why linear regression is not suitable for classification task
Define logits function
how sigmoid provides bounded output and non linearity concept
linear or sigmoid is better for model capture more complex relationships in the data
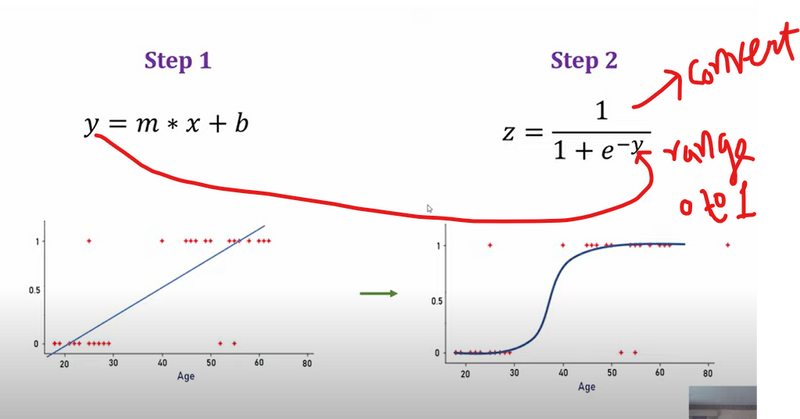
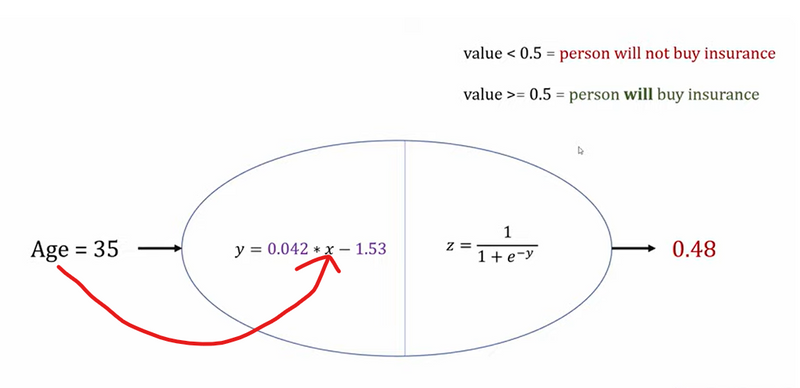
how sigmoid function converts linear equation output to range between 0 to 1
In Deep Learning (DL), the sigmoid and logit functions are often preferred over a linear regression approach when dealing with binary classification problems. Here's a detailed comparison to explain why sigmoid and logit functions are better suited for specific cases, like classification tasks:
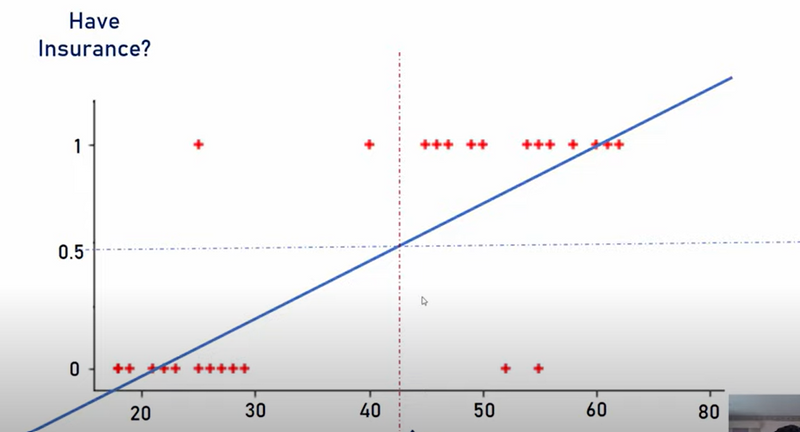
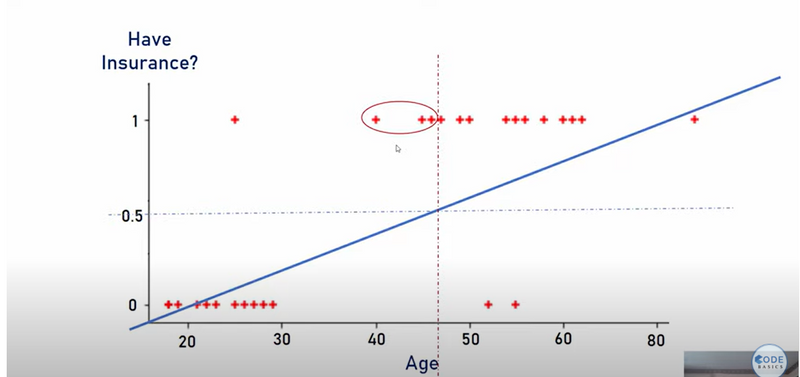
- Linear Regression and Its Limitations in DL Linear regression models predict continuous output values by applying a linear function to the input features. The output of a linear regression can range from − ∞ −∞ to + ∞ +∞, which makes it unsuitable for tasks where the output needs to be constrained, such as probabilities in classification problems.
Example:
Let's say you're predicting whether an email is spam (1) or not spam (0). Using linear regression might yield a result like 1.8 or -0.5, which doesn't make sense for a binary classification since probabilities should always be between 0 and 1.
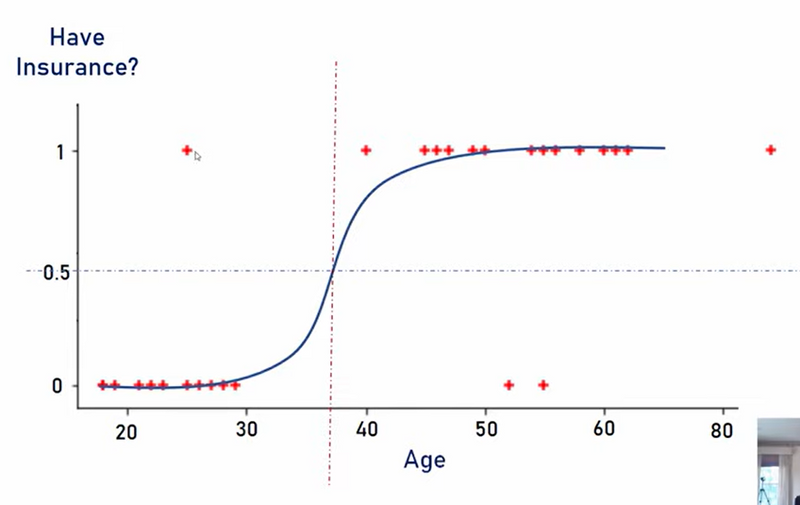
- Sigmoid and Logit for Binary Classification To handle this, Deep Learning commonly uses the sigmoid function and its inverse, the logit (log-odds) function, to ensure the output is properly bounded between 0 and 1. These functions allow us to model probabilities effectively, which are essential for classification tasks.
Sigmoid Function:
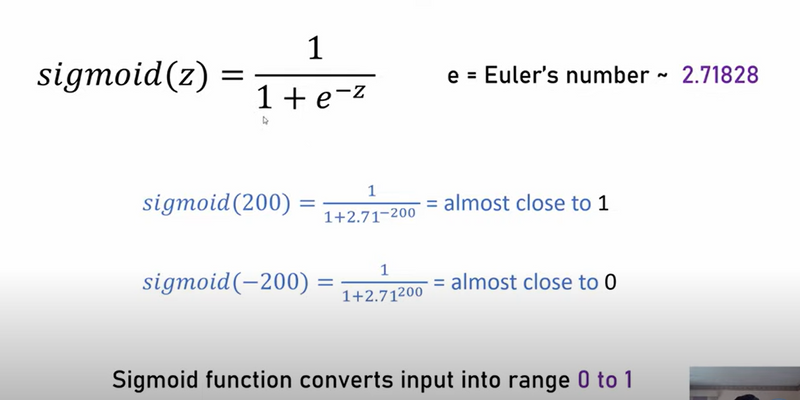
The sigmoid function maps any real-valued number to a value between 0 and 1:
Logit Function:
The logit function is the inverse of the sigmoid function. It’s used to interpret the output as log-odds, i.e., the ratio of the probability of an event happening to not happening:
Example:
Continuing with the email spam detection example, suppose we use a sigmoid function for the output layer. Given an input vector, the output is a probability (say, 0.85). This means there’s an 85% chance the email is spam. This is far more interpretable and meaningful than the raw output of linear regression.
- Advantages of Sigmoid and Logit Over Linear Regression
Bounded Output: The sigmoid function ensures that the output is between 0 and 1, which is necessary for probabilities in classification problems. Linear regression, on the other hand, can produce values outside this range.
Non-linearity: The sigmoid introduces non-linearity, allowing the model to capture more complex relationships in the data, which is critical for deep neural networks. Linear regression only captures linear relationships between input and output.
Gradient-Based Optimization: In neural networks, optimization techniques like gradient descent rely on continuous, differentiable functions. The sigmoid function is smooth and differentiable, making it suitable for gradient-based learning algorithms.
-
Deep Learning Example with Sigmoid vs Linear Regression
Example 1:
Email Spam Classification (Binary Classification)Input Features: Various characteristics of the email, such as word count, frequency of certain keywords, etc.
Linear Regression:
Neural Network with Sigmoid Activation: The network uses a linear combination in the hidden layers, but the output layer applies the sigmoid function:
In this case, using sigmoid ensures the output is interpretable as a probability, which is exactly what’s needed for binary classification.
- Conclusion Linear regression is useful when predicting continuous values, but it’s ill-suited for classification problems due to its unbounded nature and inability to model probabilities. Sigmoid and logit functions are better for classification tasks because they naturally model probabilities between 0 and 1 and introduce non-linearity to the model, which helps capture complex relationships in data.
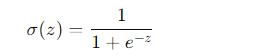
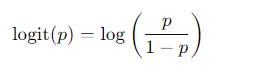
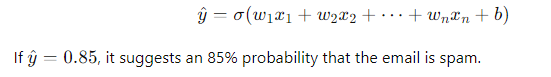

Top comments (0)