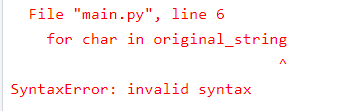
how to check particular char of string in list available or not
invalid syntax mistake
for char in original_string
if char in characters_to_remove:
solution
put colon after for
Note put colon after for ,def ,if,else
Note remember the indention of for,if,else and pass
indention of for and if
for char in original_string:
if char in characters_to_remove:
indention for,if and data
for newdata in data:
if newdata%2 == 0:
even.append(newdata)
Indention between for,if and local print global print
even = []
for newdata in data:
if newdata%2 == 0:
even.append(newdata)
print(newdata)
print(even)
indention between for,if,else,print
for max_data in words_list:
if maxdatas>max_data:
maxdatas=maxdatas
else:
maxdatas=max_data
print(maxdatas)
indention between for,if,else,pass,print
for max_data in words_list:
if maxdatas>max_data:
pass
else:
pass
print(maxdatas)
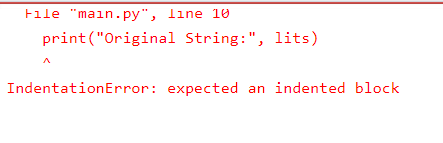
IndentationError: expected an indented block
Indention error b/w double for block
data = (4,6,9,10)
list=[]
for char in data:
if char%2==0:
list.append(char)
for lits in list:
print("Original String:", lits)
correct
data = (4, 6, 9, 10)
my_list = []
for number in data:
if number % 2 == 0:
my_list.append(number)
for item in my_list:
print("Original String:", item)
wrong
def add():
data="python"
my=["o","n"]
new=[]
for newdata in data
if my in newdata
Correct
always iterate in string,list,dictionary,tuple not single variable of list
if newdata in my
def add():
data="python"
my=["o","n"]
new=[]
for newdata in data
if newdata in my
How to add new char in empty string or exisiting string without for loop
empty_string = "" # An empty string
new_char1 = "Hello, "
new_char2 = "world!"
# Concatenating strings
new_string = empty_string + new_char1 + new_char2
# Using the += operator
empty_string += new_char1
empty_string += new_char2
print("Empty String:", empty_string)
print("New String after adding characters:", new_string)
How to add new char in empty string or exisiting string inside for loop
data = "python"
vowels = "aeiou"
mynew = ""
for char in data:
if char not in vowels:
mynew += char
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
for x in adj:
for y in fruits:
print(x, y)
output
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
mylist=[]
for x in adj:
for y in fruits:
mylist.append(f"{x} {y}")
print(mylist)
print(', '.join(mylist))
output
['red apple', 'red banana', 'red cherry', 'big apple', 'big banana', 'big cherry', 'tasty apple', 'tasty banana', 'tasty cherry']
red apple, red banana, red cherry, big apple, big banana, big cherry, tasty apple, tasty banana, tasty cherry
adj = ["red", "big", "tasty"]
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
output = []
for i in range(len(adj)):
output.append(f"{adj[i]} {fruits[i]}")
output_str = ",".join(output)
print(output_str)
output
red apple,big banana,tasty cherry
listed=[('group2', 1, 5), ('group2', 2, 5)]
for y, style, label in listed:
print(y,style,label)
output
group2 1 5
group2 2 5
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
x = np.linspace(0, 10, 100)
# Data for y-values and their corresponding styles and labels
y_values = [
(np.sin(x) + 6, 'ro', 'red circle'),
(np.cos(x) + 6, 'bo', 'blue circle'),
(np.sin(x) + 7, 'go', 'green circle'),
(np.cos(x) + 7, 'yo', 'yellow circle'),
(np.sin(x) + 8, 'ko', 'black circle'),
(np.cos(x) + 8, 'rx', 'red x-mark'),
(np.sin(x) + 9, 'bx', 'blue x-mark')
]
# Plot each y-value with its corresponding style and label
for y, style, label in y_values:
plt.plot(x, y, style, label=label)
plt.legend()
plt.show()
==========================================================
Basic Coding
1.Wap print those name that contain letters n
my=["ram","rana","rina","sham","raddhe"]
letters="n"
lists=[]
for data in my:
if letters in data:
lists.append(data)
print(lists)
output
['rana', 'rina']
=======OR=========
my = ["ram", "rana", "rina", "sham", "raddhe"]
letters = "n"
# Printing the elements containing the specified letters directly within the loop
for data in my:
if letters in data:
print(data)
output
rana
rina
2.Wap print those name that not contain letters n
my=["ram","rana","rina","sham","raddhe"]
letters="n"
lists=[]
for data in my:
if letters in data:
pass
else:
lists.append(data)
print(lists)
output
['ram', 'sham', 'raddhe']
3.Wap to remove vowels from string
data = "python"
vowels = "aeiou"
mynew = ""
for char in data:
if char not in vowels:
mynew += char
print(mynew)
output
pythn
4.Wap to replace vowels from single letters string
data = "python"
vowels = "aeiou"
mynew = ""
for char in data:
if char not in vowels:
mynew += char
else:
mynew += "h"
print(mynew)
output
pythhn
=========OR=========
Using replace
NOTE: can achive without creating new string like mynew in above prog
data = "python"
vowels = "aeiou"
for char in data:
if char not in vowels:
pass
else:
newdata=data.replace(char,"h")
print(newdata)
Output
pythhn
==============OR===============
Using sub
import re
data = "python"
vowels = "aeiou"
mychar="t"
for char in data:
if char not in vowels:
pass
else:
data=re.sub(char, "h", data)
print(data)
output
pythhn
5.Wap to print those name from list that does not contain vowel letters
my_list = ["Asm", "rana", "rina", "sham", "raddhe", "btm"]
names_without_vowels = []
for name in my_list:
has_vowel = False
for char in name:
if char.lower() in 'aeiou':
has_vowel = True
break
if not has_vowel:
names_without_vowels.append(name)
print("Names without any vowel letters:", names_without_vowels)
output
Names without any vowel letters: ['btm']
find particular name from list and put in list
simple_list = ["john", "doe", "sourav", "rahul", "alex", "sourav", "michael", "jordan", "sourav", "kohli"]
# Extracting all occurrences of "sourav" into a new list
new_list = [name for name in simple_list if name == "sourav"]
print(new_list)
['sourav', 'sourav', 'sourav']
Using re.findall to find "sourav"
import re
# Join the list into a single string
joined_string = " ".join(simple_list)
print(joined_string)
# Use re.findall to extract all occurrences of "sourav"
new_list = re.findall(r'\bsourav\b', joined_string)
print(new_list)
output
john doe sourav rahul alex sourav michael jordan sourav kohli
['sourav', 'sourav', 'sourav']
find particular name from list of array and put in list
arrays = [["john", "doe"], ["sourav", "rahul"], ["alex", "sourav"], ["michael", "jordan"], ["sourav", "kohli"]]
# Extracting all occurrences of "sourav"
new_list = []
for array in arrays:
for name in array:
if name == "sourav":
new_list.append(name)
# Adding 'ram' and 'rana' to the list
final_list = new_list + ['ram', 'rana']
print(final_list)
['sourav', 'sourav', 'sourav', 'ram', 'rana']
using list comprhension
# Extracting all occurrences of "sourav"
new_list = [name for array in arrays for name in array if name == "sourav"]
# Adding 'ram' and 'rana' to the list
final_list = new_list + ['ram', 'rana']
print(final_list)
output
['sourav', 'sourav', 'sourav', 'ram', 'rana']
6.Create a class named Book where title,publishers,price act as a data member along with caldiscount function that calculates the given discount on book price. Also create displaydata function that will call caldiscount function and display all the values. Take discount=15 as class variable
class Book:
discount = 15 # Class variable for discount percentage
def __init__(self, title, publisher, price):
self.title = title
self.publisher = publisher
self.price = price
def caldiscount(self):
# Method to calculate discount on book price
discount_amount = (self.discount / 100) * self.price
discounted_price = self.price - discount_amount
return discounted_price
def displaydata(self):
# Method to display book details including discounted price
discounted_price = self.caldiscount()
print("Title:", self.title)
print("Publisher:", self.publisher)
print("Price:", self.price)
print("Discounted Price:", discounted_price)
# Example usage:
book1 = Book("Python Programming", "ABC Publications", 500)
book1.displaydata()
output
Title: Python Programming
Publisher: ABC Publications
Price: 500
Discounted Price: 425.0
**7.Define a class CONTAINER in Python with the following specifications: -Instance Attributes
- Radius,Height # Radius and Height of Container -Volume # Volume of Container Methods
- CalVolume() # Method to calculate volume # # With the formula as given below 3.14* Radius * Height
- GetValue() # Method to allow user to enter values of # Radius and Height # Also, this method should call # CalVolume() method to calculate Volume
- ShowContainer() # To display Radius, Height and Volume**
class CONTAINER:
def __init__(self):
self.radius = 0 # Initialize radius attribute
self.height = 0 # Initialize height attribute
self.volume = 0 # Initialize volume attribute
def CalVolume(self):
# Method to calculate volume using the given formula
self.volume = 3.14 * self.radius * self.height
def GetValue(self):
# Method to allow user to enter values of radius and height
self.radius = float(input("Enter the radius of the container: "))
self.height = float(input("Enter the height of the container: "))
self.CalVolume() # Call CalVolume method to calculate volume
def ShowContainer(self):
# Method to display radius, height, and volume
print("Radius:", self.radius)
print("Height:", self.height)
print("Volume:", self.volume)
# Create an instance of the CONTAINER class
container = CONTAINER()
# Get values from the user and display container details
container.GetValue()
container.ShowContainer()
output
press enter
Enter the radius of the container: 6
Enter the height of the container: 8
Radius: 6.0
Height: 8.0
Volume: 150.72
8. combine two dictionary
dict1 = {'Mercury': 100, 'Venus': 200, 'Earth': 300}
dict2 = {'Star': 500, 'Moon': 600, 'Sun': 700}
dict1.update(dict2)
print(dict1)
output
{'Mercury': 100, 'Venus': 200, 'Earth': 300, 'Star': 500, 'Moon': 600, 'Sun': 700}
9.remove particular key value pair from dictionary
ages = {"Alice": 30, "Bob": 25, "Charlie": 35, "David": 40}
# Removing the age associated with "Charlie"
removed_age = ages.pop("Charlie")
print("Removed age:", removed_age)
print("Updated dictionary:", ages)
output
Removed age: 35
Updated dictionary: {'Alice': 30, 'Bob': 25, 'David': 40}
10.Rename key city to location in the following dictionary
sampleDict = { "name": "Kelly", "age":25, "salary": 8000, "city": "New york"}
Expected output: { "name": "Kelly", "age":25, "salary": 8000, "location": "New york"}
sampleDict = { "name": "Kelly", "age":25, "salary": 8000, "city": "New york"}
# Rename the key from "city" to "location"
sampleDict["location"] = sampleDict.pop("city")
print(sampleDict)
output
{ "name": "Kelly", "age":25, "salary": 8000, "location": "New york"}
11.Write a class circle to calculate the area of it
import math
class Circle:
def __init__(self, x):
self.x = x
def area(self):
return math.pi * self.x ** 2
x = 5
data = Circle(x)
print("Area of circle:", data.area())
output
Area of circle: 78.53981633974483
12.create a instance of class and print it
class MyClass:
def __init__(self, x):
self.x = x # Assigning instance variable x using self
def print_value(self):
print("Value of x:", self.x) # Accessing instance variable x using self
obj1 = MyClass(5) # Creating an instance of MyClass
obj2 = MyClass(10) # Creating another instance of MyClass
obj1.print_value() # Calling print_value method on obj1
obj2.print_value() # Calling print_value method on obj2
output
Value of x: 5
Value of x: 10
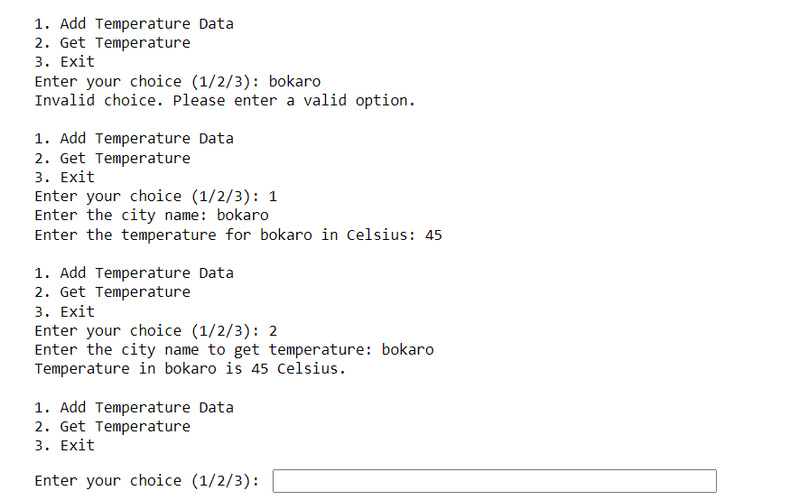
13.Write a program asks for City name and Temperature and builds a dictionary using that Later on you can input City name and it will tell you the Temperature of that City.
temperature_data = {} # Dictionary to store city names and temperatures
# Function to add city name and temperature to the dictionary
def add_temperature():
city = input("Enter the city name: ")
temperature = input("Enter the temperature for {} in Celsius: ".format(city))
temperature_data[city] = temperature
main() # Call main function again to display menu
# Function to retrieve temperature of a given city
def get_temperature():
city = input("Enter the city name to get temperature: ")
if city in temperature_data:
print("Temperature in {} is {} Celsius.".format(city, temperature_data[city]))
else:
print("Temperature data for {} not found.".format(city))
main() # Call main function again to display menu
# Main function to display menu and handle user input
def main():
print("\n1. Add Temperature Data")
print("2. Get Temperature")
print("3. Exit")
choice = input("Enter your choice (1/2/3): ")
if choice == '1':
add_temperature()
elif choice == '2':
get_temperature()
elif choice == '3':
print("Exiting program.")
else:
print("Invalid choice. Please enter a valid option.")
main() # Call main function again if choice is invalid
# Call main function to start the program
main()
output
SOME COMMON REGX QUESTION
What does the split() function do in Python?
split() function splits a string into a list of substrings based on a specified delimiter.
split a string/sentence into words then store each words in list
text = "apple, banana, cherry"
fruits = text.split(", ")
print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
How do you split a string into words using split()?
You can split a string into words by specifying a space as the delimiter.
split a string/sentence into words based on comma then store each words in list using two method findall and split
text = "Hello world, how are you?"
words = text.split()
print(words) # Output: ['Hello', 'world,', 'how', 'are', 'you?']
============OR=============
Using findall
import re
text = "Hello, world! This is a test."
words = re.findall(r'\w+', text)
print(words) # Output: ['Hello', 'world', 'This', 'is', 'a', 'test']
How do you split a string into lines using splitlines()?
You can split a multiline string into lines using the splitlines() method.
split a string/multiple senetence/paragraph into lines then store each lines (count as one element of list) in list
text = "Line 1\nLine 2\nLine 3"
lines = text.splitlines()
print(lines) # Output: ['Line 1', 'Line 2', 'Line 3']
What does the replace() function do in Python?
replace() function replaces all occurrences of a substring in a string with another substring.
replaces all occurrences of a substring/words in a string with another substring
text = "Hello, World!"
new_text = text.replace("World", "Python")
print(new_text) # Output: "Hello, Python!"
How do you replace multiple substrings in a string using replace()?
You can chain multiple replace() calls to replace multiple substrings.
how to replace multiple substring/words in a text,paragraph,multiple sentence
text = "Hello, World! Hello, World!"
new_text = text.replace("Hello", "Hi").replace("World", "Python")
print(new_text) # Output: "Hi, Python! Hi, Python!"
How do you remove all spaces from a string using replace()?
You can replace all spaces with an empty string to remove them.
how to remove all spaces in a text,paragraph,multiple sentence
text = "Hello World"
new_text = text.replace(" ", "")
print(new_text) # Output: "HelloWorld"
import string
import re
sentence = "hello world! this is an example sentence."
new_sentence = string.capwords(sentence)
sentence = "hello world! this is an example sentence."
new_sentence = sentence.title()
parts = re.findall(r'[A-Z][^A-Z]*', new_sentence)
print(new_sentence)
print(parts)
output
Hello World! This Is An Example Sentence.
['Hello ', 'World! ', 'This ', 'Is ', 'An ', 'Example ', 'Sentence.']
How do you replace digits in a string with X using regex?
You can use re.sub() with a regex pattern to replace digits with X.
how to replace all digits from sentence,paragraph
split a string/sentence into words based on uppercase letter then store each words in list
import re
text = "There are 123 apples and 456 oranges."
new_text = re.sub(r'\d', 'X', text)
print(new_text) # Output: "There are XXX apples and XXX oranges."
How do you split a string at uppercase letters using regex?
You can use a regex pattern to split a string at uppercase letters.
split a string/sentence into words based on uppercase letter then store each words in list
import re
text = "SplitAtUpperCaseLetters"
parts = re.findall(r'[A-Z][^A-Z]*', text)
print(parts) # Output: ['Split', 'At', 'Upper', 'Case', 'Letters']
How do you split a string at non-alphanumeric characters using regex?
You can use a regex pattern to split a string at non-alphanumeric characters.
split a string/sentence into words based on non-alphanumeric characters like digits,comma or any special symbol then store each words in list
import re
text = "Split, at non-alphanumeric characters!"
parts = re.split(r'\W+', text)
print(parts) # Output: ['Split', 'at', 'non', 'alphanumeric', 'characters']
How do you replace a specific word in a string using regex?
You can use re.sub() with a regex pattern to replace a specific word
import re
text = "Replace this word with another."
new_text = re.sub(r'\bword\b', 'phrase', text)
print(new_text) # Output: "Replace this phrase with another."
How do you extract all hashtags from a string using rege?
You can use a regex pattern to match hashtags in a string.
import re
text = "This is a #sample text with #hashtags."
hashtags = re.findall(r'#\w+', text)
print(hashtags) # Output: ['#sample', '#hashtags']
How do you extract all capitalized words from a string using regex?
import re
text = "This is A Test String With CAPITALIZED WORDS."
capitalized_words = re.findall(r'\b[A-Z][a-z]*\b', text)
print(capitalized_words) # Output: ['This', 'Test', 'String', 'With', 'CAPITALIZED', 'WORDS']
What does the re.findall() function do in Python?
re.findall() returns a list of all non-overlapping matches of a pattern in a string.
import re
text = "apple, banana, cherry, banana, orange"
pattern = "banana"
matches = re.findall(pattern, text)
print(matches) # Output: ['banana', 'banana']
How do you find all numbers in a string using regex?
You can use \d+ pattern to find all numbers (sequences of digits) in a string.
import re
text = "The price is $10 for item 1, $20 for item 2, and $30 for item 3."
numbers = re.findall(r'\d+', text)
print(numbers) # Output: ['10', '1', '20', '2', '30', '3']
How do you replace all occurrences of a pattern in a string using regex?
You can use the re.sub() function to replace all occurrences of a pattern in a string.
import re
text = "apple, banana, cherry"
pattern = "banana"
replacement = "grape"
new_text = re.sub(pattern, replacement, text)
print(new_text) # Output: "apple, grape, cherry"
How do you extract all capitalized words from a string using regex?
You can use a regex pattern to match capitalized words in a string.
import re
text = "This is A Test String With CAPITALIZED WORDS."
capitalized_words = re.findall(r'\b[A-Z][a-z]*\b', text)
print(capitalized_words) # Output: ['This', 'Test', 'String', 'With', 'CAPITALIZE']
How do you extract all hashtags from a string using regex?
You can use a regex pattern to match hashtags in a string.
import re
text = "This is a #sample text with #hashtags."
hashtags = re.findall(r'#\w+', text)
print(hashtags) # Output: ['#sample', '#hashtags']
=======================================================
Apply lambda function
list comprhension
How to map keywords
how to store all dictionary value(key-value pair) into list using listcomprhension
# Original list of keywords
keywords = ['swerty', 'new', 'important', 'old']
# Dictionary to map keywords to numerical values
keyword_mapping = {
'swerty': 1,
'new': 2,
'old': 3,
'important': 4
}
# Use list comprehension to map the keywords using the dictionary
mapped_keywords = [keyword_mapping[keyword] for keyword in keywords]
# Output the mapped keywords
print(mapped_keywords)
output
[1, 2, 4, 3]
# Handle missing keywords by providing a default value (e.g., None or -1)
mapped_keywords = [keyword_mapping.get(keyword, -1) for keyword in keywords]
print(mapped_keywords)
output
[1, 2, 4, 3]
remove particular key value pair from dictionary
===============================================================
print in new line or in list observe
data = [4, 16, 9, 20]
even = []
for newdata in data:
if newdata%2 == 0:
print(newdata)
output
data = [4, 16, 9, 20]
even = []
for newdata in data:
if newdata%2 == 0:
even.append(newdata)
print(even)
output
wrong
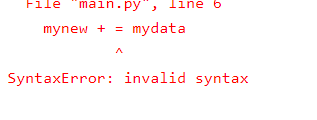
dont put gap b/w + and = operator
data="python"
vowel=["a","i","o","e","u"]
mynew=""
for mydata in data:
if mydata not in vowel:
mynew + = mydata
correct
data="python"
vowel=["a","i","o","e","u"]
mynew=""
for mydata in data:
if mydata not in vowel:
mynew += mydata
data = (4, 6, 9, 10)
my_list = []
for number in data:
if number % 2 == 0:
my_list.append(number)
print("Original String:", my_list)
for item in my_list:
print("Original String:", item)
wrong:
data = (4, 6, 9, 10)
my_list = []
for number in range(len(data)):
if number % 2 == 0:
my_list.append(number)
print("Original String:", my_list)
for item in my_list:
print("Original String:", item)
Solution
iterate over the indices and then access the elements whenever you use range
data = (4, 6, 9, 10)
my_list = []
for index in range(len(data)):
if data[index] % 2 == 0:
my_list.append(data[index])
print("Original List of Even Numbers:", my_list)
for item in my_list:
print("Even Number:", item)
wrong
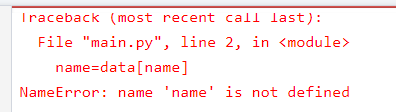
data={"name":"rakesh","age":33}
name=data[name]
print(name)
correct
whenever string is in dictionary to access its value use double quotes
data={"name":"rakesh","age":33}
name=data["name"]
print(name)
wrong
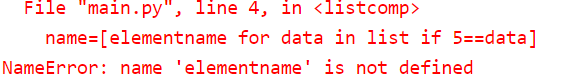
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
list=[5,8,6,7]
name=[elementname for data in list if 5==data]
print(name)
wrong
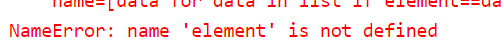
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
list=[5,8,6,7]
name=[data for data in list if element==data]
print(name)
correct
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
list=[5,8,6,7]
name=[data for data in list if 5==data]
print(name)
wrong
data = {"name": "rakesh", "age": 33}
name = data["name"]
data["hobby"] = "readingbooks"
for key, value in data.items():
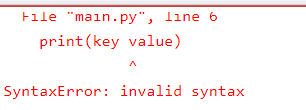
print(key value)
correct
data = {"name": "rakesh", "age": 33}
name = data["name"]
data["hobby"] = "readingbooks"
for key, value in data.items():
print(key, value)
data = {"name": "rakesh", "age": 33}
name = data["name"]
data["hobby"] = "readingbooks"
for key, value in data.items():
print(key, ":", value)
wrong
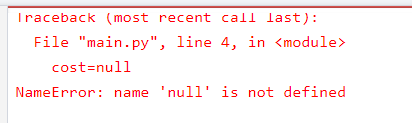
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
cost=null
for key, value in data.items():
cost +=value
print(cost)
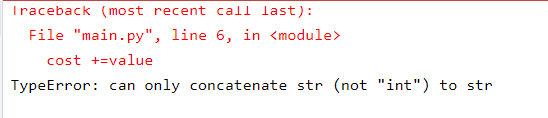
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
cost=""
for key, value in data.items():
cost +=value
print(cost)
correct
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
cost=0
for key, value in data.items():
cost +=value
print(cost)
wrong
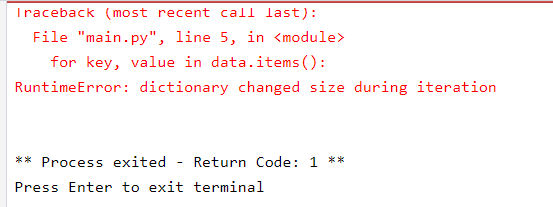
RuntimeError: dictionary changed size during iteration
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
cost=0
for key, value in data.items():
data["guava"]=40
print(cost)
correct
i have dictionary where fruit and its cost in key value pair , my task is add new fruit and its cost in existing dictionary then take new empty dictioary while iterating then add new fruit key value pair then merge both dictionary(short adding and merging)
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
cost=0
update={}
for key, value in data.items():
update["guava"]=40
cost +=value
data.update(update)
print(data,":",cost)
data = {'apple': 70, 'banana': 33, 'mango': 90}
update = {'guava': 40}
data = {'apple': 70, 'banana': 33, 'mango': 90, 'guava': 40}
Declaration of empty datatype to create or append to create new
Declaration of empty datatype for dictionary,list,string,number, a dictionary where value is in list, nested dictionary
dict={} // dict[char] +=number or dict[char] ="word
list=[] //list.append(data)
string="" // create new string mynew + = mydata
number=0 // create new string dict[char]+ = number
result_even = {'even': []}//{"group1": [1, 2, 3]}
result_dict = {'odd': {}, 'even': {}}
result_dict[key] = []
wap map each char of string as key of dictionary and elment of list as value of dictionary
WAP map each element of first list as key of dictionary and each element of second list as value of dictionary using zip
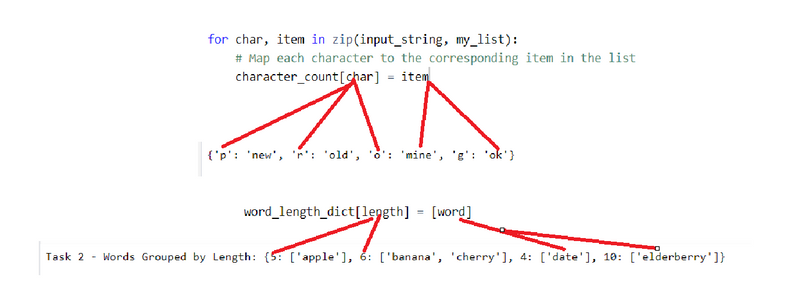
map/store each element of given string as key of dictionary and element of given list as value of dictionary
input_string = "prog"
my_list = ["new", "old", "mine", "ok"]
my_secondlist = ["raj", "ram", "kam", "saj"]
character_count = {}
dict_count = {}
for char, item,name in zip(input_string, my_list,my_secondlist):
character_count[char] = item
dict_count[name] = item
print(character_count)
print(dict_count)
output
{'p': 'new', 'r': 'old', 'o': 'mine', 'g': 'ok'}
{'raj': 'new', 'ram': 'old', 'kam': 'mine', 'saj': 'ok'}
wap to how to ggroup words by their lengths using a dictionary in Python( store item in dictionary where key is single element and value is in dictionary)
words = ["apple", "banana", "cherry", "date", "elderberry"]
word_length_dict = {}
for word in words:
length = len(word)
if length in word_length_dict:
word_length_dict[length].append(word)
else:
word_length_dict[length] = [word]
print(word_length_dict)
output
{5: ['apple'], 6: ['banana', 'cherry'], 4: ['date'], 10: ['elderberry']}
image
==========================================================
==========================================
===============================================
wap to how to group words by their lengths using a dictionary in Python then convert into dictionary
TIPS
any data type dictionary,set,tuple convert in list using list comprhension then whatever fun u r applying in list u can apply in list comprhension below sum and len fun is applying on list comprhension
Wrong
how to search particular value based on key
contacts_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
name_to_lookup = "Bob"
search=""
for key,value in contacts_dict.items():
if contacts_dict[key]==name_to_lookup:
search=contacts_dict[value]
print(search)
wrong
Correct
contacts_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
name_to_lookup = "charlie@example.com"
search=""
for key,value in contacts_dict.items():
if contacts_dict[key]==name_to_lookup:
search=contacts_dict[key]
print(search)
output
charlie@example.com
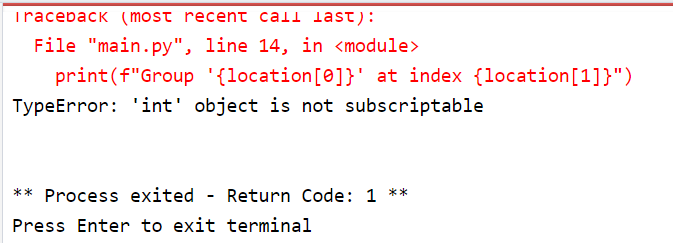
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
locations = [index for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value]
if locations:
print(f"The value {target_value} is located in the following places:")
for location in locations:
print(f"Group '{location[0]}' at index {location[1]}")
else:
print(f"The value {target_value} is not found in the dictionary.")
Correct
grouped_dict = {
"group1": [1, 2, 7, 3],
"group2": [4, 5, 5, 6],
"group3": [7, 8, 9, 8]
}
target_value = 5
locations = [(group, index) for group, elements in grouped_dict.items() for index, value in enumerate(elements) if value == target_value]
if locations:
print(f"The value {target_value} is located in the following places:")
for location in locations:
print(f"Group '{location[0]}' at index {location[1]}")
else:
print(f"The value {target_value} is not found in the dictionary.")
wrong
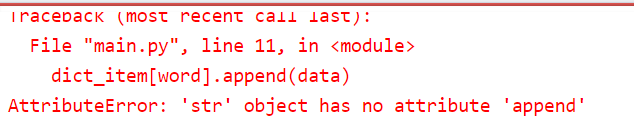
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
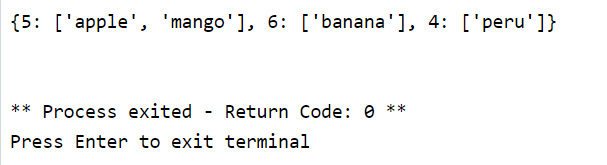
listing=["apple","banana","peru","mango"]
dict_item={}
length=0
for data in listing:
word=len(data)
if word not in dict_item:
dict_item[word]=data
else:
dict_item[word].append(data)
print(dict_item)
correct
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
listing=["apple","banana","peru","mango"]
dict_item={}
length=0
for data in listing:
word=len(data)
if word not in dict_item:
dict_item[word]=[data]
else:
dict_item[word].append(data)
print(dict_item)
=========or==========
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
listing=["apple","banana","peru","mango"]
dict_item={}
length=0
for data in listing:
word=len(data)
if word not in dict_item:
dict_item[word]=[]
dict_item[word].append(data)
print(dict_item)
wrong
contacts_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
name_to_lookup = "Bob"
search = ""
for data in contacts_dict:
if contacts_dict[data] == name_to_lookup:
search = contacts_dict[data]
print(search)
Correct
contacts_dict = {
"Alice": "alice@example.com",
"Bob": "bob@example.com",
"Charlie": "charlie@example.com",
}
name_to_lookup = "Bob"
search = ""
for key, value in contacts_dict.items():
if key == name_to_lookup:
search = value
print(search)
output
bob@example.com
two ways to find sum of value in list
my_list = [8, 9, 7, 9, 56]
sum=0
for data in my_list:
sum +=data
print(sum)
2nd way
my_list = [8, 9, 7, 9, 56]
new_sum = sum(my_list)
two way to access if dictionary contain only keys
data = {"name", "age"}
for news in data:
print(news)
data = {"name", "age"}
# Convert the set to a list
data_list = list(data)
# Access the first element
first_element = data_list[0]
print(first_element)
output
wrong
data = {"name", "age"}
name=data["name"]
wrong
data = {"name", "age"}
name=data[1]
wrong
data = {"name", "age"}
for keys in data.keys():
wrong
data = {"name", "age"}
for keys in data.items():
wrong
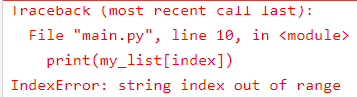
input_string = "programming"
my_list = "python"
character_count = {}
# Check if len(my_list) is greater than 0 before accessing elements
if len(my_list) > 0:
# Iterate over the characters and indices using enumerate
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
print(my_list[index])
correct
input_string = "programming"
my_list = "python"
character_count = {}
# Check if len(my_list) is greater than 0 before accessing elements
if len(my_list) > 0:
# Iterate over the characters and indices using enumerate
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
if index < len(my_list):
print(my_list[index])
p
y
t
h
o
n
input_string = "programming"
my_list = "python"
character_count = {}
# Check if len(my_list) is greater than 0 before accessing elements
if len(my_list) > 0:
# Iterate over the characters and indices using enumerate
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
my_list_char = my_list[index % len(my_list)]
print(my_list_char)
wrong
two ways to find sum of dictionary
1st way
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
sum_of_values = 0
for value in data.values():
sum_of_values += value
print(sum_of_values)
2nd way
sum(data.values())
two ways to find length of dictionary
1st way
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
len=0
sum_of_values = 0
for key in data.keys():
len += 1
print(len)
2nd way
my_dict = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33, "mango": 90}
dict_length = len(my_dict)
3 ways to find avg of dictionary
1st way
data = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33}
name = data["apple"]
data["mango"] = 90
len=0
sum_of_values = 0
avg=0
for key,values in data.items():
len += 1
sum_of_values +=values
avg=sum_of_values/len
print(avg)
2nd way
my_dict = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33, "mango": 90}
total = 0
count = 0
for value in my_dict.values():
total += value
count += 1
if count > 0:
average = total / count
print("Average value:", average)
else:
print("The dictionary is empty.")
3rd way
my_dict = {"apple": 70, "banana": 33, "mango": 90}
if len(my_dict) > 0:
average = sum(my_dict.values()) / len(my_dict)
print("Average value:", average)
else:
print("The dictionary is empty.")
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
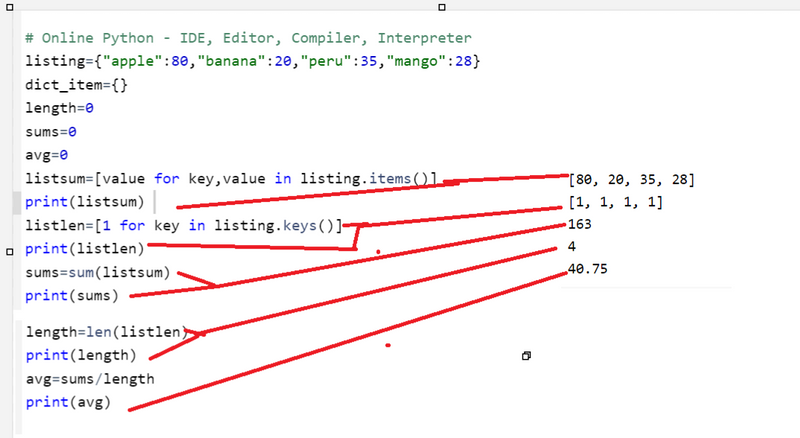
listing={"apple":80,"banana":20,"peru":35,"mango":28}
dict_item={}
length=0
sums=0
avg=0
for index in range(len(listing.keys())):
pass
avg=sum(listing.values())/(index+1)
print(avg)
difference between enumerate and zip method
enumerate
Purpose: To add a counter to an iterable and return it as an enumerate object, which is useful when you need both the index and the value from the iterable.
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
# Using enumerate to get index and value
for index, fruit in enumerate(fruits):
print(f"Index: {index}, Fruit: {fruit}")
Index: 0, Fruit: apple
Index: 1, Fruit: banana
Index: 2, Fruit: cherry
zip
Purpose: To aggregate elements from two or more iterables (lists, tuples, etc.) and return them as tuples. Useful for combining multiple sequences element-wise.
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']
scores = [85, 92, 88]
# Using zip to combine names and scores
for name, score in zip(names, scores):
print(f"Name: {name}, Score: {score}")
Name: Alice, Score: 85
Name: Bob, Score: 92
Name: Charlie, Score: 88
find avg of all values if dictionary using list comprehension
# Online Python - IDE, Editor, Compiler, Interpreter
listing={"apple":80,"banana":20,"peru":35,"mango":28}
dict_item={}
length=0
sums=0
avg=0
listsum=[value for key,value in listing.items()]
print(listsum)
listlen=[1 for key in listing.keys()]
print(listlen)
sums=sum(listsum)
print(sums)
length=len(listlen)
print(length)
avg=sums/length
print(avg)
output
** 2 ways max data**
words_list = [20,60,70,80]
maxdatas=0
for max_data in words_list:
if maxdatas>max_data:
maxdatas=maxdatas
else:
maxdatas=max_data
print(maxdatas)
max(list)
how to find index of particular value of list
list[3]
listing = [6, 9, 6, 0, 45, 8]
data = ["good is located in " + str(index) if value == 8 else "bad" for index, value in enumerate(listing)]
print(data)
Merge two list and Remove Duplicates
list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list2 = [2, 3, 4]
merged_list = list(set(list1 + list2))
print(merged_list)
Output (order may vary):
text
[1, 2, 3, 4]
Cheatsheet
data.update(update)//update specfic value in dictionary
Dict['Emp_ages'] = 20 //add new value in dictionary
for key in data.keys(): or for group in data.keys(): //print all key in dictionary
for value in data.values()://print all value in dictionary
for key,value in data.items(): or for group,ein data.items(): // print both
if char in characters_to_remove: // for list
if char not in characters_to_remove: // for list
if char not in vowels// for string
if length in word_length_dict: // for dictionary
empty_string += new_char1
for index in range(len(data))://iterating with only index in range
if data[index] % 2 == 0:
original_string = original_string.replace(char, "")
for index, char in enumerate(input_string): // map char to corresponding list
for char, item in zip(input_string, my_list):
for char, item in character_count.items():
print(f"Character '{char}' is for {item}.")
character_count[char] +=1
length = len(word)
word_length_dict[length] = [word]
word_length_dict[length].append(word)
dict(sorted(my_dict.items(), key=lambda item: item[1]))
sorted_dict = dict(sorted(my_dict.items(), key=itemgetter(1)))
max_value = max(my_dict.values())
average_value = sum(my_dict.values()) / len(my_dict)
del contact_dict[key_to_remove]
contact_email = contacts_dict.get(name_to_lookup, "Contact not found")
print("Task 10 - Email for '{}':", contact_email)
my_list = [8, 9, 7, 9, 56]
new_sum = sum(my_list)
my_list = [8, 9, 7, 9, 56]
len= len(my_list)
my_list = my_list + [new_data] // add new data in list
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] // add new data in list
new_data = 6
my_list.append(new_data)
dict["mango"]=90 // add new key value pair in dictionary
new_movie = {"director": "Director3", "genre": "Genre3"}
movies_dict["Movie3"] = new_movie // add new key value pair in dictionary
if seconlargestd < newdata < maxdata //second largest
merged_dict = {**dict1, **dict2, **dict3}
top_rated_songs = [title for title, rating in song_ratings.items() if rating == 5]
merged_list = list(set(list1 + list2))
strings_list = ["Hello", "World", "!"] // u can join particular string based on condition while iterating in loop
concatenated_string = ' '.join(strings_list)
full_urls = ['https://www.icc-cricket.com' + url for url in url_list] //how to concatenate
my_list.insert(index_to_insert, value_to_add)
my_list.insert(3, value_to_add)
for index, text in enumerate(list): //Find Particular element index
subset = my_list[::2] // print even no
reversed_list = my_list[::-1]
subset = my_list[:3] # Get elements at index 0, 1, and 2 ([1, 2, 3])
subset = my_list[2:] # Get elements from index 2 to the end ([3, 4, 5])
subset = my_list[1:4] # Get elements at index 1, 2, and 3 ([2, 3, 4])
key_list = list(data.keys())
for key in data.keys():
list.append(key)
value_list = list(data.values())
for value in data.values():
list.append(value)
index = my_list.index(value_to_find) // how to find index of list
Merge two list and Remove Duplicates
list1 = [1, 2, 3]
list2 = [2, 3, 4]
merged_list = list(set(list1 + list2))
print(merged_list)
Output (order may vary):
[1, 2, 3, 4]
Summary
put colon not semicolon after for ,def ,if,else
after print or declaration of variable not put semicolon
indention of for and if
indention of if and else
indention for,if and data or print
Indention between for,if and local print global print
indention between for,if,else,print
indention between for,if,else,pass,print
always iterate in string,list,dictionary,tuple not single variable of list
How to add new char in empty string or exisiting string
print in new line or in list observe
How to add new char in empty string or exisiting string without for loop or inside for loop
Indention error b/w double for block
dont put gap b/w + and = operator
iterate over the indices and then access the elements whenever you use range
whenever string is in dictionary to access its value use double quotes
print key and value by comma or colon
not concatenate string with integer while doing calculation of sum of all dictionary value
RuntimeError: dictionary changed size during iteration
Declaration of empty datatype to create or append to create new like list,dictionary,string,integer,list of dictionary,dictionary of dictionary
Mapping char to corresponding item in list using zip
difference between char_count[item]=char or char_count[item]=[char] and word_count[length].append(word) inside for loop
how to search particular value based on key
two ways to find sum,length of value in list
3 ways to find avg of value in list
two way to access if dictionary contain only keys
two ways to find sum,len of dictionary
3ways to find avg of dictionary
2 ways to find max data in list
find second largest data
how to convert string to list
QUESTION
how to access list value or string value using index
how to access value from list of dictionary
difference between enumerate and zip method
.How to add new char in empty string or existing string
.How to Mapping char to corresponding item in list and dictionary OR how to convert list to dictionary
how to convert dictionary to list
how to search particular value based on key
how to find second largest data
how to convert dictionary keys or value in list
how to combine two list
how to reverse list
how to get specific range of element from list
how to get last 3 element of list
how to get skip fist element from list
how to combine dictionary
how to concatenate string in each element of list
how to update specific value in dictionary
how to find index of particular value of list or string
how to iterate index of list
how to string to list
Solution
my_list[index]
synonyms = {"quick": ["fast", "swift", "speedy"]}
list(synonyms.keys())
zip method iterates over element pairs and contain two parameter argument while enumerate iterates over element and index and contain one parameter argument of list
empty_string += new_char1
using enumerate or zip
using list comrehension or append while iterating dictionary
movies_dict["Movie3"]
if seconlargestd < newdata < maxdata //second largest
key_list = list(data.keys()) or list.append(key) inside for loop
merged_list = list(set(list1 + list2)) or listnew=list1 + list2
reversed_list = my_list[::-1]
subset = my_list[1:4]
subset = my_list[:3]
subset = my_list[1:]
merged_dict = {**dict1, **dict2, **dict3}
full_urls = ['https://www.icc-cricket.com' + url for url in url_list]
data.update(update)
list[3] or [data for data in list if 5==data] or using enumerte
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
character_count[char] = my_list[index]
#printing
for index, char in enumerate(input_string):
my_list_char = my_list[index % len(my_list)]
print(my_list[index])
data= ["good is located in " + str(index) if value == 8 else "bad" for index, value in enumerate(listing)]
using enumerate
list(string) or append inside for loop
All Important Programming Question
programming-with-data-visualization-lpd
Draw plot a multiple line with different attribute using for loop and use list of tuple where x is common for all,y,marker and label
how to draw a line plot from table or dataframe
Visualizing Daily Stock Prices Over a Month for multiple stock
Monthly average temperatures for multiple cities using diffent marker for each city in different subplot in 2 row and 2 colunm
Visualize sales data for multiple products across different regions using different colors and markers
Monthly sales data for multiple products across different regions if sales increasing above 300 then draw horizontal line
plot a multiple line using for loop and use list of tuple where x is common for all,y,marker and label is different with enumerate and without enumerate
Compare student scores in different subjects using different colors and markers in different subplot 2 row and 2 col using bar and pie chart
(first colunm represent bar and second colunm represent pie)
Compare student scores in different subjects using different colors and markers
Monthly sales data for multiple products across different regions
if sales increasing above 300 then draw horizontal line
list-out-checklist-of-nlp-terminology-in-machine-learning
How to convert given string into list of words ,list of sentence
How to remove stop words
How to perform steaming and lammenization
basic-preprocessing-machine-learning
Filtering a Pandas DataFrame in Python to Select Rows with Prices Between $1000 and $2500
Display particular range of row
how to Add new col in existing table based on existing column
minimum,maximum,average,mean,median,mode,Replacing Empty Spaces in 'TotalCharges'
Identifying and Counting Missing Values in Each Column or part
Find following things
(1)Determining the Number of Unique Values in the particular colunm
(ii) Counting the Occurrences of Each Unique Value
(iii)summary analysis of table to show mean,median,std dev
(iv)remove particular column without affecting existing table
how to calculate sum of each column in table and then put in list then above output put in table
How to perform grouping,aggregating,joining and merging,concatenating
How to find correlation
how-to-extracting-and-transforming-information-from-table-in-python
How to convert given list of list,List of dictionaries,Grouped dictionary of lists
How pandas table convert into list of dictionary and dictionary of list
how to transpose row to colunm and colunm to row
Find sum of list value in list of dictionary
Lambda
how to find square of each element of all column or particular colunm of table
creating new colm that contain the square of value if mean value of col greater than current value else add 10 to current val
create a new column value high/low/medium based on existing column greater or less than
common-coding-mistake-in-python-1nkm
how to map dictionary between string and list and between two list using zip
how to create two words of of list from two list while words of first list should be connected to all words of second list like red banana
create a list that contain two words are getting from two seprate list **
**Wap to replace vowels from single letters string
combine two dictionary
remove and rename particular key value pair from dictionary
how to convert a string into list of words using split and findall both ways
how to replace multiple substrings in a string
how to remove the first and last spaces from the given sentence
How do you replace digits or words in a string with X using regex?
how to replace all empty space from string or sentence
different way to find sum,avg,length from list,dictionary
wap to how to group words by their lengths using a dictionary in Python



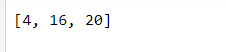







Top comments (0)