Keycloak gives you more than 20+ mapper types, but real confusion starts when developers ask:
“Ye mapper internally Keycloak ke kis table me store hota hai?”
“User Attribute vs User Property ke database tables alag kyun hote hain?”
“Role mapper ka data kaha save hota hai?”
“Client Scope add karne se backend me kya change hota hai?”
This blog finally solves these questions with full technical breakdown, database tables, architecture diagrams, and real Laravel / microservices use cases.
📑
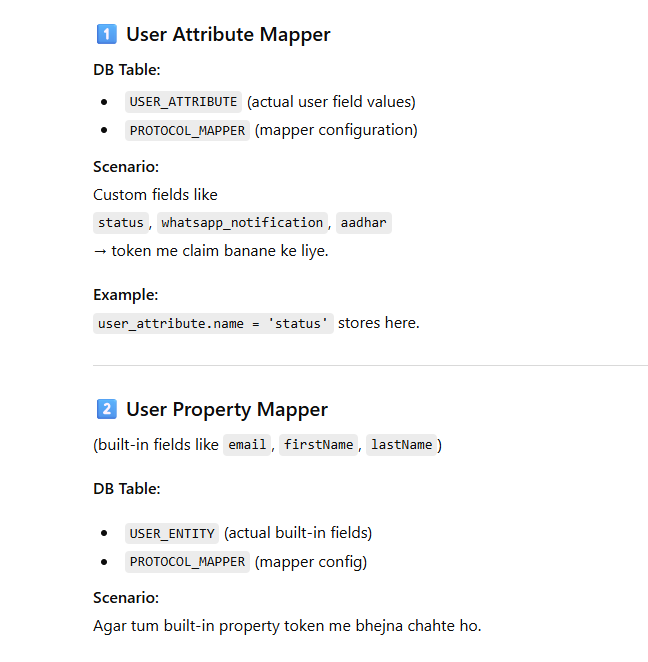
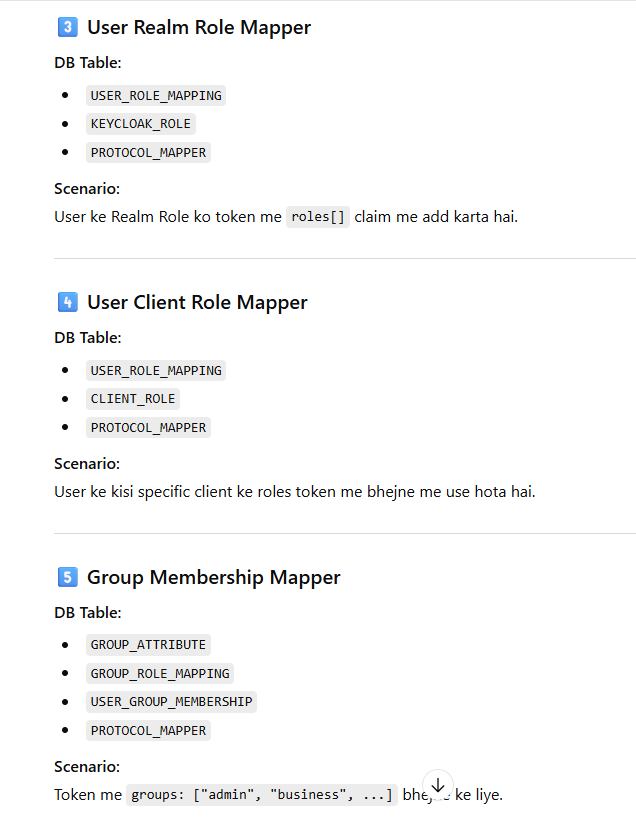
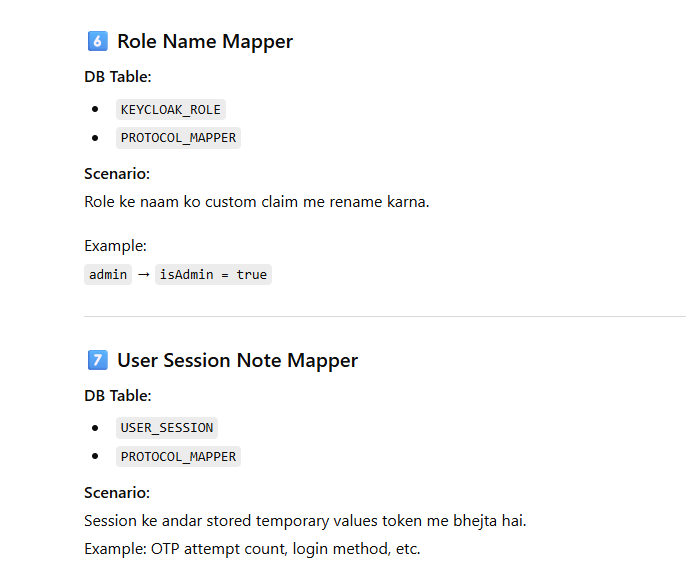
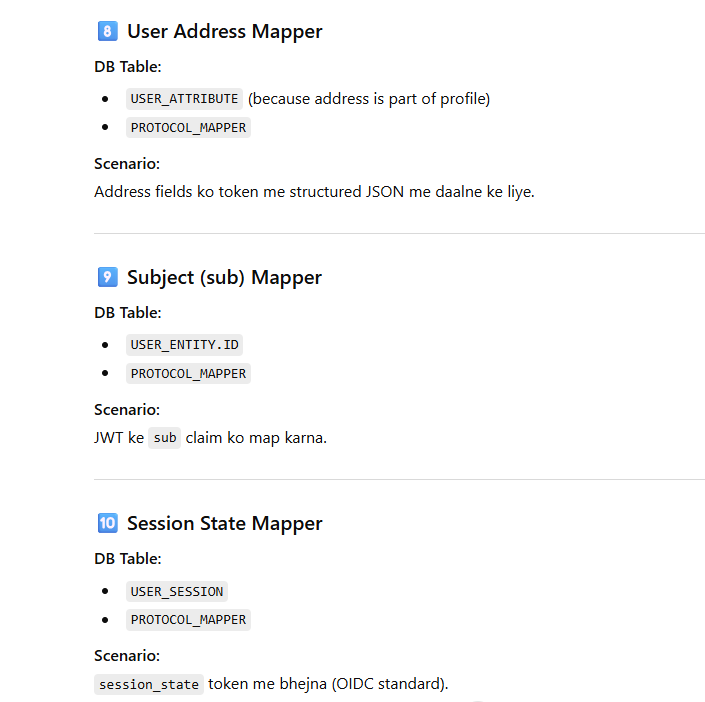
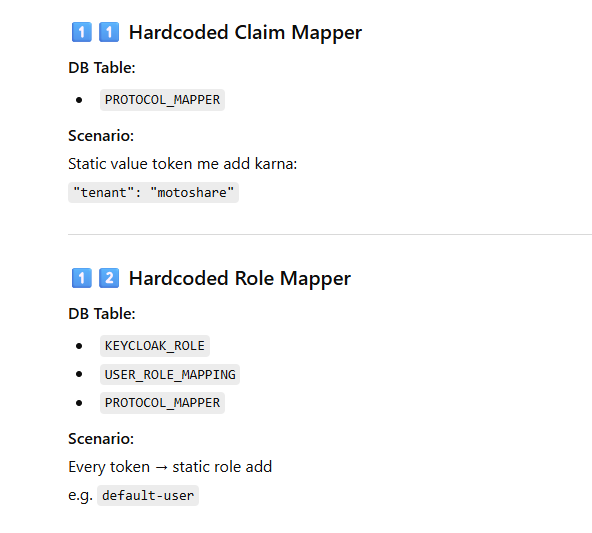
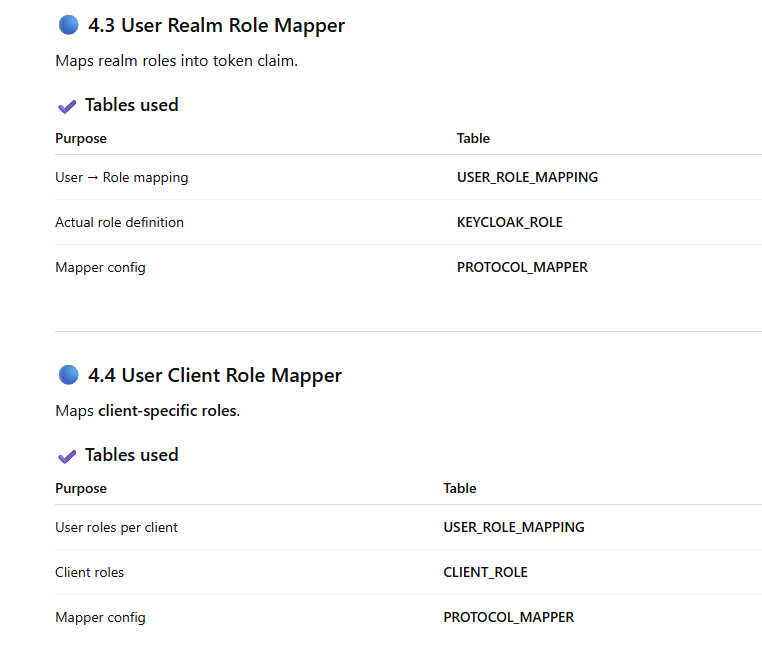
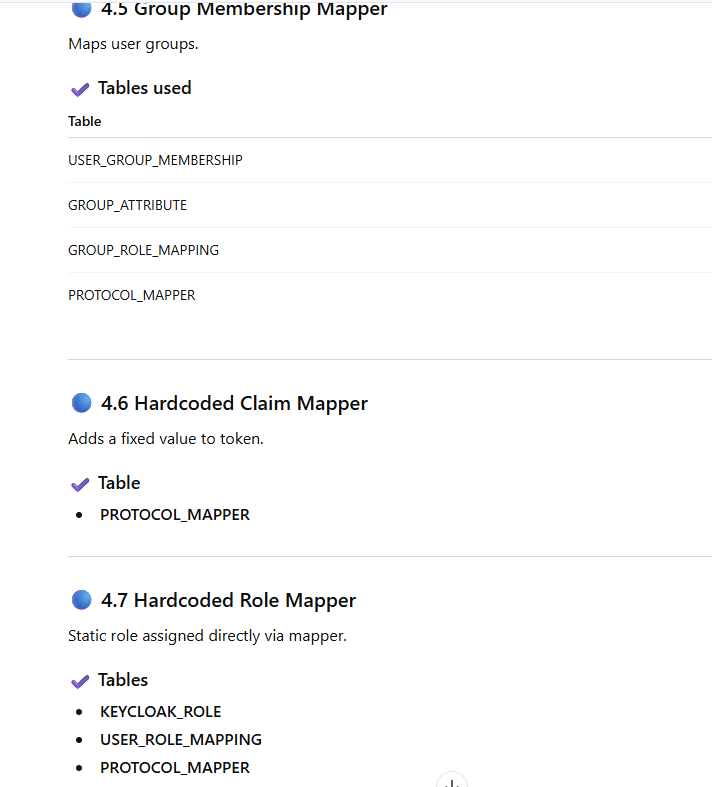
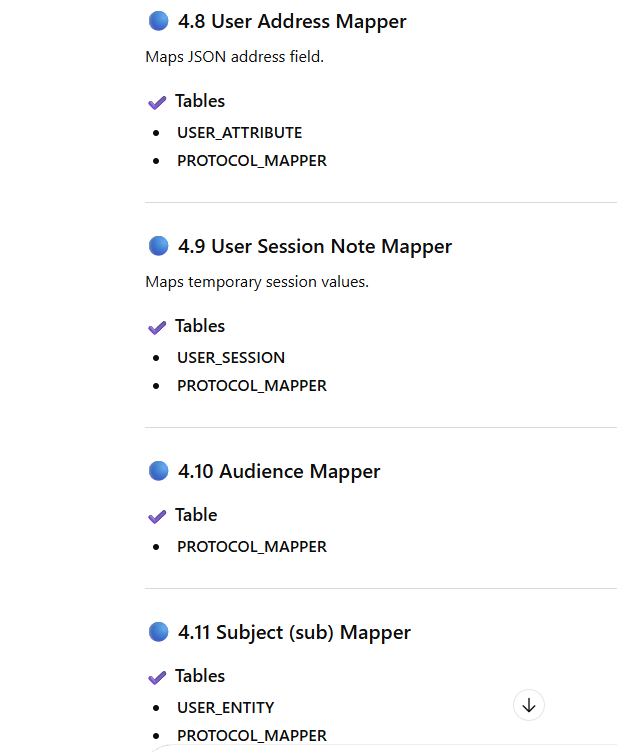
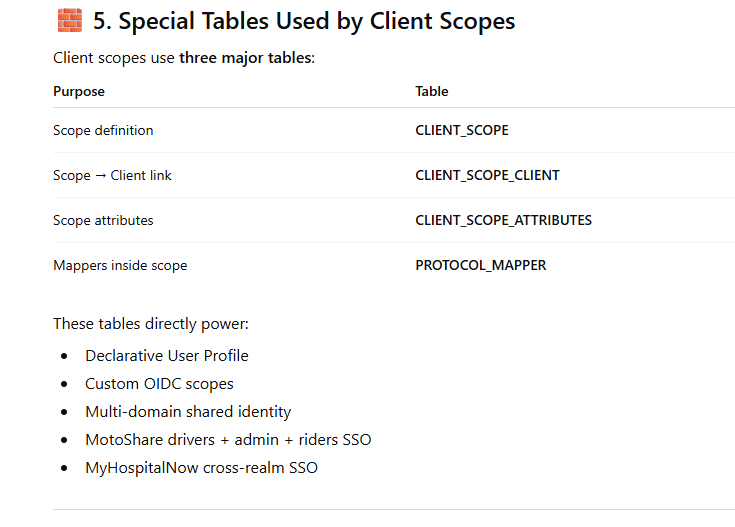
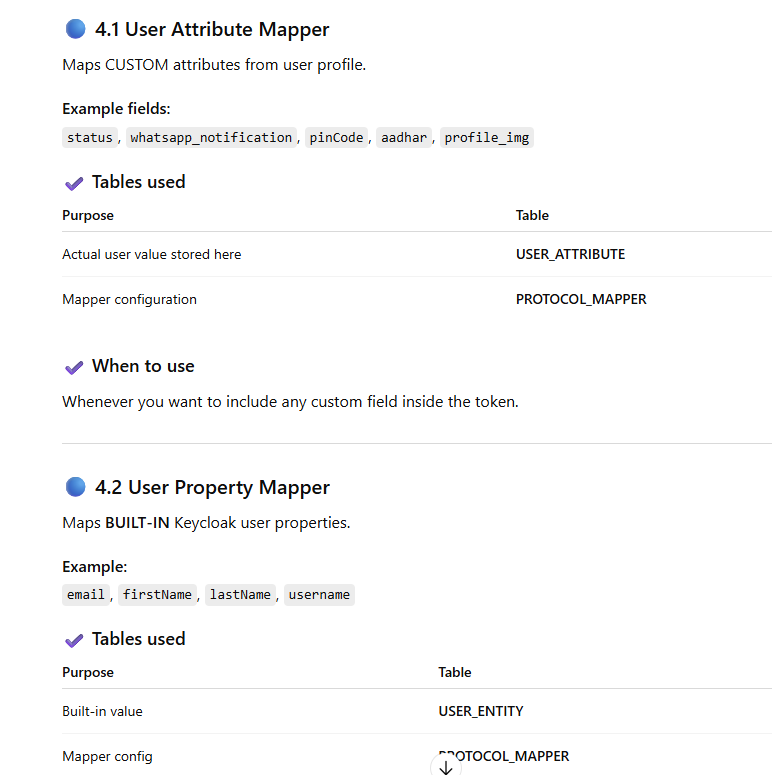
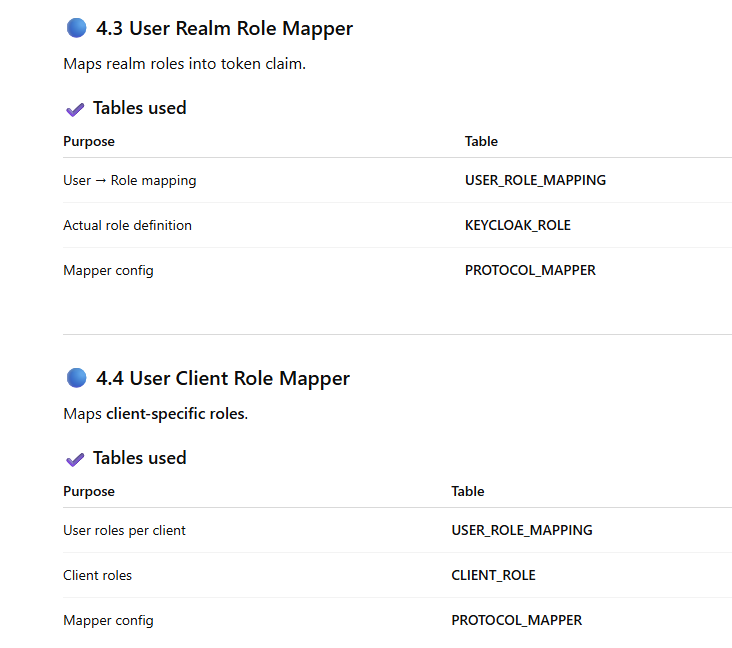
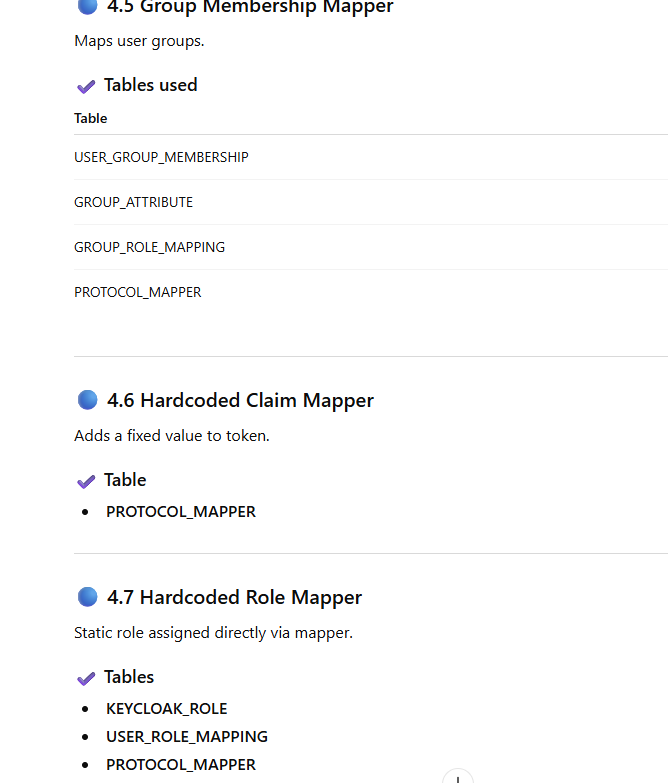
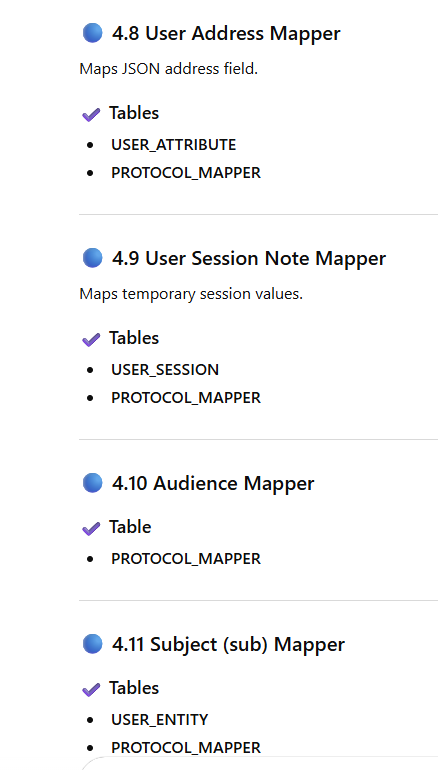
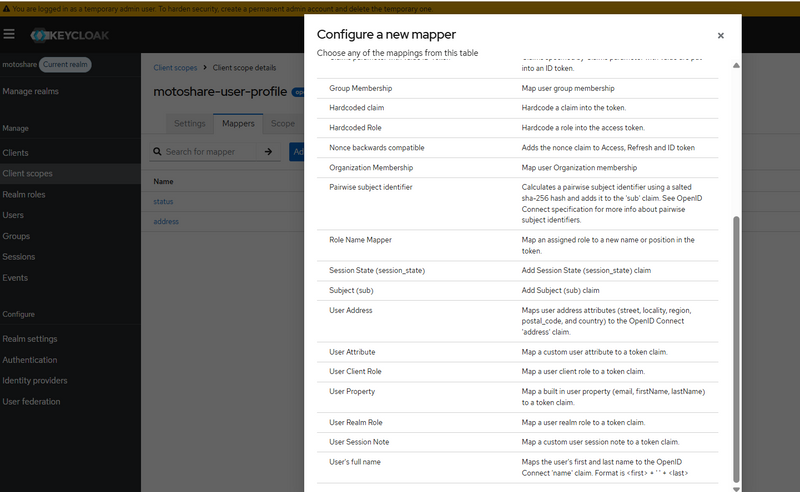
Now Mapping Each Mapper Type → Actual Table With Scenario
🎯
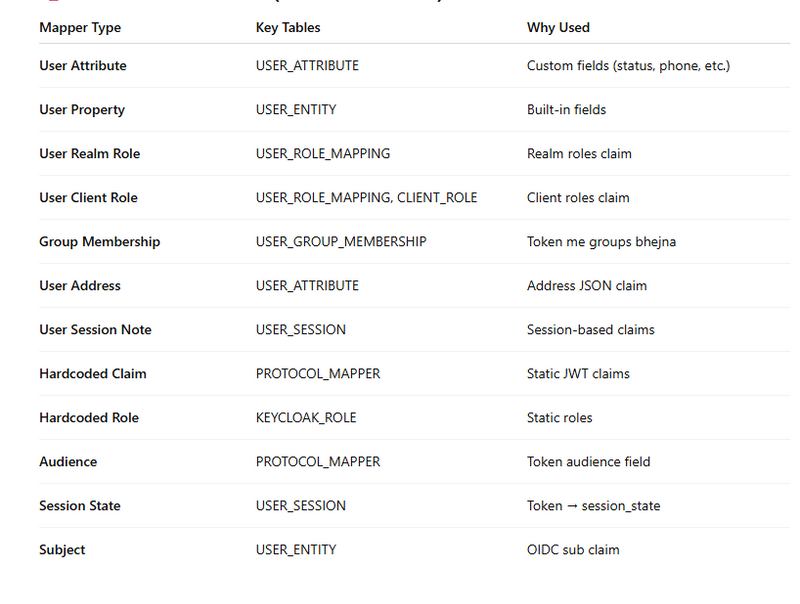
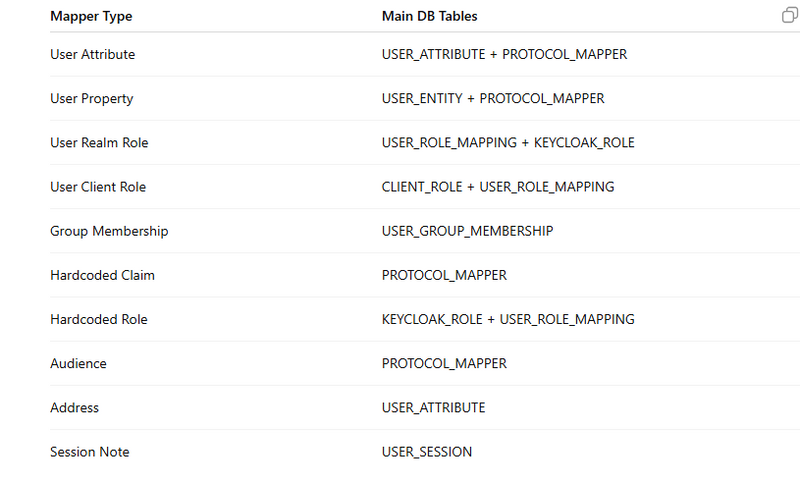
SUMMARY TABLE (SUPER USEFUL)
Mapper Types & Their Corresponding Database Tables
how-to-enable-use-custom-user-attributes-in-keycloak
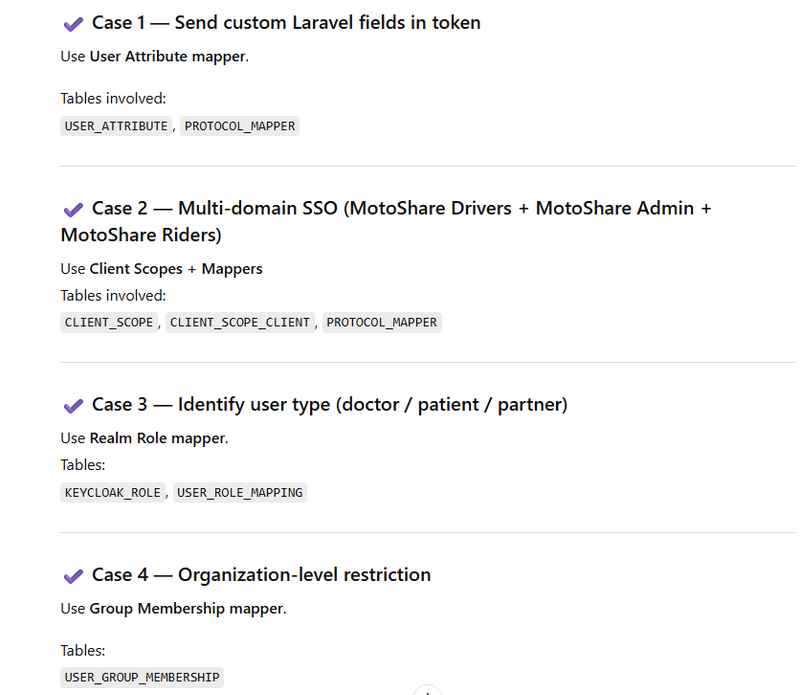
Real Use Cases (MotoShare & MyHospitalNow)
🧩 2. High-Level Architecture Diagram




Top comments (0)