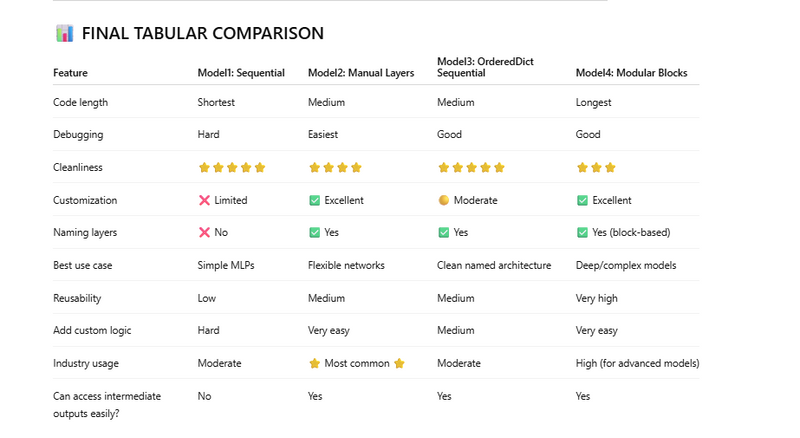
Using nn.Sequential (cleanest & shortest)
Using Explicit Layers (most common in production)
Using OrderedDict inside Sequential
Custom Model With “Blocks”
MODEL TYPE 1: Using nn.Sequential (Fastest & Shortest Way)
✅ Definition
You create the whole network as a single block, stacking layers in order.
class Model1(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(num_features, 8),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)
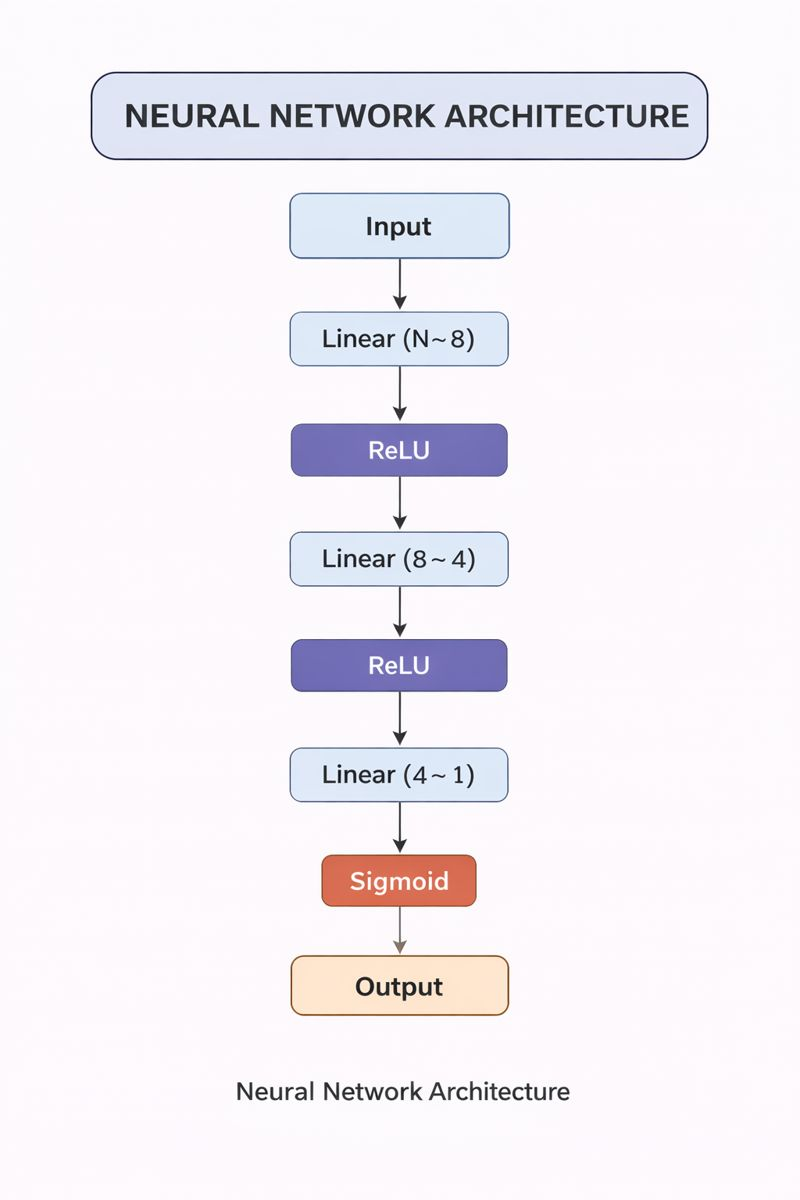
🔄 Flow of Data in Model1
Input X
↓
Linear(num_features → 8)
↓
ReLU
↓
Linear(8 → 4)
↓
ReLU
↓
Linear(4 → 1)
↓
Sigmoid → Output (0–1)
🎯 When to Use
Quick prototyping
Simple feed-forward models
When debugging layer names is not important
⭐ MODEL TYPE 2: Explicit Layer Definitions (Most Common / Most Flexible)
✅ Definition
You define each layer manually and call them step-by-step in forward().
class Model2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(num_features, 8)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(8, 4)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.fc3(x)
x = self.sigmoid(x)
return x
🔄 Flow of Data in Model2
Input X
↓
fc1 (Linear)
↓
ReLU
↓
fc2 (Linear)
↓
ReLU
↓
fc3 (Linear)
↓
Sigmoid → Output (0–1)
When to Use
When you need full control
When debugging is important
When adding:
Dropout
BatchNorm
Custom activation logic
This is the most used method in real-world ML projects.
⭐ MODEL TYPE 3: Using OrderedDict inside Sequential
(A mix of Model1 + Model2 — clean code + named layers)
✅ Definition
from collections import OrderedDict
class Model3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.network = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('fc1', nn.Linear(num_features, 8)),
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
('fc2', nn.Linear(8, 4)),
('relu2', nn.ReLU()),
('fc3', nn.Linear(4, 1)),
('sigmoid', nn.Sigmoid())
]))
def forward(self, x):
return self.network(x)
🔄 Flow of Data in Model3
Same flow as Model1, but now each layer has a name:
X → fc1 → relu1 → fc2 → relu2 → fc3 → sigmoid → Output
🎯 When to Use
Need clean Sequential style
Want readable layer names
Need to access intermediate outputs (e.g., model.network.fc1)
Want structured debugging
⭐ MODEL TYPE 4: Modular Block-Based Model (Advanced / Scalable)
✅ Definition
You build small blocks (like Lego pieces) and assemble them.
Useful for deep networks, CNNs, Transformers, etc.
class Block(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, out):
super().__init__()
self.layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(inp, out),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, x):
return self.layer(x)
class Model4(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_features):
super().__init__()
self.b1 = Block(num_features, 8)
self.b2 = Block(8, 4)
self.out = nn.Linear(4, 1)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.b1(x)
x = self.b2(x)
x = self.out(x)
return self.sigmoid(x)
🔄 Flow of Data in Model4
Input
↓
Block 1 (Linear → ReLU)
↓
Block 2 (Linear → ReLU)
↓
Output Linear
↓
Sigmoid
🎯 When to Use
Deep learning models
Repeated patterns (CNN, RNN, Transformer blocks)
When architecture grows large
Best for maintainability


Top comments (0)