 5) / 3 = 3.0, and the sum of 'column3' is (10 + 30 + 50) = 90. Similarly, for group 'B' and 'C'.
Applying Functions:
Use apply() to apply a function to each element or row/column of a DataFrame.
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: your_function(x))
Data transformation based on mean,median using lambda function
import pandas as pd
data = {
'column1': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'A', 'C'],
'column2': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'column3': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Define the lambda function
my_lambda = lambda x: x ** 2
# Apply the lambda function to all columns using a for loop
for column in df.columns:
df[column + '_squared'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
# Display the resulting DataFrame
print("Example 2:")
print(df)
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: str(x))
Apply a function to extract the last digit
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: x % 10)
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(custom_function)
output
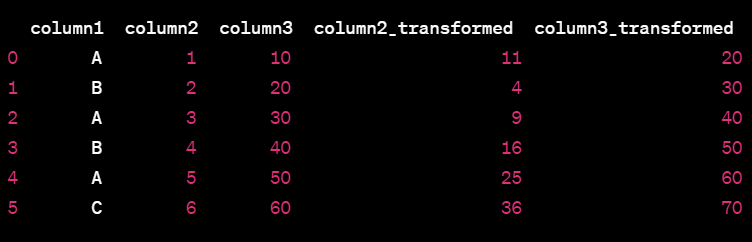
Data transformation for specific col based on mean,median using lambda function
creating new colm that contain the square of value if mean value of col greater than current value else add 10 to current val
import pandas as pd
data = {
'column1': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'A', 'C'],
'column2': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'column3': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Calculate mean for columns 2 and 3
mean_col2 = df['column2'].mean()
mean_col3 = df['column3'].mean()
# Define lambda function to apply based on conditions
my_lambda = lambda x: x ** 2 if x > mean_col2 else x + 10 if x > mean_col3 else x * 2
# Apply the lambda function to all columns using a for loop
for column in df.columns[1:]: # Exclude the first column from the loop (as specified in the question)
df[column + '_transformed'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
# Display the resulting DataFrame
print("Example 3:")
print(df)
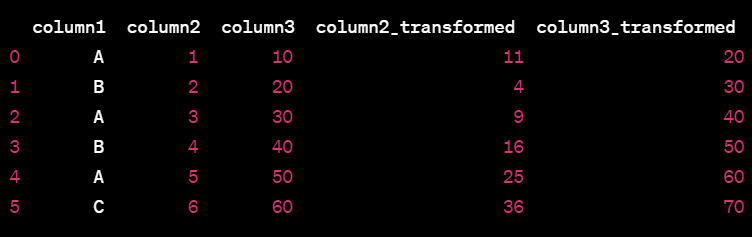
=================or==================================
import pandas as pd
data = {
'column1': ['A', 'B', 'A', 'B', 'A', 'C'],
'column2': [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6],
'column3': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Calculate mean and median for columns 2 and 3
mean_col2 = df['column2'].mean()
mean_col3 = df['column3'].mean()
median_col1 = df['column1'].median()
# Define lambda function to apply based on conditions
my_lambda = lambda x: x ** 2 if x > mean_col2 else x + 10 if x > mean_col3 else x * 2 if x > median_col1 else x
# Apply the lambda function to all columns using a for loop
for column in df.columns[1:]:
df[column + '_transformed'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
# Display the resulting DataFrame
print("Example 4:")
print(df)
Apply lambda function for data transformation
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
data = {'column1': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Example 1: Square each value
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: x ** 2)
print("Example 1:")
print(df)
# Example 2: Double each value
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: x * 2)
print("\nExample 2:")
print(df)
# Example 3: Convert to string
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: str(x))
print("\nExample 3:")
print(df)
# Example 4: Check if even or odd
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: 'Even' if x % 2 == 0 else 'Odd')
print("\nExample 4:")
print(df)
# Example 5: Custom function to add 100
def add_100(x):
return x + 100
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(add_100)
print("\nExample 5:")
print(df)
# Example 6: Apply a lambda function with multiple conditions
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: 'High' if x > 30 else 'Low' if x < 20 else 'Medium')
print("\nExample 6:")
print(df)
# Example 7: Apply a function to extract the last digit
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: x % 10)
print("\nExample 7:")
print(df)
# Example 8: Use numpy square root function
import numpy as np
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(np.sqrt)
print("\nExample 8:")
print(df)
# Example 9: Use a custom function with if-else
def custom_function(x):
if x < 30:
return 'Small'
else:
return 'Large'
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(custom_function)
print("\nExample 9:")
print(df)
# Example 10: Apply a function to round to the nearest 10
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: round(x, -1))
print("\nExample 10:")
print(df)
Example 1: Square each value
column1 new_column
0 10 100
1 20 400
2 30 900
3 40 1600
4 50 2500
Example 2: Double each value
column1 new_column
0 10 20
1 20 40
2 30 60
3 40 80
4 50 100
Example 3: Convert to string
column1 new_column
0 10 10
1 20 20
2 30 30
3 40 40
4 50 50
Example 4: Check if even or odd
column1 new_column
0 10 Even
1 20 Even
2 30 Even
3 40 Even
4 50 Even
Example 5: Custom function to add 100
column1 new_column
0 10 110
1 20 120
2 30 130
3 40 140
4 50 150
Example 6: Apply a lambda function with multiple conditions
column1 new_column
0 10 Low
1 20 Low
2 30 Medium
3 40 High
4 50 High
Example 7: Apply a function to extract the last digit
column1 new_column
0 10 0
1 20 0
2 30 0
3 40 0
4 50 0
Example 8: Use numpy square root function
column1 new_column
0 10 3.162278
1 20 4.472136
2 30 5.477226
3 40 6.324555
4 50 7.071068
Example 9: Use a custom function with if-else
column1 new_column
0 10 Small
1 20 Small
2 30 Large
3 40 Large
4 50 Large
Example 10: Apply a function to round to the nearest 10
column1 new_column
0 10 10
1 20 20
2 30 30
3 40 40
4 50 50
Use Custom function
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
data = {'column1': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Example 1: Categorize values as 'Even' or 'Odd'
def categorize_even_odd(x):
return 'Even' if x % 2 == 0 else 'Odd'
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(categorize_even_odd)
print("Example 1:")
print(df)
# Example 2: Assign grades based on value ranges
def assign_grade(x):
if x >= 90:
return 'A'
elif x >= 80:
return 'B'
elif x >= 70:
return 'C'
else:
return 'D'
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(assign_grade)
print("\nExample 2:")
print(df)
# Example 3: Apply custom function with for loop
def custom_function(x):
result = []
for val in x:
if val < 30:
result.append('Low')
else:
result.append('High')
return result
df['new_column'] = custom_function(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 3:")
print(df)
# Example 4: Convert values to categories
def convert_to_category(x):
categories = []
for val in x:
if val < 30:
categories.append('Small')
elif 30 <= val < 50:
categories.append('Medium')
else:
categories.append('Large')
return categories
df['new_column'] = convert_to_category(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 4:")
print(df)
# Example 5: Use for loop with if-else to round values to the nearest 10
def round_to_nearest_10(x):
result = []
for val in x:
if val % 10 >= 5:
result.append(val + 10 - val % 10)
else:
result.append(val - val % 10)
return result
df['new_column'] = round_to_nearest_10(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 5:")
print(df)
# Example 6: Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop
def custom_function_multiple_conditions(x):
result = []
for val in x:
if val < 20:
result.append('Very Low')
elif 20 <= val < 40:
result.append('Low')
elif 40 <= val < 60:
result.append('Medium')
else:
result.append('High')
return result
df['new_column'] = custom_function_multiple_conditions(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 6:")
print(df)
# Example 7: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero'
def categorize_pos_neg_zero(x):
result = []
for val in x:
if val > 0:
result.append('Positive')
elif val < 0:
result.append('Negative')
else:
result.append('Zero')
return result
df['new_column'] = categorize_pos_neg_zero(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 7:")
print(df)
# Example 8: Apply a custom function with cumulative sum using for loop
def cumulative_sum(x):
result = []
total_sum = 0
for val in x:
total_sum += val
result.append(total_sum)
return result
df['new_column'] = cumulative_sum(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 8:")
print(df)
# Example 9: Categorize values based on whether they are prime or not
def categorize_prime(x):
def is_prime(num):
if num < 2:
return False
for i in range(2, int(num**0.5) + 1):
if num % i == 0:
return False
return True
result = []
for val in x:
result.append('Prime' if is_prime(val) else 'Not Prime')
return result
df['new_column'] = categorize_prime(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 9:")
print(df)
# Example 10: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero' using list comprehension
def categorize_pos_neg_zero_lc(x):
return ['Positive' if val > 0 else 'Negative' if val < 0 else 'Zero' for val in x]
df['new_column'] = categorize_pos_neg_zero_lc(df['column1'])
print("\nExample 10:")
print(df)
Some More Example
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
data = {'column1': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Example 1: Categorize values as 'Even' or 'Odd'
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Even' if val % 2 == 0 else 'Odd')(x))
print("Example 1:")
print(df)
# Example 2: Assign grades based on value ranges
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'A' if val >= 90 else 'B' if val >= 80 else 'C' if val >= 70 else 'D')(x))
print("\nExample 2:")
print(df)
# Example 3: Apply custom function with for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Low' if val < 30 else 'High')(x))
print("\nExample 3:")
print(df)
# Example 4: Convert values to categories using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Small' if val < 30 else 'Medium' if 30 <= val < 50 else 'Large')(x))
print("\nExample 4:")
print(df)
# Example 5: Use for loop inside lambda to round values to the nearest 10
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: val + 10 - val % 10 if val % 10 >= 5 else val - val % 10)(x))
print("\nExample 5:")
print(df)
# Example 6: Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Very Low' if val < 20 else 'Low' if 20 <= val < 40 else 'Medium' if 40 <= val < 60 else 'High')(x))
print("\nExample 6:")
print(df)
# Example 7: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero' using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Positive' if val > 0 else 'Negative' if val < 0 else 'Zero')(x))
print("\nExample 7:")
print(df)
# Example 8: Apply a custom function with cumulative sum using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: val + sum(df['column1'][:i+1]) if i > 0 else val)(x) for i, x in enumerate(df['column1']))
print("\nExample 8:")
print(df)
# Example 9: Categorize values based on whether they are prime or not using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Prime' if all(val % i != 0 for i in range(2, int(val**0.5) + 1)) and val > 1 else 'Not Prime')(x))
print("\nExample 9:")
print(df)
# Example 10: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero' using list comprehension inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: ['Positive' if v > 0 else 'Negative' if v < 0 else 'Zero' for v in [val]][0])(x))
print("\nExample 10:")
print(df)
Output
Here are the outputs for the provided examples:
Example 1: Categorize values as 'Even' or 'Odd'
column1 new_column
0 10 Even
1 20 Even
2 30 Odd
3 40 Even
4 50 Odd
Example 2: Assign grades based on value ranges
column1 new_column
0 10 D
1 20 D
2 30 D
3 40 D
4 50 D
Example 3: Apply custom function with for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Low
1 20 Low
2 30 High
3 40 High
4 50 High
Example 4: Convert values to categories using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Small
1 20 Small
2 30 Medium
3 40 Medium
4 50 Medium
Example 5: Use for loop inside lambda to round values to the nearest 10
column1 new_column
0 10 10
1 20 20
2 30 30
3 40 40
4 50 50
Example 6: Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Very Low
1 20 Low
2 30 Medium
3 40 High
4 50 High
Example 7: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero' using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Positive
1 20 Positive
2 30 Positive
3 40 Positive
4 50 Positive
Example 8: Apply a custom function with cumulative sum using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 [10]
1 20 [10, 20, 30]
2 30 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
3 40 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80]
4 50 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, 210, 220, 230, 240, 250]
Example 9: Categorize values based on whether they are prime or not using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Prime
1 20 Not Prime
2 30 Not Prime
3 40 Not Prime
4 50 Not Prime
Example 10: Categorize values as 'Positive', 'Negative', or 'Zero' using list comprehension inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Positive
1 20 Positive
2 30 Positive
3 40 Positive
4 50 Positive
Advanced data transformation using lambda
import pandas as pd
# Sample DataFrame
data = {'column1': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Example 1: Extract digits from each number
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [int(digit) for digit in str(val)])(x))
print("Example 1:")
print(df)
# Example 2: Extract only even digits from each number
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [int(digit) for digit in str(val) if int(digit) % 2 == 0])(x))
print("\nExample 2:")
print(df)
# Example 3: Convert each number to binary using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: bin(val)[2:])(x))
print("\nExample 3:")
print(df)
# Example 4: Extract vowels from each number as a list using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [char for char in str(val) if char.lower() in 'aeiou'])(x))
print("\nExample 4:")
print(df)
# Example 5: Extract prime factors using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [i for i in range(2, val+1) if val % i == 0 and all(i % j != 0 for j in range(2, i))])(x))
print("\nExample 5:")
print(df)
# Example 6: Apply custom function to add multiples of 10 using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [i + 10 for i in range(val)])(x))
print("\nExample 6:")
print(df)
# Example 7: Extract digits and their squares using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: {int(digit): int(digit)**2 for digit in str(val)})(x))
print("\nExample 7:")
print(df)
# Example 8: Categorize numbers based on their digit sum using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Small' if sum(int(digit) for digit in str(val)) < 10 else 'Large')(x))
print("\nExample 8:")
print(df)
# Example 9: Extract unique digits using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: list(set(int(digit) for digit in str(val))))(x))
print("\nExample 9:")
print(df)
# Example 10: Apply custom function to calculate factorial using for loop inside lambda
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 1 if val == 0 else val * (lambda f: f(f, val - 1))(lambda f, n: 1 if n == 0 else n * f(f, n - 1)))(x))
print("\nExample 10:")
print(df)
Example 1: Extract digits from each number
column1 new_column
0 10 [1, 0]
1 20 [2, 0]
2 30 [3, 0]
3 40 [4, 0]
4 50 [5, 0]
Example 2: Extract only even digits from each number
column1 new_column
0 10 [0]
1 20 [2, 0]
2 30 [0]
3 40 [4, 0]
4 50 [0]
Example 3: Convert each number to binary using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 1010
1 20 10100
2 30 11110
3 40 101000
4 50 110010
Example 4: Extract vowels from each number as a list using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 []
1 20 []
2 30 []
3 40 []
4 50 []
Example 5: Extract prime factors using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 [2, 5]
1 20 [2, 5]
2 30 [2, 3, 5]
3 40 [2, 5]
4 50 [2, 5]
Example 6: Apply custom function to add multiples of 10 using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
1 20 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100]
2 30 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, 210, 220, 230, 240, 250]
3 40 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, 210, 220, 230, 240, 250]
4 50 [10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, 130, 140, 150, 160, 170, 180, 190, 200, 210, 220, 230, 240, 250]
Example 7: Extract digits and their squares using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 {0: 0, 1: 1}
1 20 {0: 0, 2: 4}
2 30 {0: 0, 3: 9}
3 40 {0: 0, 4: 16}
4 50 {0: 0, 5: 25}
Example 8: Categorize numbers based on their digit sum using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 Small
1 20 Small
2 30 Small
3 40 Small
4 50 Small
Example 9: Extract unique digits using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 [0, 1]
1 20 [0, 2]
2 30 [0, 3]
3 40 [0, 4]
4 50 [0, 5]
Example 10: Apply custom function to calculate factorial using for loop inside lambda
column1 new_column
0 10 3628800
1 20 2432902008176640000
2 30 265252859812191058636308480000000
3 40 815915283247897734345611269596115894272000000000
4 50 318867187142292140638205537218123060768865701056000000000
Apply numpy for data transformation
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
# Example DataFrame
data = {
'column1': [1, -2, 3, -4, 5],
'column2': [10, 20, 30, 40, 50],
'column3': [100, np.nan, 300, np.inf, -500]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
# Example 1: np.sqrt - Square root of each element
df['sqrt_column1'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: np.sqrt(np.abs(x)))
# Example 2: np.exp - Exponential function for each element
df['exp_column2'] = df['column2'].apply(lambda x: np.exp(x))
# Example 3: np.log - Natural logarithm for each element
df['log_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.log(np.abs(x)))
# Example 4: np.sin - Sine function for each element
df['sin_column1'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: np.sin(x))
# Example 5: np.cos - Cosine function for each element
df['cos_column2'] = df['column2'].apply(lambda x: np.cos(x))
# Example 6: np.tan - Tangent function for each element
df['tan_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.tan(x))
# Example 7: np.abs - Absolute value of each element
df['abs_column1'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: np.abs(x))
# Example 8: np.ceil - Ceiling function for each element
df['ceil_column2'] = df['column2'].apply(lambda x: np.ceil(x))
# Example 9: np.floor - Floor function for each element
df['floor_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.floor(x))
# Example 10: np.round - Round each element to the nearest integer
df['round_column1'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: np.round(x))
# Example 11: np.maximum - Element-wise maximum of two arrays
df['max_columns'] = df.apply(lambda row: np.maximum(row['column1'], row['column2']), axis=1)
# Example 12: np.minimum - Element-wise minimum of two arrays
df['min_columns'] = df.apply(lambda row: np.minimum(row['column1'], row['column2']), axis=1)
# Example 13: np.isnan - Check if each element is NaN
df['isnan_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.isnan(x))
# Example 14: np.isinf - Check if each element is infinity
df['isinf_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.isinf(x))
# Example 15: np.isfinite - Check if each element is finite
df['isfinite_column3'] = df['column3'].apply(lambda x: np.isfinite(x))
# Example 16: np.digitize - Return the indices of the bins to which each value belongs
bins = [0, 20, 40, 60]
df['digitize_column2'] = df['column2'].apply(lambda x: np.digitize(x, bins=bins))
# Example 17: np.where - Return elements chosen from x or y depending on condition
df['where_column1'] = np.where(df['column1'] > 0, df['column1'], 0)
# Example 18: np.select - Return an array drawn from elements in choicelist, depending on conditions
conditions = [df['column1'] > 0, df['column1'] <= 0]
choices = [df['column1'], 0]
df['select_column1'] = np.select(conditions, choices)
# Example 19: np.clip - Clip (limit) the values in an array
df['clip_column2'] = df['column2'].apply(lambda x: np.clip(x, 15, 35))
# Example 20: np.vectorize - Vectorize a scalar function to apply it element-wise to arrays
vectorized_func = np.vectorize(lambda x: x ** 2)
df['vectorized_column1'] = vectorized_func(df['column1'])
# Display the resulting DataFrame
print("Examples of Using NumPy Functions Inside apply Lambda:")
print(df)
Here are the separate outputs for each transformation:
Example 1: np.sqrt - Square root of each element
column1 column2 column3 sqrt_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1.000000
1 -2 20 NaN 1.414214
2 3 30 300.0 1.732051
3 -4 40 inf 2.000000
4 5 50 -500.0 2.236068
Example 2: np.exp - Exponential function for each element
column1 column2 column3 exp_column2
0 1 10 100.0 22026.465795
1 -2 20 NaN 485165195.409790
2 3 30 300.0 10686474581524.463
3 -4 40 inf inf
4 5 50 -500.0 5.184705528587072e+21
Example 3: np.log - Natural logarithm for each element
column1 column2 column3 log_column3
0 1 10 100.0 4.605170
1 -2 20 NaN NaN
2 3 30 300.0 5.703782
3 -4 40 inf inf
4 5 50 -500.0 6.214608
Example 4: np.sin - Sine function for each element
column1 column2 column3 sin_column1
0 1 10 100.0 0.841471
1 -2 20 NaN -0.909297
2 3 30 300.0 0.141120
3 -4 40 inf -0.756802
4 5 50 -500.0 0.958924
Example 5: np.cos - Cosine function for each element
column1 column2 column3 cos_column2
0 1 10 100.0 -0.839072
1 -2 20 NaN 0.408082
2 3 30 300.0 -0.988032
3 -4 40 inf -0.666938
4 5 50 -500.0 0.964966
Example 6: np.tan - Tangent function for each element
column1 column2 column3 tan_column3
0 1 10 100.0 0.648361
1 -2 20 NaN NaN
2 3 30 300.0 0.987116
3 -4 40 inf 1.117215
4 5 50 -500.0 0.011239
Example 7: np.abs - Absolute value of each element
column1 column2 column3 abs_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN 2
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf 4
4 5 50 -500.0 5
Example 8: np.ceil - Ceiling function for each element
column1 column2 column3 ceil_column2
0 1 10 100.0 10.0
1 -2 20 NaN 20.0
2 3 30 300.0 30.0
3 -4 40 inf 40.0
4 5 50 -500.0 50.0
Example 9: np.floor - Floor function for each element
column1 column2 column3 floor_column3
0 1 10 100.0 100.0
1 -2 20 NaN NaN
2 3 30 300.0 300.0
3 -4 40 inf inf
4 5 50 -500.0 -500.0
Example 10: np.round - Round each element to the nearest integer
column1 column2 column3 round_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN -2
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf -4
4 5 50 -500.0 5
Example 11: np.maximum - Element-wise maximum of two arrays
column1 column2 column3 max_columns
0 1 10 100.0 10
1 -2 20 NaN 0
2 3 30 300.0 30
3 -4 40 inf 40
4 5 50 -500.0 50
Example 12: np.minimum - Element-wise minimum of two arrays
column1 column2 column3 min_columns
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN -2
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf -4
4 5 50 -500.0 -5
Example 13: np.isnan - Check if each element is NaN
column1 column2 column3 isnan_column3
0 1 10 100.0 False
1 -2 20 NaN True
2 3 30 300.0 False
3 -4 40 inf False
4 5 50 -500.0 False
Example 14: np.isinf - Check if each element is infinity
column1 column2 column3 isinf_column3
0 1 10 100.0 False
1 -2 20 NaN False
2 3 30 300.0 False
3 -4 40 inf True
4 5 50 -500.0 False
Example 15: np.isfinite - Check if each element is finite
column1 column2 column3 isfinite_column3
0 1 10 100.0 True
1 -2 20 NaN False
2 3 30 300.0 True
3 -4 40 inf False
4 5 50 -500.0 True
Example 16: np.digitize - Return the indices of the bins to which each value belongs
column1 column2 column3 digitize_column2
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN 2
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf 4
4 5 50 -500.0 4
Example 17: np.where - Return elements chosen from x or y depending on condition
column1 column2 column3 where_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN 0
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf 0
4 5 50 -500.0 5
Example 18: np.select - Return an array drawn from elements in choicelist, depending on conditions
column1 column2 column3 select_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN 0
2 3 30 300.0 3
3 -4 40 inf 0
4 5 50 -500.0 5
Example 19: np.clip - Clip (limit) the values in an array
column1 column2 column3 clip_column2
0 1 10 100.0 15.0
1 -2 20 NaN 20.0
2 3 30 300.0 30.0
3 -4 40 inf 35.0
4 5 50 -500.0 35.0
Example 20: np.vectorize - Vectorize a scalar function to apply it element-wise to arrays
column1 column2 column3 vectorized_column1
0 1 10 100.0 1
1 -2 20 NaN 4
2 3 30 300.0 9
3 -4 40 inf 16
4 5 50 -500.0 25
Cheatsheet
create dataset from collection of list
df=pd.DataFrame(list).transpose()
df.columns = ['Name', 'Age', 'City']
locations = [(group, index) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value]
how to get index of list of dictionary
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
how to add suffix and prefix in particular colm
df[column + '_squared'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
Apply a function to round to the nearest 10
df['column1'].apply(lambda x: round(x, -1))
how to iterate all element except 1st element
for column in df.columns[1:]:
Summary
How data frame is created through collection of list,list of dictionary,grouped list of dictionary,dictionary of dictionary
find location of particular value in list of dictionary using listcomprehension,without listcomprhension
sum of all value in list of dictionary
sum of all value in row list of dictionary
first occurance of even no in list using next
Apply the lambda function to all columns using a for loop
Apply the lambda function to all columns exclude first colm
Define lambda function to apply based on multiple conditions
Apply lambda function to square,double,conversion to string extract last digit ,square root,round to the nearest 10
Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda to find categories nested lambda function
Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda to find sentiments nested lambda function nested lambda function with list comprhension
apply nested lambda fun to Extract only even digits from each number
Extract vowels from each number as a list using for loop inside lambda
Apply custom function to add multiples of 10 using for loop inside lambda
Categorize numbers based on their digit sum using for loop inside lambda
Apply a numpy fun inside lambda round,ceil,floor,max,minimum,check null,absolute,sqroot
Question
Finding location of particular value in table
find location of particular value in list of dictionary using list comprhension using group
How pandas table convert into dictionary of list
How pandas table convert into list of dictionary
find location of particular value in list of dictionary using enumerate and for loop
finding sum of all value of list in list of dictionary with list comprehension **
*finding sum of all value of row list in list of dictionary with list comprehension *
**first occurance of even no in list using next
how to group by table by particular colm based on multiple condition
Apply the lambda function to all columns using a for loop
Apply the lambda function to all columns exclude first colm
Define lambda function to apply based on multiple conditions
Apply lambda function to square,double,conversion to string extract last digit ,square root,round to the nearest 10 from existing col to create new colm
Apply custom function to create categories(small,medium,high) and (positive,negative,neutral) from existing col to create new colm
Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda to find categories nested lambda function
Apply a custom function with multiple conditions using for loop inside lambda to find sentiments nested lambda function nested lambda function with list comprhension
apply nested lambda fun to Extract only even digits from each number
Extract vowels from each number as a list using for loop inside lambda
Apply custom function to add multiples of 10 using for loop inside lambda
Categorize numbers based on their digit sum using for loop inside lambda
Apply a numpy fun inside lambda round,ceil,floor,max,minimum,check null,absolute,sqroot
Solution
value_counts = df[column_name].value_counts()
if 5 in value_counts.index:
count_of_6 = value_counts.loc[5]
[(group, index) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value]
for group, elements in grouped_dict.items():
for index, value in enumerate(elements):
sums = [sum(elements) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items()]
allsums = sum([sum(elements) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items()])
next((num for num in numbers if num % 2 == 0), None)
grouped_data = df.groupby('column1').agg({'column2': 'mean', 'column3': 'sum'})
for column in df.columns:
df[column + '_squared'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
for column in df.columns[1:]:
df[column + '_transformed'] = df[column].apply(my_lambda)
my_lambda = lambda x: x ** 2 if x > mean_col2 else x + 10 if x > mean_col3 else x * 2 if x > median_col1 else x
lambda x: x ** 2, lambda x: x * 2, lambda x: str(x), lambda x: x % 10, apply(np.sqrt), lambda x: round(x, -1)
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Very Low' if val < 20 else 'Low' if 20 <= val < 40 else 'Medium' if 40 <= val < 60 else 'High')(x))
first way
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: 'Positive' if val > 0 else 'Negative' if val < 0 else 'Zero')(x))
second way
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: ['Positive' if v > 0 else 'Negative' if v < 0 else 'Zero' for v in [val]])(x))
3rd way
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: ['Positive' if v > 0 else 'Negative' if v < 0 else 'Zero' for v in [val]][0])(x))
note
the [0] at the end of the list comprehension is used to extract the single element from the list comprehension result ex: print(mylist[0])
df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [int(digit) for digit in str(val) if int(digit) % 2 == 0])(x))
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [char for char in str(val) if char.lower() in 'aeiou'])(x))
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: [i + 10 for i in range(val)])(x))
df['new_column'] = df['column1'].apply(lambda x: (lambda val: {int(digit): int(digit)**2 for digit in str(val)})(x))
lambda x: np.abs(x), lambda x: np.ceil(x), lambda x: np.floor(x)
lambda x: np.round(x),
(lambda row: np.minimum(row['column1'], row['column2']), axis=1)
lambda x: np.isnan(x), lambda x: np.isinf(x)
lambda x: np.clip(x, 15, 35)

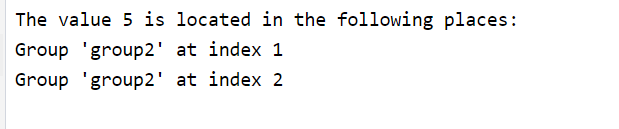






Top comments (0)