Microservice framework enterprise architecture
WHY DO WE NEED TOKEN EXCHANGE BETWEEN MICROSERVICES
Why token introspection is needed
Keycloak Client Mapping for Multi-Domain Architecture
.
Microservice framework enterprise architecture
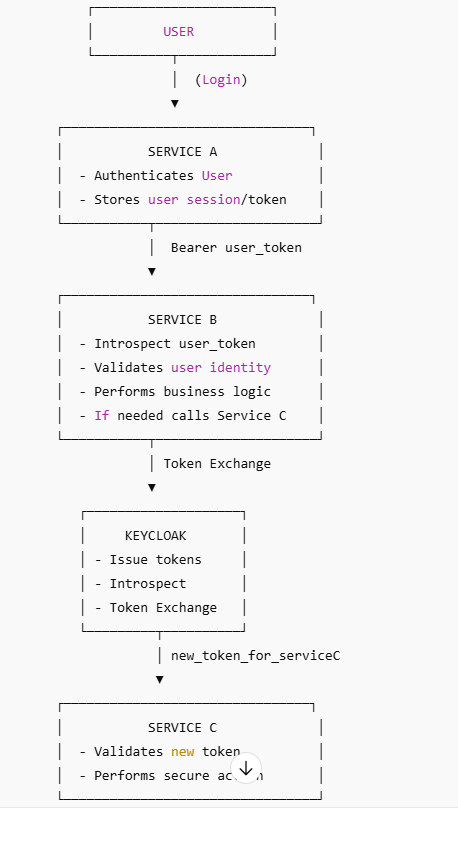
PART 1 — SERVICE A (Laravel)
Goal:
Get own Keycloak token
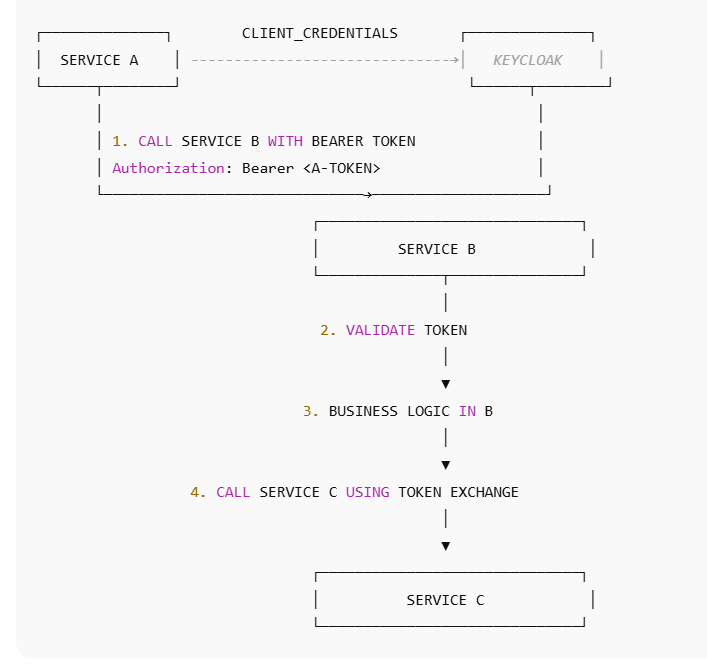
Call Service B with Bearer token
A. SERVICE A → Get Token From Keycloak
app/Services/KeycloakService.php
namespace App\Services;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
class KeycloakService
{
public function getServiceToken()
{
$kcBase = env('KEYCLOAK_BASE_URL');
$realm = env('KEYCLOAK_REALM');
$client = env('SERVICE_A_CLIENT_ID');
$secret = env('SERVICE_A_CLIENT_SECRET');
$response = Http::asForm()->post("$kcBase/realms/$realm/protocol/openid-connect/token", [
"grant_type" => "client_credentials",
"client_id" => $client,
"client_secret" => $secret,
]);
return $response->json()['access_token'] ?? null;
}
}
B. SERVICE A → Controller Calling Service B
app/Http/Controllers/ServiceAController.php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Services\KeycloakService;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
class ServiceAController extends Controller
{
public function sendToServiceB(KeycloakService $kc)
{
$token = $kc->getServiceToken();
$response = Http::withToken($token)
->post("https://service-b.internal/api/process", [
"order_id" => 9876,
"amount" => 1500
]);
return $response->json();
}
}
C. SERVICE A Route
routes/web.php
Route::get('/run-service-b', [ServiceAController::class, 'sendToServiceB']);
D. SERVICE A Blade Example
resources/views/call.blade.php
<a href="/run-service-b" class="btn btn-primary">
Call Service B
</a>
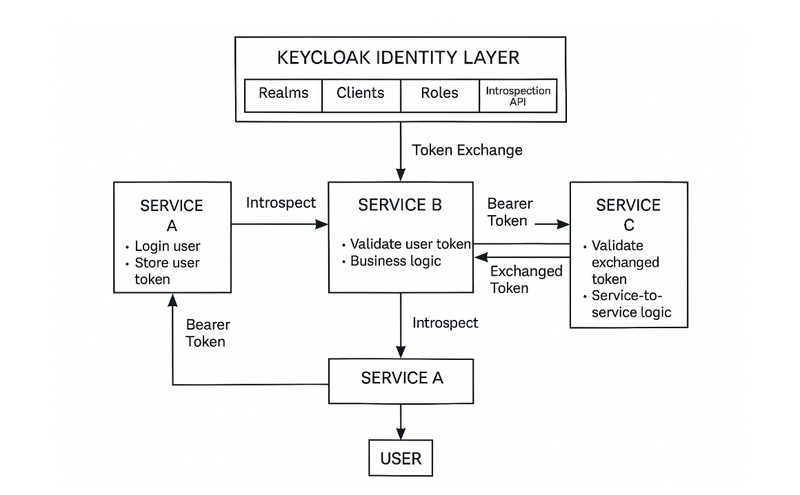
⭐ PART 2 — SERVICE B (Laravel Microservice)
Goals:
Receive request from Service A
Validate Keycloak token
Process logic in controller
Optionally call Service C
A. SERVICE B Middleware (Token Validation)
app/Http/Middleware/KeycloakServiceAuth.php
namespace App\Http\Middleware;
use Closure;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
class KeycloakServiceAuth
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$token = $request->bearerToken();
if (!$token) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Missing token'], 401);
}
$kcBase = env('KEYCLOAK_BASE_URL');
$realm = env('KEYCLOAK_REALM');
$introspectUrl = "$kcBase/realms/$realm/protocol/openid-connect/token/introspect";
$resp = Http::asForm()->post($introspectUrl, [
"token" => $token,
"client_id" => env('SERVICE_B_CLIENT_ID'),
"client_secret" => env('SERVICE_B_CLIENT_SECRET'),
]);
if (!$resp->ok() || !$resp->json()['active']) {
return response()->json(['error' => 'Invalid token'], 401);
}
$request->attributes->set("kc", $resp->json());
return $next($request);
}
}
B. Register Middleware
app/Http/Kernel.php
protected $routeMiddleware = [
'kc.service' => \App\Http\Middleware\KeycloakServiceAuth::class,
];
C. SERVICE B → Controller
app/Http/Controllers/ServiceBController.php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Services\ServiceCClient;
class ServiceBController extends Controller
{
public function process(Request $request, ServiceCClient $serviceC)
{
$kc = $request->attributes->get("kc"); // introspected token
$orderId = $request->order_id;
// Business logic example
$processed = "Order $orderId processed by Service B";
// Now call Service C
$result = $serviceC->sendToServiceC($kc['exp']); // dummy example
return response()->json([
"service_b" => $processed,
"service_c" => $result
]);
}
}
D. SERVICE B → Route
routes/api.php
Route::post('/process', [ServiceBController::class, 'process'])->middleware('kc.service');
⭐ PART 3 — SERVICE B → SERVICE C CALL
A. SERVICE B Token Exchange to Service C
app/Services/ServiceCClient.php
namespace App\Services;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Http;
class ServiceCClient
{
public function sendToServiceC($subjectToken)
{
$kcBase = env('KEYCLOAK_BASE_URL');
$realm = env('KEYCLOAK_REALM');
$tokenUrl = "$kcBase/realms/$realm/protocol/openid-connect/token";
$resp = Http::asForm()->post($tokenUrl, [
"grant_type" => "urn:ietf:params:oauth:grant-type:token-exchange",
"client_id" => env('SERVICE_B_CLIENT_ID'),
"client_secret" => env('SERVICE_B_CLIENT_SECRET'),
"subject_token" => $subjectToken,
"subject_token_type" => "urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:access_token",
"requested_token_type" => "urn:ietf:params:oauth:token-type:access_token"
]);
$exchangedToken = $resp->json()['access_token'];
return Http::withToken($exchangedToken)
->post("https://service-c.internal/api/compute", [
"value" => 10
])->json();
}
}
⭐ PART 4 — SERVICE C (Laravel)
SERVICE C Controller
app/Http/Controllers/ServiceCController.php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
class ServiceCController extends Controller
{
public function compute(Request $request)
{
return [
"result" => $request->value * 2,
"msg" => "Service C successfully processed request"
];
}
}
SERVICE C Route
routes/api.php
Route::post('/compute', [ServiceCController::class, 'compute'])
->middleware('kc.service');
SUMMARY ARCHITECTURE IS COMPLETE & FULLY FUNCTIONAL
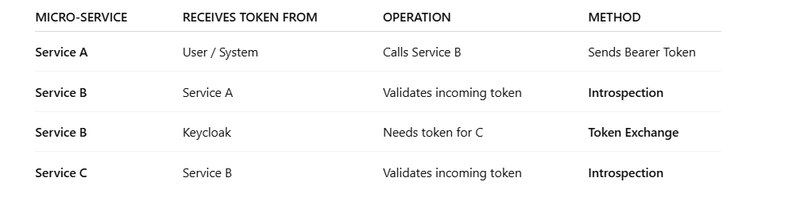
✔ Service A → calls Service B
✔ Service B → validates token
✔ Service B → calls Service C via token exchange
✔ Service C → validates token
✔ Fully secure zero-trust microservice-to-microservice architecture
✔ All code provided (controllers, middleware, routes, services)
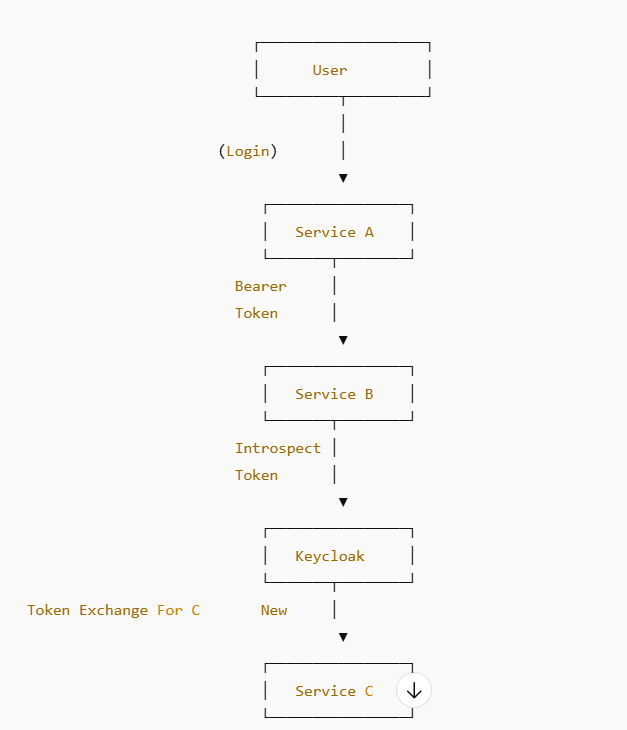
WHY DO WE NEED TOKEN EXCHANGE BETWEEN MICROSERVICES
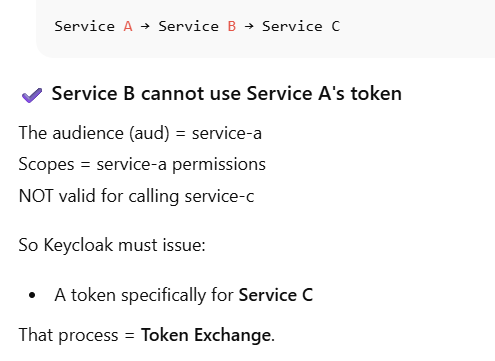
Because Service A’s token should NOT be trusted by Service B
When Service A calls Service B with its own token:
The token audience (aud) = service-a
The token scope = permissions of service-a
The issuer knows this token was created for Service A, not Service B
So Service B cannot trust that token.
👉 If Service B uses Service A’s token, it is NOT secure.
Token Exchange fixes this:
Service A’s token → sent to Keycloak
Keycloak issues a NEW token intended for Service B
Token audience changes to service-b
Token permissions change to only service-b allowed actions
This means:
✔ Each service gets its own token
✔ No service impersonates another
✔ Zero Trust architecture enforced
⭐ 2. Proper Isolation of Microservices (Zero Trust Architecture)
In a real microservice system:
Each service must have separate permissions
Each service must get a token designed only for itself
No service can accidentally or intentionally escalate privileges
If Service B accepted Service A’s token as-is, then:
🛑 Service A could call ANY endpoint of Service B
🛑 Service A could impersonate a user in B
🛑 If Service A is hacked → all microservices are compromised
Token Exchange ensures:
✔ Service A cannot use its own token to act inside B
✔ Service B only accepts tokens whose audience = B
✔ Tokens are issued per-service, per-use
⭐ 3. Keycloak Can Apply Authorization Policies Per Service
Keycloak needs to know:
Who is calling the service?
What is the service allowed to do?
Example:
Service A permissions:
orders.read
Service B permissions:
orders.approve
inventory.adjust
Service C permissions:
analytics.run
Only Token Exchange allows Keycloak to generate these per-service scopes.
⭐ 4. Service B Needs a Token It Can Use to Call Other Services
This is the most important:
If Service B must call Service C, then:
Service B CANNOT use Service A’s token
Service B MUST obtain its own token from Keycloak
Token Exchange gives:
Service A token → Keycloak → new token → Service B
Then:
Service B token → Keycloak token exchange → Service C token
Without Token Exchange?
🛑 Service B cannot authenticate to Service C securely.
🛑 Service B would need SERVICE C’s client_secret (very dangerous).
🛑 You would break isolation between microservices.
⭐ 5. Token Exchange Allows “Delegation” Without Sharing Passwords
Real-world example:
A user logs in to Domain A
→ Access token created
→ Laravel syncs with Keycloak
Now Domain B needs to act on behalf of the user.
Using Token Exchange:
✔ Domain B gets a token representing the same user
✔ But with permissions tailored for Domain B only
✔ Without ever seeing the user’s password
✔ Without copying Domain A’s token
This is the exact reason OAuth2 Token Exchange exists.
SUMMARY — SIMPLE EXPLANATION
Why token introspection is needed
WHY SERVICE B SHOULD NOT DO TOKEN EXCHANGE
Service A sends a token to Service B
This token’s purpose is:
Authenticate Service A
Identify the identity calling
Ensure Service A is authorized to call Service B
What does Service B need to do?
Only validate the incoming token:
/introspect
This checks:
Is the token issued by Keycloak?
Is it active?
Is it expired?
Does the service have permission?
Is the client correct?
🔐 Token introspection is ENOUGH for Service B
Service B does NOT need a new token unless:
Service B wants to call another service (Service C).
So:
✔ Good:
Service B validates Service A’s token using introspection.
✔ Correct:
Service B does NOT need Token Exchange to process the request.
WHEN SERVICE B DOES NEED TOKEN EXCHANGE
@startuml
actor User
User -> ServiceA: Login / API Request
ServiceA -> Keycloak: Password Grant / OIDC
Keycloak --> ServiceA: Access Token (user_token)
User -> ServiceA: Call API with user_token
ServiceA -> ServiceB: HTTP Request\nAuthorization: Bearer user_token
ServiceB -> Keycloak: /introspect(user_token)
Keycloak --> ServiceB: { active: true, email, roles }
ServiceB --> ServiceA: OK (token valid)
== Service B Needs to Call Service C ==
ServiceB -> Keycloak: Token Exchange Request\nsubject_token = user_token
Keycloak --> ServiceB: new_token_for_serviceC
ServiceB -> ServiceC: HTTP Request\nAuthorization: Bearer new_token_for_serviceC
ServiceC -> Keycloak: /introspect(new_token_for_serviceC)
Keycloak --> ServiceC: { active: true, roles: service-c }
ServiceC --> ServiceB: OK (business response)
ServiceB --> ServiceA: Final Response
ServiceA --> User: Output Data
@enduml
TOKEN FLOW DIAGRAM (USER → A → B → C)
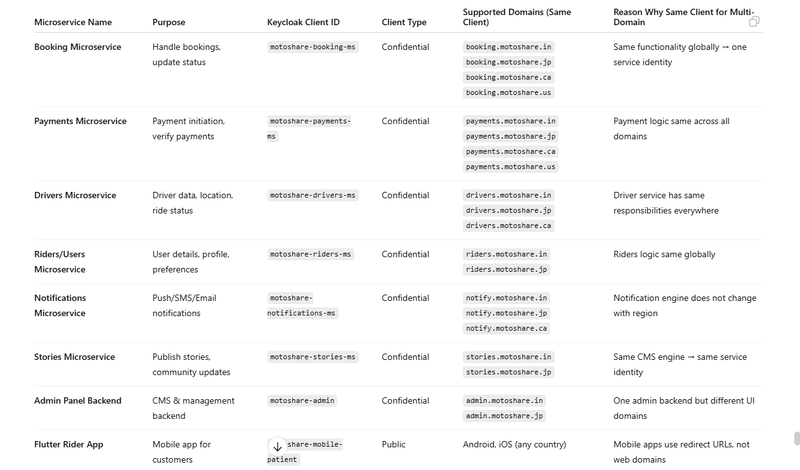
Keycloak Client Mapping for Multi-Domain Architecture
You MUST use MULTIPLE CLIENTS for each microservices
You MUST use SINGLE CLIENTS for multiple domain







Top comments (0)