In Apache Spark, which follows the functional programming paradigm, operations like
map()
filter()
reduce()
reduceByKey()
flatMap
sorted() with a Custom Sort Key
are used to transform data in a functional way.
Coordinating executors and task scheduling in spark
Handling semi-structured data
Lambda Functions (Anonymous Functions)
# Lambda function that adds 10 to a given number
add_ten = lambda x: x + 10
print(add_ten(5)) # Output: 15
map()
rdd.map(lambda x: x * x)
===========other way=============
def square(x):
return x * x
rdd.map(square)
# map() example in Python
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Using a lambda function to square each number
squared_numbers = map(lambda x: x ** 2, numbers)
print(list(squared_numbers)) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
result = rdd.map(lambda x: x ** 2)
print(result.collect()) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
filter() Function: Filters elements based on a function that returns a boolean value. It’s used to remove unwanted data, retaining only elements that match a specific condition.
# filter() example in Python
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
# Using a lambda function to filter even numbers
even_numbers = filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers)
print(list(even_numbers)) # Output: [2, 4, 6]
In Spark, filter() works similarly to remove unwanted elements from an RDD:
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
even_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
print(even_rdd.collect()) # Output: [2, 4, 6]
- reduce() Function: Performs a rolling computation over the items of an iterable and returns a single result. It’s often used for aggregating data. from functools import reduce
# reduce() example in Python: Sum of all elements
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
sum_result = reduce(lambda x, y: x + y, numbers)
print(sum_result) # Output: 15
In Spark, reduceByKey() is commonly used to aggregate values by key, where the transformation happens on a per-key basis:
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3), ("b", 4)])
reduced_rdd = rdd.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)
print(reduced_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('a', 4), ('b', 6)]
- reduceByKey() in Spark: Aggregates values with the same key using a provided function.
# Example in Spark-like fashion
rdd = sc.parallelize([('apple', 1), ('banana', 2), ('apple', 3), ('banana', 4)])
# Reduce by key (summing values for each key)
reduced_rdd = rdd.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)
print(reduced_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('banana', 6), ('apple', 4)]
- flatMap() Function: Similar to map(), but it can return zero or more output items for each input item. It's useful when you need to flatten a structure (like a list of lists) into a single list.
# flatMap() example in Python using list comprehension
numbers = [1, 2, 3]
result = list(map(lambda x: [x, x * 2], numbers)) # Nested lists
# Output of result: [[1, 2], [2, 4], [3, 6]]
flattened_result = [item for sublist in result for item in sublist] # Flattening
print(flattened_result) # Output: [1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6]
In Spark, flatMap() allows for emitting a variable number of output elements for each input element:
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3])
flat_map_rdd = rdd.flatMap(lambda x: [x, x * 2])
print(flat_map_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 2, 2, 4, 3, 6]
- Example Combining map(), filter(), and reduce():
A typical Spark-style transformation that involves chaining map(), filter(), and reduceByKey() to process data.
rdd = sc.parallelize([('apple', 1), ('banana', 2), ('apple', 3), ('banana', 4), ('orange', 1)])
# Step 1: Filter fruits with a name starting with 'a'
filtered_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x[0].startswith('a'))
# Step 2: Map to change values (multiplying the fruit count by 10)
mapped_rdd = filtered_rdd.map(lambda x: (x[0], x[1] * 10))
# Step 3: Reduce by key (sum the counts)
reduced_rdd = mapped_rdd.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)
print(reduced_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('apple', 40)]
sorted() with a Custom Sort Key:
words = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date']
# Sort words by the length of each word
sorted_words = sorted(words, key=lambda word: len(word))
print(sorted_words) # Output: ['apple', 'date', 'banana', 'cherry']
Spark RDD Equivalent:
from pyspark import SparkContext
# Initialize SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "Sort Example")
# Create an RDD from the list
words_rdd = sc.parallelize(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date'])
# Sort words by the length of each word
sorted_words_rdd = words_rdd.sortBy(lambda word: len(word))
# Collect and print the result
print(sorted_words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['apple', 'date', 'banana', 'cherry']
# Stop SparkContext
sc.stop()
Filtering Words with Length Greater Than 5
In Python:
words = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry']
# Filter words with length greater than 5
long_words = filter(lambda word: len(word) > 5, words)
print(list(long_words)) # Output: ['banana', 'cherry', 'elderberry']
Spark RDD Equivalent:
from pyspark import SparkContext
# Initialize SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "Filter Example")
# Create an RDD from the list
words_rdd = sc.parallelize(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry', 'date', 'elderberry'])
# Filter words with length greater than 5
long_words_rdd = words_rdd.filter(lambda word: len(word) > 5)
# Collect and print the result
print(long_words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['banana', 'cherry', 'elderberry']
# Stop SparkContext
sc.stop()
- Combining Names and Scores into Tuples (zip)
In Python:
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']
scores = [85, 90, 88]
# Create a list of tuples (name, score)
combined = zip(names, scores)
print(list(combined)) # Output: [('Alice', 85), ('Bob', 90), ('Charlie', 88)]
Spark RDD Equivalent:
from pyspark import SparkContext
# Initialize SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "Zip Example")
# Create RDDs for names and scores
names_rdd = sc.parallelize(['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie'])
scores_rdd = sc.parallelize([85, 90, 88])
# Zip the two RDDs together
combined_rdd = names_rdd.zip(scores_rdd)
# Collect and print the result
print(combined_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('Alice', 85), ('Bob', 90), ('Charlie', 88)]
# Stop SparkContext
sc.stop()
- Using all() and any() on RDDs
In Python:
numbers = [2, 4, 6, 8]
# Check if all numbers are even
print(all(map(lambda x: x % 2 == 0, numbers))) # Output: True
numbers = [2, 4, 7, 8]
# Check if any number is greater than 5
print(any(map(lambda x: x > 5, numbers))) # Output: True
Spark RDD Equivalent:
from pyspark import SparkContext
# Initialize SparkContext
sc = SparkContext("local", "All and Any Example")
# Create an RDD for numbers
numbers_rdd = sc.parallelize([2, 4, 6, 8])
# Check if all numbers are even (all() equivalent)
all_even = numbers_rdd.map(lambda x: x % 2 == 0).reduce(lambda x, y: x and y)
# Create an RDD with some numbers greater than 5
numbers_rdd_2 = sc.parallelize([2, 4, 7, 8])
# Check if any number is greater than 5 (any() equivalent)
any_greater_than_5 = numbers_rdd_2.map(lambda x: x > 5).reduce(lambda x, y: x or y)
# Collect and print the results
print(all_even) # Output: True
print(any_greater_than_5) # Output: True
# Stop SparkContext
sc.stop()
Key Points:
Lambda Functions: Short, anonymous functions used for quick transformations.
map(): Transforms each element in an iterable.
filter(): Filters elements based on a condition.
reduce() / reduceByKey(): Aggregates elements into a single result.
flatMap(): Flattens a collection of lists into a single list.
rdd.map(lambda x: x * x).filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
Transforming Data with map():
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
squared_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * x) # Square each element
print(squared_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Filtering Data with filter():
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
even_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0) # Filter even numbers
print(even_rdd.collect()) # Output: [2, 4]
Reducing Data with reduceByKey():
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)])
result = rdd.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b) # Sum values by key
print(result.collect()) # Output: [('a', 4), ('b', 2)]
Sampling Data with sample():
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
sampled_rdd = rdd.sample(False, 0.5) # Randomly sample 50% of data
print(sampled_rdd.collect()) # Output: A random sample, e.g., [2, 5, 7]
Using Lambda with map() and filter() in Sequence:
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
result = rdd.map(lambda x: x * 2).filter(lambda x: x > 5) # Double and filter out numbers <= 5
print(result.collect()) # Output: [6, 8, 10, 12]
Map: Squaring Elements
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
squared_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * x)
print(squared_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 4, 9, 16, 25]
Map: Convert Strings to Uppercase
rdd = sc.parallelize(['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'])
uppercase_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x.upper())
print(uppercase_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['APPLE', 'BANANA', 'CHERRY']
Filter: Even Numbers
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
even_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
print(even_rdd.collect()) # Output: [2, 4, 6]
Filter: Numbers Greater Than 3
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
greater_than_three = rdd.filter(lambda x: x > 3)
print(greater_than_three.collect()) # Output: [4, 5]
ReduceByKey: Sum Values by Key
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)])
result = rdd.reduceByKey(lambda x, y: x + y)
print(result.collect()) # Output: [('a', 4), ('b', 2)]
FlatMap: Flatten Lists of Lists
rdd = sc.parallelize([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
flattened_rdd = rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x)
print(flattened_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Map: Add 5 to Each Element
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
incremented_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x + 5)
print(incremented_rdd.collect()) # Output: [6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
GroupByKey: Group by Key
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)])
grouped_rdd = rdd.groupByKey()
print(grouped_rdd.mapValues(list).collect()) # Output: [('a', [1, 3]), ('b', [2])]
MapValues: Square Values of Key-Value Pairs
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("c", 3)])
squared_values_rdd = rdd.mapValues(lambda x: x * x)
print(squared_values_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('a', 1), ('b', 4), ('c', 9)]
Join: Join Two RDDs by Key
rdd1 = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2)])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([("a", 3), ("b", 4)])
joined_rdd = rdd1.join(rdd2)
print(joined_rdd.collect()) # Output: [('a', (1, 3)), ('b', (2, 4))]
Map: Convert Numbers to Strings
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3])
string_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: str(x))
print(string_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['1', '2', '3']
Map: Apply Function to Tuple Elements
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2)])
result = rdd.map(lambda x: (x[0], x[1] * 2))
print(result.collect()) # Output: [('a', 2), ('b', 4)]
Filter: Strings Longer Than 3 Characters
rdd = sc.parallelize(["apple", "banana", "cherry", "fig"])
long_words_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: len(x) > 3)
print(long_words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
Sample: Sample Data with 50% Probability
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
sampled_rdd = rdd.sample(False, 0.5)
print(sampled_rdd.collect()) # Output: A random subset, e.g., [2, 4, 6, 8]
Map: Multiply Each Element by 10
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
multiplied_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * 10)
print(multiplied_rdd.collect()) # Output: [10, 20, 30, 40]
Map: Convert List of Numbers to Binary
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
binary_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: bin(x))
print(binary_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['0b1', '0b10', '0b11', '0b100']
Filter: Words with More Than 5 Characters
rdd = sc.parallelize(["spark", "hadoop", "flink", "kafka", "java"])
long_words_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: len(x) > 5)
print(long_words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['hadoop', 'flink']
FlatMap: Split Lines into Words
rdd = sc.parallelize(["hello world", "hi there", "how are you"])
words_rdd = rdd.flatMap(lambda line: line.split(" "))
print(words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['hello', 'world', 'hi', 'there', 'how', 'are', 'you']
Map: Square the Elements if Even
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
squared_even_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * x if x % 2 == 0 else x)
print(squared_even_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 4, 3, 16, 5]
Reduce: Multiply All Elements Together
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
product = rdd.reduce(lambda x, y: x * y)
print(product) # Output: 24
Map: Add 1 to Each Number
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
incremented_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x + 1)
print(incremented_rdd.collect()) # Output: [2, 3, 4, 5]
GroupByKey: Group Elements by Key
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)])
grouped_rdd = rdd.groupByKey()
print(grouped_rdd.mapValues(list).collect()) # Output: [('a', [1, 3]), ('b', [2])]
Map: Round Each Number to Two Decimal Places
rdd = sc.parallelize([1.234, 2.456, 3.678])
rounded_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: round(x, 2))
print(rounded_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1.23, 2.46, 3.68]
Map: Add Key-Value Pair to Each Element
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
key_value_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: (x, x * 2))
print(key_value_rdd.collect()) # Output: [(1, 2), (2, 4), (3, 6), (4, 8)]
Reduce: Find Maximum Value
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 5, 2, 7, 3])
max_value = rdd.reduce(lambda x, y: x if x > y else y)
print(max_value) # Output: 7
Map: Format Date in String
rdd = sc.parallelize([1609459200, 1612137600]) # Unix timestamps
formatted_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: str(datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp(x).date()))
print(formatted_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['2021-01-01', '2021-02-01']
FlatMap: Convert Each Line to Words
rdd = sc.parallelize(["hello world", "how are you"])
words_rdd = rdd.flatMap(lambda line: line.split())
print(words_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['hello', 'world', 'how', 'are', 'you']
Map: Convert Numbers to Strings
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
string_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: str(x))
print(string_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5']
Filter: Get Negative Numbers
rdd = sc.parallelize([-1, 2, -3, 4, -5])
negative_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x < 0)
print(negative_rdd.collect()) # Output: [-1, -3, -5]
Map: Prefix Elements with "Item-"
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3])
prefixed_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: f"Item-{x}")
print(prefixed_rdd.collect()) # Output: ['Item-1', 'Item-2', 'Item-3']
Coordinating executors and task scheduling in spark
Basic RDD Creation and Execution (Simple Task Scheduling)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], numSlices=3)
squared_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * x)
squared_rdd.collect() # Tasks will be scheduled across executors
Task Scheduling: Spark divides the data into 3 partitions, scheduling one task per partition.
- Parallelizing a Large Dataset Across Executors
rdd = sc.parallelize(range(1, 1000000), numSlices=4)
rdd.reduce(lambda a, b: a + b) # Task scheduling across 4 executors
Task Scheduling: Data is split into 4 partitions, and Spark schedules tasks for each partition on different executors.
- Data Transformation with Map (Task Scheduling Per Partition)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], numSlices=2)
mapped_rdd = rdd.map(lambda x: x * 10)
mapped_rdd.collect() # Two tasks scheduled, one for each partition
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules 2 tasks, one for each partition.
- Filter Transformation (Data Filtering Across Partitions)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6], numSlices=3)
filtered_rdd = rdd.filter(lambda x: x % 2 == 0)
filtered_rdd.collect() # Filtered tasks executed across 3 executors
Task Scheduling: Tasks are distributed across 3 partitions, and Spark filters the data on each executor.
- GroupByKey (Shuffling and Task Scheduling)
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3), ("b", 4)], numSlices=2)
grouped_rdd = rdd.groupByKey()
grouped_rdd.collect() # Task scheduling involves data shuffling
Task Scheduling: Tasks involve shuffling data, and Spark distributes tasks based on keys to ensure they are grouped properly.
- ReduceByKey (Task Scheduling for Aggregation)
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)], numSlices=2)
reduced_rdd = rdd.reduceByKey(lambda a, b: a + b)
reduced_rdd.collect() # Tasks executed to aggregate by key
Task Scheduling: Spark executes tasks to reduce data by key, distributing tasks across executors.
- Sorting Data (Shuffle and Task Scheduling)
rdd = sc.parallelize([5, 1, 4, 2, 3], numSlices=2)
sorted_rdd = rdd.sortBy(lambda x: x)
sorted_rdd.collect() # Spark schedules tasks and performs shuffle
Task Scheduling: Sorting requires shuffling across executors, and Spark schedules tasks accordingly.
- Repartitioning RDD (Task Scheduling for Shuffling Data)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], numSlices=2)
repartitioned_rdd = rdd.repartition(4) # Repartitioning the data into 4 partitions
repartitioned_rdd.collect() # Tasks are rescheduled across 4 partitions
Task Scheduling: Data shuffle happens when repartitioning, and Spark schedules tasks for the new partition configuration.
- Caching Data for Optimization (Task Scheduling with Cached Data)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], numSlices=2)
rdd.cache() # Caching the RDD
rdd.collect() # Tasks are scheduled once, and cached data is r
eused
Task Scheduling: Tasks are scheduled once, and cached data is reused, optimizing subsequent computations.
Accumulators for Task Coordination (Shared Variables Across Executors)
accum = sc.accumulator(0)
def add_to_accum(x):
global accum
accum.add(x)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
rdd.foreach(add_to_accum)
print(accum.value) # Output: 10 (tasks coordinate to modify the accumulator)
Task Scheduling: Each task can modify shared variables like accumulators across executors.
Using Broadcast Variables (Efficient Task Coordination)
broadcast_var = sc.broadcast([1, 2, 3])
rdd = sc.parallelize([4, 5, 6])
rdd.map(lambda x: x + sum(broadcast_var.value)).collect() # Tasks use broadcasted data
Task Scheduling: Broadcast variables allow all tasks to access the same data without duplication across executors.
Parallelize Data from External File (Task Scheduling on External FS)
rdd = sc.textFile("hdfs://namenode:8020/data/logs/*.log", minPartitions=3)
rdd.count() # Spark schedules tasks to read from H
DFS
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks to read data from HDFS, dividing the file into 3 partitions.
- RDD from Multiple Files (Task Scheduling for Multi-File Input)
rdd = sc.textFile("file:///tmp/*.txt")
rdd.map(lambda x: len(x)).collect() # Tasks are scheduled across the files
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks for each file across the available executors.
- Using foreach to Apply a Function Across Partitions
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4], numSlices=2)
rdd.foreach(lambda x: print(x)) # Each task prints an element
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules a task per partition to apply the foreach function.
- Transformations with flatMap (Task Scheduling with Flat Data)
rdd = sc.parallelize(["hello world", "how are you"])
flat_rdd = rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x.split())
flat_rdd.collect() # Task schedules data into flat format
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks to split data and flatten the structure.
- Checkpointing (Task Coordination for Fault Tolerance)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
rdd.checkpoint() # RDD checkpointing to improve fault tolerance
rdd.collect() # Tasks are scheduled after checkpointing
Task Scheduling: Spark creates checkpointed RDDs, optimizing data recovery in case of failure.
- Create RDD from Pandas DataFrame (Task Scheduling for Data Interchange)
import pandas as pd
pdf = pd.DataFrame({"col1": [1, 2, 3], "col2": [4, 5, 6]})
rdd = sc.parallelize(pdf.values)
rdd.collect() # Task scheduling for converting DataFrame to RDD
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks to convert pandas DataFrame data to RDD.
- Using combineByKey for Custom Aggregation
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3)])
combined_rdd = rdd.combineByKey(lambda x: (x, 1),
lambda x, y: (x[0] + y, x[1] + 1),
lambda x, y: (x[0] + y[0], x[1] + y[1]))
combined_rdd.collect() # Custom task scheduling for aggregation
Task Scheduling: Tasks aggregate key-value pairs using custom logic across partitions.
- Using mapPartitions for Partition-Level Processing
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5], numSlices=2)
partition_rdd = rdd.mapPartitions(lambda x: [sum(x)])
print(partition_rdd.collect()) # [3, 7] (sum of each partition)
Task Scheduling: Each partition runs a task to process data at the partition level.
- Repartitioning with repartition (Task Scheduling for Redistribution)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4], numSlices=2)
rdd_repartitioned = rdd.repartition(4) # Tasks rescheduled across 4 partitions
rdd_repartitioned.collect()
Task Scheduling: Tasks are reshuffled and distributed across 4 partitions after repartitioning.
- mapPartitionsWithIndex (Task Scheduling for Indexed Processing)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
indexed_rdd = rdd.mapPartitionsWithIndex(lambda idx, it: [(idx, sum(it))])
print(indexed_rdd.collect()) # [(0, 3), (1, 7)]
Task Scheduling: Each task processes data indexed by partition.
- coalesce to Reduce Partitions (Efficient Task Scheduling)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4], numSlices=4)
rdd_coalesced = rdd.coalesce(2) # Reduces partitions to 2
print(rdd_coalesced.collect())
Task Scheduling: Spark reduces partitions for more efficient task scheduling and fewer tasks.
- cartesian Product of Two RDDs (Task Scheduling for Cross Product)
rdd1 = sc.parallelize([1, 2])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([3, 4])
cartesian_rdd = rdd1.cartesian(rdd2)
cartesian_rdd.collect() # Tasks schedule to produce cartesian product
Task Scheduling: Tasks compute the cartesian product between two RDDs.
sample to Take a Random Subset (Task Scheduling for Sampling)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
sampled_rdd = rdd.sample(False, 0.5)
print(sampled_rdd.collect()) # Sampled data tasks across partitions
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks to sample a subset of data.
distinct to Remove Duplicates (Task Scheduling for Unique Data)
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4])
distinct_rdd = rdd.distinct() # Tasks schedule to remove duplicates
print(distinct_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]
Task Scheduling: Tasks remove duplicate elements across partitions.
union to Merge Two RDDs (Task Scheduling for Merging Data)
rdd1 = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([4, 5, 6])
union_rdd = rdd1.union(rdd2) # Merging tasks across two RDDs
print(union_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Task Scheduling: Tasks combine two RDDs into one.
intersection to Find Common Elements (Task Scheduling for Intersection)
rdd1 = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([3, 4, 5, 6])
intersection_rdd = rdd1.intersection(rdd2) # Common elements task scheduling
print(intersection_rdd.collect()) # Output: [3, 4]
Task Scheduling: Tasks find the intersection of two RDDs.
subtract to Remove Elements from RDD (Task Scheduling for Set Difference)
rdd1 = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4])
rdd2 = sc.parallelize([3, 4, 5, 6])
difference_rdd = rdd1.subtract(rdd2) # Removing tasks to subtract elements
print(difference_rdd.collect()) # Output: [1, 2]
Task Scheduling: Tasks remove elements from the first RDD that are present in the second RDD.
countByKey to Count Occurrences by Key
rdd = sc.parallelize([("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("a", 3), ("b", 4)])
count_by_key = rdd.countByKey() # Tasks to count occurrences by key
print(count_by_key) # Output: {'a': 2, 'b': 2}
Task Scheduling: Spark schedules tasks to count occurrences for each key in the RDD.
mapPartitions to Process Data in Partitions
rdd = sc.parallelize([1, 2, 3, 4], numSlices=2)
partition_rdd = rdd.mapPartitions(lambda it: [sum(it)])
print(partition_rdd.collect()) # Output: [3, 7] (sum of each partition)
Handling semi-structured data
- Creating a DataFrame from a JSON File
df = spark.read.json("path/to/file.json")
df.show()
Data Source: JSON file.
Operation: Load semi-structured data (JSON) into a Spark DataFrame.
[
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 25}
]
+-----+---+
| name|age|
+-----+---+
|Alice| 30|
| Bob| 25|
+-----+---+
- Creating a DataFrame from a List of Dictionaries (JSON-like)
data = [{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}, {"name": "Bob", "age": 25}]
df = spark.read.json(sc.parallelize([str(d) for d in data]))
df.show()
Data Source: List of dictionaries.
Operation: Create a DataFrame from a Python list of dictionaries.
data = [{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}, {"name": "Bob", "age": 25}]
+-----+---+
| name|age|
+-----+---+
|Alice| 30|
| Bob| 25|
+-----+---+
- Flattening Nested JSON Data into Columns
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested.json")
df.select("person.name", "person.age").show()
Data Source: Nested JSON.
Operation: Flatten nested fields into top-level columns.
[
{"id": 1, "info": {"name": "Alice", "age": 30}},
{"id": 2, "info": {"name": "Bob", "age": 25}}
]
+---+-----+---+
| id| name|age|
+---+-----+---+
| 1|Alice| 30|
| 2| Bob| 25|
+---+-----+---+
- Extracting Elements from a List of JSON Objects
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested_json_array.json")
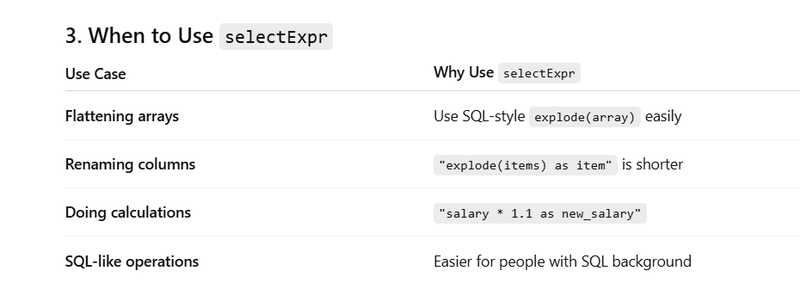
df.selectExpr("explode(items) as item").show()
Data Source: JSON array inside a JSON object.
Operation: Using explode to flatten a list of JSON objects.
{
"items": [{"product": "A", "amount": 50}, {"product": "B", "amount": 70}]
}
+--------+------+
| product|amount|
+--------+------+
| A| 50|
| B| 70|
+--------+------+
Another Example
Example JSON (nested_json_array.json)
{
"id": 1,
"items": ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
}
Without explode
df = spark.read.json("nested_json_array.json")
df.show(truncate=False)
+---+------------------------+
|id |items |
+---+------------------------+
|1 |[apple, banana, cherry] |
+---+------------------------+
With selectExpr("explode(items) as item")
df.selectExpr("explode(items) as item").show()
+------+
| item |
+------+
|apple |
|banana|
|cherry|
+------+
- Aggregating Data in a Nested Structure
data = [{"name": "Alice", "sales": [{"product": "A", "amount": 50}, {"product": "B", "amount": 70}]},
{"name": "Bob", "sales": [{"product": "A", "amount": 30}, {"product": "C", "amount": 90}]}]
df = spark.read.json(sc.parallelize([str(d) for d in data]))
df.selectExpr("name", "aggregate(sales, 0, (acc, x) -> acc + x.amount) as total_sales").show()
Data Source: Nested list of dictionaries (sales data).
Operation: Use aggregate to sum values within nested lists.
[
{"name": "Alice", "sales": [{"product": "A", "amount": 50}, {"product": "B", "amount": 70}]},
{"name": "Bob", "sales": [{"product": "A", "amount": 30}, {"product": "C", "amount": 90}]}
]
+-----+-----------+
| name|total_sales|
+-----+-----------+
|Alice| 120|
| Bob| 120|
+-----+-----------+
- Normalizing Nested JSON to Flatten it
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested_json.json")
df.select("id", "info.name", "info.age").show()
Data Source: Nested JSON.
Operation: Flatten nested JSON to extract specific fields.
{
"id": 1,
"info": {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 30
}
}
+---+-----+---+
| id| name|age|
+---+-----+---+
| 1|Alice| 30|
+---+-----+---+
- Using explode() for Nested Arrays in JSON
df = spark.read.json("path/to/array_json.json")
df.select(explode(df["products"]).alias("product")).show()
Data Source: JSON with nested arrays.
Operation: explode() to flatten arrays of objects.
{
"products": ["A", "B", "C"]
}
+------+
|product|
+------+
| A|
| B|
| C|
+------+
- Creating a DataFrame from a List of Lists
data = [["Alice", 30], ["Bob", 25]]
df = spark.createDataFrame(data, ["name", "age"])
df.show()
Data Source: List of lists.
Operation: Convert a list of lists to a DataFrame.
data = [["Alice", 30], ["Bob", 25]]
+-----+---+
| name|age|
+-----+---+
|Alice| 30|
| Bob| 25|
+-----+---+
- Filtering Nested JSON Data df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested_json.json") df.filter("info.age > 30").show()
Data Source: Nested JSON.
Operation: Filtering based on nested field values.
[
{"name": "Alice", "info": {"age": 35}},
{"name": "Bob", "info": {"age": 25}}
]
+-----+-----+---+
| name| info|age|
+-----+-----+---+
|Alice| {35}| 35|
+-----+-----+---+
- Handling Semistructured Data with selectExpr()
df = spark.read.json("path/to/semi_structured_data.json")
df.selectExpr("name", "age + 5 as age_plus_five").show()
Data Source: Semi-structured data (JSON).
Operation: Use selectExpr() to create derived fields.
[
{"name": "Alice", "age": 30},
{"name": "Bob", "age": 25}
]
+-----+----------+
| name|age_plus_five|
+-----+----------+
|Alice| 35|
| Bob| 30|
+-----+----------+
- Working with Arrays in DataFrame
df = spark.createDataFrame([("Alice", [1, 2, 3]), ("Bob", [4, 5, 6])], ["name", "numbers"])
df.select("name", "numbers").show()
Data Source: Arrays in DataFrame.
Operation: Work with columns that contain arrays.
df = spark.createDataFrame([("Alice", [1, 2, 3]), ("Bob", [4, 5, 6])], ["name", "numbers"])
+-----+---------+
| name| numbers|
+-----+---------+
|Alice|[1, 2, 3]|
| Bob|[4, 5, 6]|
+-----+---------+
- Joining DataFrames with Nested JSON Fields
df1 = spark.read.json("path/to/first.json")
df2 = spark.read.json("path/to/second.json")
df1.join(df2, df1.id == df2.id).select("df1.name", "df2.address").show()
Data Source: Nested JSON files.
Operation: Join DataFrames based on nested fields.
{
"id": 1,
"name": "Alice",
"address": {"city": "New York"}
}
+---+-----+--------+
| id| name| address|
+---+-----+--------+
| 1|Alice|[city=NY]|
+---+-----+--------+
- Extracting and Flattening Nested Lists in DataFrame
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested_list.json")
df.select("id", explode("items").alias("item")).show()
Data Source: JSON with nested lists.
Operation: Flatten a nested list into rows using explode().
{
"orders": [{"product": "A", "quantity": 10}, {"product": "B", "quantity": 20}]
}
+------+--------+--------+
|product|quantity| order|
+------+--------+--------+
| A| 10|{A,10}|
| B| 20|{B,20}|
+------+--------+--------+
- Working with Nested Lists in RDDs
rdd = sc.parallelize([{"name": "Alice", "sales": [100, 200]}, {"name": "Bob", "sales": [300, 400]}])
rdd.flatMap(lambda x: x["sales"]).collect() # Flatten sales list
Data Source: RDD with nested lists.
Operation: Use flatMap() to flatten nested lists.
[100, 200, 300, 400]
- Exploding Nested JSON Arrays into Rows
df = spark.read.json("path/to/orders.json")
df.select(explode(df["orders"]).alias("order")).select("order.item", "order.quantity").show()
Data Source: JSON array inside a field.
Operation: Flatten the nested array and extract fields.
{
"orders": [{"item": "A", "quantity": 10}, {"item": "B", "quantity": 20}]
}
+-----+--------+
| item|quantity|
+-----+--------+
| A| 10|
| B| 20|
+-----+--------+
- Parsing JSON from a DataFrame Column
df = spark.read.json("path/to/data.json")
df.withColumn("info", from_json(df["json_column"], schema)).show()
Data Source: JSON stored in a column.
Operation: Parse JSON data from a DataFrame column using from_json().
{
"json_column": '{"name": "Alice", "age": 30}'
}
+-----------------------+
| json_column |
+-----------------------+
| {"name": "Alice", "age": 30}|
+-----------------------+
- Aggregating Nested Data in JSON
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested.json")
df.groupBy("name").agg(sum("info.salary").alias("total_salary")).show()
Data Source: Nested JSON.
Operation: Aggregating nested data using groupBy() and agg().
[
{"name": "Alice", "info": {"salary": 1000}},
{"name": "Bob", "info": {"salary": 1500}}
]
+-----+-----------+
| name|total_salary|
+-----+-----------+
|Alice| 1000|
| Bob| 1500|
+-----+-----------+
- Handling Null Values in JSON
df = spark.read.json("path/to/nested_json.json")
df.fillna({"info.age": 0}).show()
Data Source: Nested JSON with potential nulls.
Operation: Replace null values in nested fields using fillna().
[
{"name": "Alice", "info": {"age": null}},
{"name": "Bob", "info": {"age": 30}}
]
+-----+-----+
| name| info|
+-----+-----+
|Alice| null|
| Bob| 30|
+-----+-----+
- Parsing Complex Semi-Structured Data from JSON
df = spark.read.json("path/to/complex_json.json")
df.selectExpr("id", "info.details.name", "info.details.age").show()
Data Source: Complex semi-structured JSON.
Operation: Extract nested data with selectExpr().
{
"id": 1,
"info": {
"details": {
"name": "Alice",
"age": 30
}
}
}
+---+-----+---+
| id| name|age|
+---+-----+---+
| 1|Alice| 30|
+---+-----+---+
- A*ccessing Nested Fields in Semi-Structured Data*
df = spark.read.json("path/to/semi_structured.json")
df.select("user.name", "user.details.age").show()
Data Source: Semi-structured JSON.
Operation: Access and flatten nested fields using select().
{
"user": {"name": "Alice", "details": {"age": 30}}
}
+-----+----+
| name| age|
+-----+----+
|Alice| 30|
+-----+----+

Top comments (0)