Password-based Authentication
Description: Classic email/password login; supported out of the box in Laravel using Laravel Fortify or the built-in Auth scaffolding.
Example:
Route::post('/login', function () {
$credentials = request(['email', 'password']);
if (Auth::attempt($credentials)) {
return redirect()->intended('dashboard');
}
return back()->withErrors(['error' => 'Login failed']);
});
Token-based Authentication (JWT or Laravel Passport/Sanctum)
Description: Backend issues a token after login, which is sent with every API request.
Example with Laravel Sanctum:
public function login(Request $request)
{
$user = User::where('email', $request->email)->first();
if ($user && Hash::check($request->password, $user->password)) {
return ['token' => $user->createToken('apitoken')->plainTextToken];
}
return response(['error' => 'Invalid credentials'], 401);
}
// Usage in API calls
$curl = curl_init();
curl_setopt($curl, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, ['Authorization: Bearer {token}']);
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Description: User enters password, then confirms via another factor (like OTP, SMS, email code).
Example with Laravel Fortify:
// Fortify can be configured as per docs, e.g. config/fortify.php
'features' => [Features::twoFactorAuthentication()],
User will be prompted for a code sent to their device after standard login.
API Key Authentication
Description: Client sends an assigned key in headers; backend verifies it.
Example:
// app/Http/Middleware/ApiKeyMiddleware.php
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$key = $request->header('x-api-key');
if ($key !== config('services.myapi.key')) {
return response('Unauthorized', 401);
}
return $next($request);
}
// Register this middleware on your route
OAuth2 (Authorization Code/Client Credentials)
Description: Standard for allowing delegated access.
Example Using Laravel Passport:
// To use Client Credentials Grant, configure Password and Client Credentials Grant in OAuth clients
// Get token (from service)
$http = new \GuzzleHttp\Client;
$response = $http->post('http://your-app/oauth/token', [
'form_params' => [
'grant_type' => 'client_credentials',
'client_id' => 'client-id',
'client_secret' => 'client-secret',
'scope' => '',
],
]);
$accessToken = json_decode((string) $response->getBody(), true)['access_token'];
HTTP Basic Authentication
Description: Sends username and password in every HTTP header.
Example:
// routes/web.php
Route::get('/secret', function () {
// ...
})->middleware('auth.basic');
Call with:
curl -u user@example.com:password http://your-app/secret
Social Authentication
Description: Lets users log in using social accounts (Facebook, Google, etc.) via Laravel Socialite.
Example:
// config/services.php
'github' => [
'client_id' => '...',
'client_secret' => '...',
'redirect' => 'http://your-app/auth/github/callback',
],
// routes/web.php
Route::get('auth/github', [LoginController::class, 'redirectToProvider']);
Route::get('auth/github/callback', [LoginController::class, 'handleProviderCallback']);
// In Controller
use Socialite;
public function redirectToProvider() {
return Socialite::driver('github')->redirect();
}
public function handleProviderCallback() {
$user = Socialite::driver('github')->user();
// $user->token ...
}
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Description: Login at one service gives access to others (typically via SAML, OAuth, or OpenID Connect).
Example using Passport for simple SSO between Laravel apps:
Configure both apps to use the same Passport server, and validate tokens across services.
Mutual TLS (mTLS) Authentication
Description: Services require certificates for both sides, usually handled at web server/proxy or mesh layer.
Example Nginx Config:
# In nginx site conf
ssl_client_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/ca.crt;
ssl_verify_client on;
In Laravel, trust requests already validated by nginx.
Session-based Authentication
Description: Laravel's default web authentication; stores logged-in state in session/cookies.
Example:
// Standard login with sessions using Auth facade
Auth::attempt(['email' => $email, 'password' => $password]);
// User is now authenticated via session cookie
Password-based: Simple login/register forms
Token-based/JWT: Laravel Passport, jwt-auth, Sanctum for API authentication
API Key: Used for internal service-to-service or 3rd-party API access
OAuth2/Social/SSO: For delegated and federated authentication
mTLS: For strongest internal service trust.
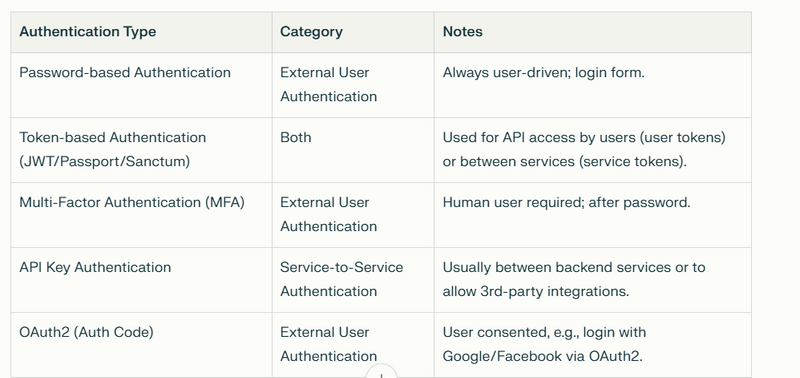
External User Authentication:
Password-based
MFA
Social Authentication
OAuth2 (Auth Code)
Single Sign-On (SSO)
Session-based
Service-to-Service Authentication:
API Key
OAuth2 (Client Credentials)
Mutual TLS (mTLS)
Both:
Token-based (JWT, Passport, Sanctum can be for users or services)
HTTP Basic (typically for simple/batch APIs or legacy services, but not ideal for users)






Top comments (0)