Why Do We Need Virtual Host Configuration in Apache
role and purpose of dns server and web server
Key reasons why Apache Virtual Hosts are needed
url mapping to to a different directory on the filesystem using alias
How to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS and then forwards secure HTTPS requests to the Traccar service running on port 8082
How to redirects HTTP to HTTPS and proxies requests to different front-end services (React, Vue, Angular) while using a shared backend API
Troubleshoot
Why Do We Need Virtual Host Configuration in Apache
Virtual host configuration in Apache is essential for hosting multiple websites (domains) on a single server instance. Without it, an Apache server can only serve content for a single site, but with virtual hosts, developers and administrators can easily run several completely independent websites using the same server and even the same IP address.
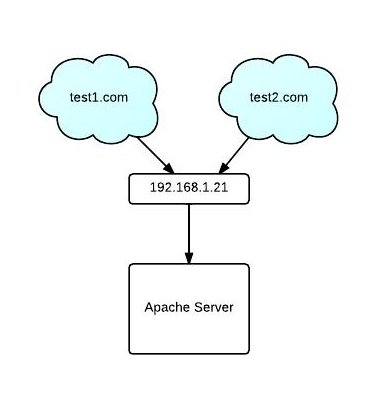
A Virtual Host (vhost) is a configuration block in Apache that allows the server to respond differently based on the domain name, IP address, or port in the incoming HTTP request.
It enables one server (even with one IP address) to host multiple websites, each with its own content, settings, and behavior.
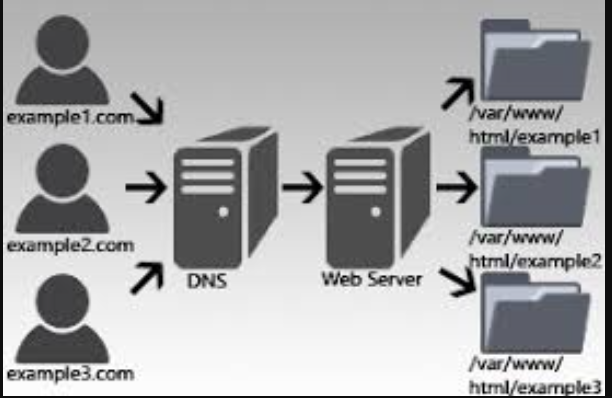
DNS Server
Role: Maps a domain name (like example1.com) to the corresponding server's IP address.
What Happens: When a user tries to visit a website (e.g., example1.com), their browser first queries the DNS server to find the IP address of that domain. The DNS server responds with the address of the web server hosting the site.
Example (No code needed for DNS, but here’s a conceptual mapping):
DNS mapping is done by AWS
DNS mapping is typically done by the domain owner or administrator through their domain registrar or DNS hosting provide
example1.com --> 192.0.2.10
example2.com --> 192.0.2.10
example3.com --> 192.0.2.10
All domains point to the same server IP, which enables name-based virtual hosting.
Web Server
Role: Hosts multiple websites on the same server and serves content based on the domain name requested by the client.
What Happens: After DNS points the browser to the web server's IP, the web server uses the domain name from the request (Host header) to determine which site to serve. Each site’s files are stored in separate directories (as shown in the figure: /var/www/html/example1, etc.).
Example: Apache Configuration for Name-based Virtual Hosts
Below is a sample Apache configuration to set up virtual hosts:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example1.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example1
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example2.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example2
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName example3.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/example3
</VirtualHost>
--------------------above code in nginx-------------------
server {
listen 80;
server_name example1.com;
root /var/www/html/example1;
index index.html index.htm;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example2.com;
root /var/www/html/example2;
index index.html index.htm;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name example3.com;
root /var/www/html/example3;
index index.html index.htm;
}
<VirtualHost *:80>
DocumentRoot "/opt/lampp/htdocs/motoshare-test/public"
ServerName demo.motoshare.in
ErrorLog "logs/motoshare_test_log"
CustomLog "logs/motoshare_test-access_log" common
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/motoshare-test/public">
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
Key reasons why Apache Virtual Hosts are needed
Multiple Sites on a Single Server: Run numerous websites with different domains (e.g., example.com and test.com) on one physical or virtual machine.
Separation and Customization: Each site can have its own document root, configuration, error logs, and even PHP settings, making management cleaner and more isolated.
Resource Optimization: Saves costs by efficiently utilizing server resources instead of requiring a separate server for each website.
Flexible Hosting: Supports both IP-based and name-based virtual hosting. Name-based is more common today, where the requested hostname in the HTTP header determines which site Apache serves
Url mapping to to a different directory on the filesystem using alias
In Apache Virtual Host configuration, aliases can be very useful to create URL mappings to a different directory on the filesystem. This is commonly done using the Alias directive.
What is Aliasing in Apache Virtual Host?
Aliasing allows you to map a URL path to a specific filesystem path. This is useful for:
Making URLs shorter and more user-friendly.
Organizing content across different directories.
Mapping static files to a specific location.
🔹 1. Basic Aliasing with Alias Directive
Scenario: You want to make the URL /images point to a specific folder on your server /var/www/html/images/.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName mydomain.com
# Alias directive to map '/images' URL to '/var/www/html/images'
Alias /images /var/www/html/images/
<Directory "/var/www/html/images">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
/images in the URL is mapped to /var/www/html/images on the server filesystem.
The Alias directive allows requests to http://mydomain.com/images/* to serve files from /var/www/html/images.
🔹 2. Aliasing for Multiple Virtual Hosts
Scenario: You have multiple subdomains (sub1.mydomain.com and sub2.mydomain.com), each serving different content from different directories.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/sub1
ServerName sub1.mydomain.com
# Alias to serve /images from a different directory
Alias /images /var/www/media/images
<Directory "/var/www/media/images">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/sub2
ServerName sub2.mydomain.com
# Alias to serve different images directory
Alias /images /var/www/media/sub2_images
<Directory "/var/www/media/sub2_images">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
sub1.mydomain.com/images maps to /var/www/media/images.
sub2.mydomain.com/images maps to /var/www/media/sub2_images.
Each subdomain uses a different folder for images.
🔹 3. Aliasing with mod_rewrite for URL Redirection
Scenario: You want to redirect requests from one URL path to another.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName mydomain.com
# Alias '/oldpath' to '/newpath'
Alias /oldpath /var/www/html/newpath
<Directory "/var/www/html/newpath">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
# Use mod_rewrite to rewrite URLs for redirection
RewriteEngine On
RewriteRule ^/oldpath(.*)$ /newpath$1 [R=301,L]
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
Alias allows /oldpath to be mapped to /newpath.
mod_rewrite handles the permanent redirect (301) so that http://mydomain.com/oldpath redirects to http://mydomain.com/newpath.
🔹 4. Aliasing with mod_userdir for User-Specific Directories
Scenario: Allow each user to have their own website by using mod_userdir.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /home
ServerName mydomain.com
# Alias to serve individual user's content
Alias /~username /home/username/public_html
<Directory "/home/username/public_html">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
This makes /~username URL accessible to the public, serving files from /home/username/public_html.
Each user can have their own sub-directory under /home/username/ for their content.
🔹 5. Aliasing for Static Files in a Web Application
Scenario: Your web application has a static file directory like /assets, and you want to serve it via a cleaner URL.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/myapp
ServerName myapp.mydomain.com
# Alias to map '/assets' URL to a specific directory for static files
Alias /assets /var/www/myapp/static/assets
<Directory "/var/www/myapp/static/assets">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
Requests to http://myapp.mydomain.com/assets/* will serve static content from /var/www/myapp/static/assets.
This is ideal for serving images, JavaScript files, CSS, etc.
🔹 6. Aliasing to a Different Port or Host
Scenario: Redirecting requests for a URL to another server or port.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName mydomain.com
# Alias to forward requests to a different server/port
Alias /app http://localhost:8080/app
<Directory "/var/www/html/app">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
Alias here is used to forward the request for /app to a different server or port (e.g., localhost:8080).
Useful for microservices or when you want to separate concerns.
Aliasing with Directory Listings
Scenario: You want to show a directory listing of a specific folder under a URL.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin webmaster@mydomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
ServerName mydomain.com
# Alias directory listing
Alias /downloads /var/www/html/downloads
<Directory "/var/www/html/downloads">
Options Indexes
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
✅ Explanation:
By using Options Indexes, Apache will automatically generate a directory listing when accessing http://mydomain.com/downloads.
Good for exposing downloadable content.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@dronesnow.in
DocumentRoot "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/homepage"
ServerName dronesnow.in
ServerAlias www.dronesnow.in
ErrorLog "logs/dronesnow.in-error_log"
CustomLog "logs/dronesnow.in-access_log" common
Redirect permanent / https://dronesnow.in/
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/homepage">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /blog /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/blog
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/blog">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /forum /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/forum/public
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/forum/public">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /shop /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/shop/magento/pub
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/shop/magento/pub">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /pilots /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/professional/professnow-new/public
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/professional/professnow-new/public">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /institutes /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/institute/php/public
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/institute/php/public">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
Alias /videos /opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/videos/phpvibe
<Directory "/opt/lampp/htdocs/dronesnow/videos/phpvibe">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Allow from all
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
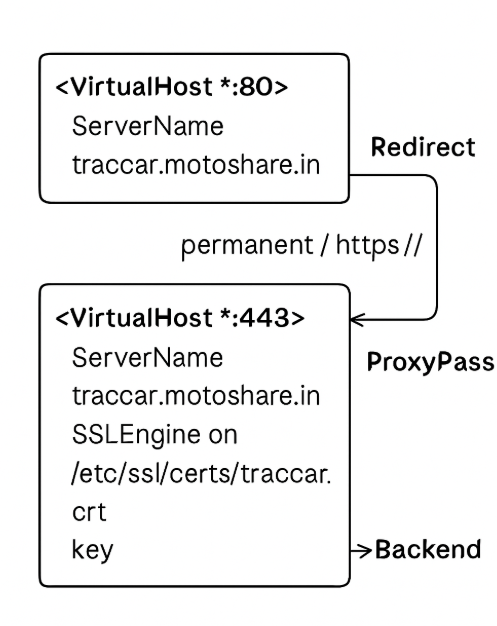
HTTP traffic is redirected to HTTPS and then forwards secure HTTPS requests to the Traccar service running on port 8082
read for proxy
/opt/lampp/etc/extra/httpd-vhosts.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName traccar.motoshare.in
Redirect permanent / https://traccar.motoshare.in/
</VirtualHost>
/opt/lampp/etc/extra/httpd-ssl.conf
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName traccar.motoshare.in
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile "/opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/traccar.motoshare.in.cer"
SSLCertificateKeyFile "/opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/traccar.motoshare.in.key"
SSLCACertificateFile "/opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/fullchain.cer"
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8082/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8082/
</VirtualHost>
-------------------------Nginx--------------------------
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name traccar.motoshare.in;
# SSL Configuration
ssl_certificate /opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/traccar.motoshare.in.cer;
ssl_certificate_key /opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/traccar.motoshare.in.key;
ssl_trusted_certificate /opt/lampp/etc/certs/traccar.motoshare.in/fullchain.cer;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384';
# Proxy Settings
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8082/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
}
The variables $host, $remote_addr, $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for, and $scheme are built-in Nginx variables that represent specific pieces of information about the incoming HTTP request. These variables are available in the Nginx configuration and can be used for logging, proxying, and header passing
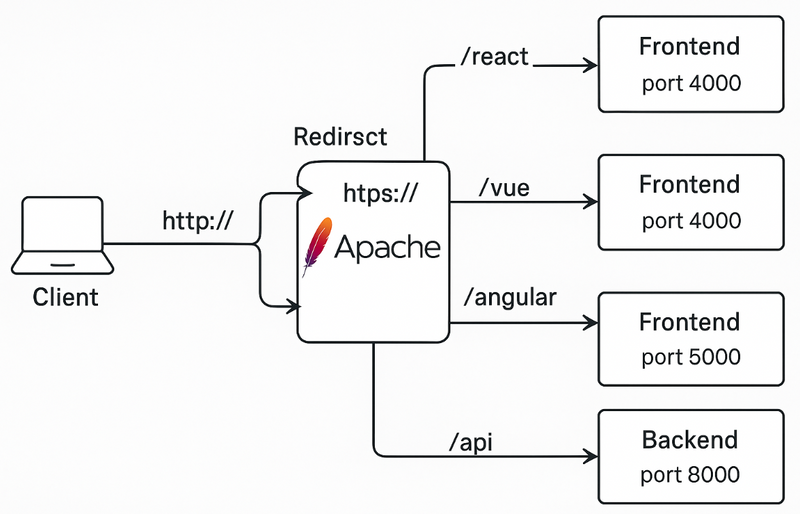
How to redirects HTTP to HTTPS and proxies requests to different front-end services (React, Vue, Angular) while using a shared backend API
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName myapp.mydomain.com
# Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Redirect permanent / https://myapp.mydomain.com/
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName myapp.mydomain.com
# SSL Configuration
SSLEngine On
SSLCertificateFile "/etc/ssl/certs/myapp.mydomain.com.crt"
SSLCertificateKeyFile "/etc/ssl/private/myapp.mydomain.com.key"
SSLCACertificateFile "/etc/ssl/certs/myapp.mydomain.com.chain.pem"
# Proxying React service running on port 3000
ProxyPass /react http://localhost:3000/
ProxyPassReverse /react http://localhost:3000/
# Proxying Vue service running on port 8081
ProxyPass /vue http://localhost:8081/
ProxyPassReverse /vue http://localhost:8081/
# Proxying Angular service running on port 4200
ProxyPass /angular http://localhost:4200/
ProxyPassReverse /angular http://localhost:4200/
# Laravel Backend API (assuming it's running on port 8000)
ProxyPass /api http://localhost:8000/api
ProxyPassReverse /api http://localhost:8000/api
# Optional: Serve static content or assets for React/Vue/Angular if necessary
Alias /react/static /var/www/myapp/react/static
Alias /vue/static /var/www/myapp/vue/static
Alias /angular/static /var/www/myapp/angular/static
<Directory "/var/www/myapp/react/static">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory "/var/www/myapp/vue/static">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory "/var/www/myapp/angular/static">
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
</VirtualHost>
--------OR---------------------------------
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName yourdomain.com
ServerAlias www.yourdomain.com
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/certs/your_cert.crt
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/private/your_key.key
# Ensure these modules are loaded
ProxyPreserveHost On
# Proxy /react to React app (port 3000)
ProxyPass /react http://localhost:3000/
ProxyPassReverse /react http://localhost:3000/
# Proxy /vue to Vue app (port 4000)
ProxyPass /vue http://localhost:4000/
ProxyPassReverse /vue http://localhost:4000/
# Proxy /angular to Angular app (port 5000)
ProxyPass /angular http://localhost:5000/
ProxyPassReverse /angular http://localhost:5000/
# Proxy /api to backend API (port 8000) - shared for all
ProxyPass /api http://localhost:8000/api
ProxyPassReverse /api http://localhost:8000/api
# Optional: Static root to one of the frontends
ProxyPass / http://localhost:3000/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:3000/
</VirtualHost>
--------------above in In NGINX----------------------
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name myapp.mydomain.com;
# SSL Configuration
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/myapp.mydomain.com.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/private/myapp.mydomain.com.key;
ssl_trusted_certificate /etc/ssl/certs/myapp.mydomain.com.chain.pem;
ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3;
ssl_ciphers 'ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384';
# Proxying React service running on port 3000
location /react/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Proxying Vue service running on port 8081
location /vue/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8081/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Proxying Angular service running on port 4200
location /angular/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:4200/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Proxying Laravel Backend API (assuming it's running on port 8000)
location /api/ {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8000/api/;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
}
# Optional: Serve static content or assets for React/Vue/Angular if necessary
location /react/static/ {
alias /var/www/myapp/react/static/;
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location /vue/static/ {
alias /var/www/myapp/vue/static/;
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
location /angular/static/ {
alias /var/www/myapp/angular/static/;
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}
}
Troubleshoot
custom-error-handling-and-indexing-in-apache-http-server
sudo tail -f /opt/lampp/logs/access_log
tail -f storage/logs/laravel.log
tail -f /opt/traccar/logs/tracker-server.log



Top comments (0)