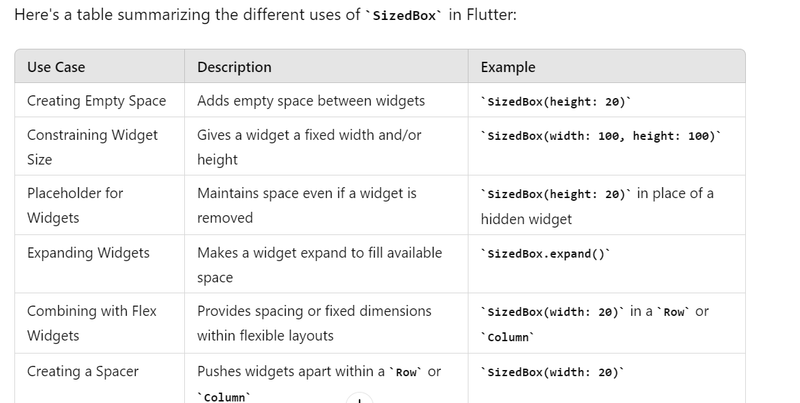
SizedBox is a widget in Flutter that is commonly used to create space and constraints within the layout. Here are several reasons and examples of why and how to use SizedBox in Flutter:
- Creating Empty Space SizedBox can be used to create space between widgets.
Example:
Column(
children: <Widget>[
Text('First Widget'),
SizedBox(height: 20), // 20 pixels of vertical space
Text('Second Widget'),
],
)
- Constraining Widget Size SizedBox can be used to give a widget a fixed width and/or height.
Example:
SizedBox(
width: 100,
height: 100,
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Center(child: Text('Fixed Size')),
),
)
- Placeholder for Widgets SizedBox can act as a placeholder, maintaining space even if a widget is temporarily removed.
Example:
bool _isVisible = false;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: <Widget>[
_isVisible ? Text('Visible Widget') : SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_isVisible = !_isVisible;
});
},
child: Text('Toggle Visibility'),
),
],
);
}
- Expanding Widgets When used with an infinite dimension (double.infinity), SizedBox can make a widget expand to fill available space.
Example:
SizedBox.expand(
child: Container(
color: Colors.red,
child: Center(child: Text('Expanded')),
),
)
- Combining with Flex Widgets SizedBox can be combined with Row, Column, and other flex widgets to provide spacing or fixed dimensions within flexible layouts.
Example:
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(color: Colors.blue),
),
SizedBox(width: 20), // Spacer of 20 pixels
Expanded(
child: Container(color: Colors.green),
),
],
)
- Creating a Spacer SizedBox can be used as a spacer to push widgets apart within a Row or Column.
Example:
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Text('Start'),
SizedBox(width: 20), // Spacer of 20 pixels
Text('Middle'),
SizedBox(width: 20), // Spacer of 20 pixels
Text('End'),
],
)
Benefits of Using SizedBox
Simplicity: SizedBox is a simple and readable way to add spacing and size constraints in your widget tree.
Performance: It is lightweight and performs well, especially for adding space and constraints.
Clarity: Improves code clarity by explicitly showing that the purpose of the widget is to provide a specific amount of space or size.
Complete Example
Here's a complete example demonstrating several uses of SizedBox:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() {
runApp(MyApp());
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
home: Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text('SizedBox Examples')),
body: Padding(
padding: const EdgeInsets.all(16.0),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
// Creating Empty Space
Text('First Widget'),
SizedBox(height: 20),
Text('Second Widget'),
// Constraining Widget Size
SizedBox(height: 20),
SizedBox(
width: 100,
height: 100,
child: Container(
color: Colors.blue,
child: Center(child: Text('Fixed Size')),
),
),
// Placeholder for Widgets
SizedBox(height: 20),
PlaceholderWidget(),
// Expanding Widgets
SizedBox(height: 20),
SizedBox.expand(
child: Container(
color: Colors.red,
child: Center(child: Text('Expanded')),
),
),
// Combining with Flex Widgets
SizedBox(height: 20),
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Expanded(
child: Container(color: Colors.blue),
),
SizedBox(width: 20),
Expanded(
child: Container(color: Colors.green),
),
],
),
// Creating a Spacer
SizedBox(height: 20),
Row(
children: <Widget>[
Text('Start'),
SizedBox(width: 20),
Text('Middle'),
SizedBox(width: 20),
Text('End'),
],
),
],
),
),
),
);
}
}
class PlaceholderWidget extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_PlaceholderWidgetState createState() => _PlaceholderWidgetState();
}
class _PlaceholderWidgetState extends State<PlaceholderWidget> {
bool _isVisible = false;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: <Widget>[
_isVisible ? Text('Visible Widget') : SizedBox(height: 20),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () {
setState(() {
_isVisible = !_isVisible;
});
},
child: Text('Toggle Visibility'),
),
],
);
}
}

Top comments (0)